A loanword is a term adopted from one language into another without translation, often reflecting cultural exchange or technological advances. These words enrich the vocabulary and can reveal historical connections between languages and societies. Explore the article to discover how loanwords shape your everyday communication.
Table of Comparison
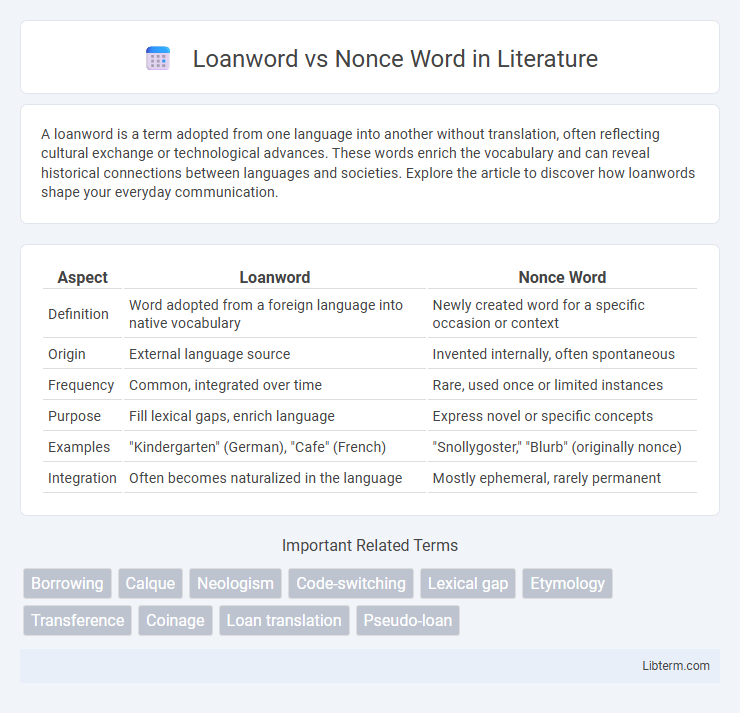
| Aspect | Loanword | Nonce Word |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Word adopted from a foreign language into native vocabulary | Newly created word for a specific occasion or context |
| Origin | External language source | Invented internally, often spontaneous |
| Frequency | Common, integrated over time | Rare, used once or limited instances |
| Purpose | Fill lexical gaps, enrich language | Express novel or specific concepts |
| Examples | "Kindergarten" (German), "Cafe" (French) | "Snollygoster," "Blurb" (originally nonce) |
| Integration | Often becomes naturalized in the language | Mostly ephemeral, rarely permanent |
Introduction to Loanwords and Nonce Words
Loanwords are borrowed terms from one language incorporated into another with little or no modification, enriching the recipient language's vocabulary and reflecting cultural exchange. Nonce words, created spontaneously for a specific occasion or context, often serve to express unique ideas or fill temporary lexical gaps without permanent adoption. Understanding these concepts reveals how languages evolve through borrowing established words and inventing new ones for immediate communicative needs.
Defining Loanwords: Meaning and Examples
Loanwords are terms adopted from one language into another without translation, often reflecting cultural or technological exchanges; examples include "ballet" from French and "karaoke" from Japanese. These words retain their original meaning or adapt slightly while enriching the recipient language's vocabulary. Loanwords demonstrate linguistic borrowing processes and help trace historical interactions between language communities.
Exploring Nonce Words: Definition and Significance
Nonce words are unique linguistic creations devised for a specific occasion or context, often without intention for long-term use, serving as a tool for creative expression or immediate communication needs. Unlike loanwords, which are borrowed from other languages and become integrated into the lexicon, nonce words highlight the flexibility and inventiveness of language users in generating novel terms on demand. Their significance lies in offering insight into cognitive processes of word formation and reflecting cultural nuances or emerging trends within a language.
Historical Development of Loanwords
Loanwords have historically entered languages through trade, conquest, and cultural exchange, enriching vocabulary with terms adapted from foreign sources. These borrowed words often undergo phonological and morphological changes to fit the target language's system, reflecting centuries of linguistic interaction. Unlike nonce words, which are created for immediate, context-specific use, loanwords represent enduring lexical integration derived from sustained contact between language communities.
Creation and Usage of Nonce Words
Nonce words are created spontaneously for a single occasion or specific context, often to fill a lexical gap or for playful linguistic effect. Unlike loanwords borrowed from other languages and integrated into regular vocabulary, nonce words typically lack established usage and may not persist beyond their initial context. Their creation often involves creative morphological processes such as blending, compounding, or affixation to convey novel concepts or temporary meanings.
Impact of Loanwords on Language Evolution
Loanwords significantly influence language evolution by introducing new vocabulary that reflects cultural exchange, technological advancement, and globalization. They often fill lexical gaps, enriching the target language with specialized terms and concepts, thereby expanding its expressive capacity. Over time, loanwords can undergo phonological and semantic adaptation, becoming fully integrated and shaping the linguistic identity of the receiving language.
Nonce Words in Literature and Pop Culture
Nonce words are inventive linguistic creations used temporarily to convey unique concepts or emotions, often appearing in literature and pop culture to enrich narrative voice and inject originality. Authors like Lewis Carroll and Dr. Seuss famously coined nonce words to enhance imaginative worlds, while in pop culture, such terms frequently emerge in song lyrics, movies, and social media to capture zeitgeist or characterize speech. These ephemeral words reflect creativity and adaptiveness in language, distinguishing themselves from loanwords, which are borrowed and assimilated from other languages for permanent use.
Differences Between Loanwords and Nonce Words
Loanwords are established words borrowed from one language into another with widespread and lasting usage, reflecting cultural or technological exchange. Nonce words are created spontaneously for a specific occasion or purpose, often with limited or no long-term adoption in the language. The key difference lies in loanwords' integration into everyday vocabulary, while nonce words remain ephemeral and context-dependent.
The Role of Context in Word Adoption
Loanwords become integrated into a language through repeated use in specific cultural or social contexts that demand new terminology, often related to technology, cuisine, or fashion. Nonce words are typically created spontaneously for unique, situational needs and may not persist without broader contextual reinforcement. The surrounding linguistic and situational environment plays a crucial role in determining whether a word evolves from a fleeting nonce term into a stable loanword within a language.
Conclusion: Comparing Linguistic Influence and Function
Loanwords enhance a language by incorporating established terms from other languages, enriching vocabulary and reflecting cultural exchange. Nonce words serve as creative linguistic tools, often coined for specific contexts and may not become permanent fixtures in the lexicon. Comparing their linguistic influence, loanwords contribute to long-term language evolution, while nonce words highlight flexibility and innovation in communication.
Loanword Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com