Dialogism explores the dynamic interaction between multiple voices or perspectives within a text, highlighting how meaning is shaped through conversation and contrast. This concept, rooted in literary theory and philosophy, reveals how your interpretation can be influenced by the interplay of diverse narratives and viewpoints. Discover how dialogism enriches understanding and invites you to engage deeply with complex texts throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
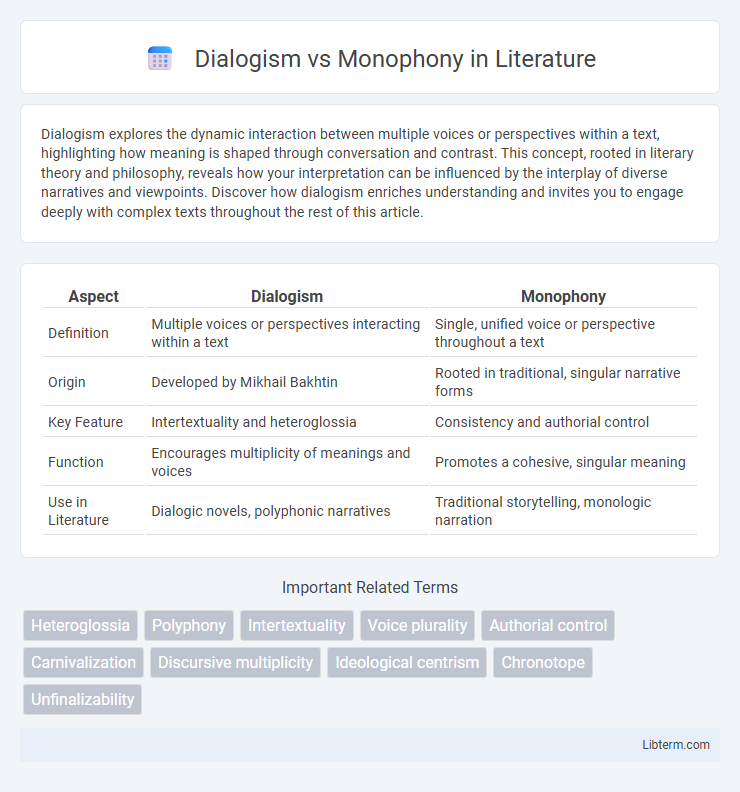
| Aspect | Dialogism | Monophony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple voices or perspectives interacting within a text | Single, unified voice or perspective throughout a text |
| Origin | Developed by Mikhail Bakhtin | Rooted in traditional, singular narrative forms |
| Key Feature | Intertextuality and heteroglossia | Consistency and authorial control |
| Function | Encourages multiplicity of meanings and voices | Promotes a cohesive, singular meaning |
| Use in Literature | Dialogic novels, polyphonic narratives | Traditional storytelling, monologic narration |
Introduction to Dialogism and Monophony
Dialogism emphasizes the interaction between multiple voices or perspectives within a text, highlighting how meaning emerges through this dynamic exchange. Monophony refers to a single, unified voice or perspective that conveys information without interplay or contradiction. Understanding dialogism versus monophony involves exploring how texts either engage diverse viewpoints or present a solitary narrative.
Defining Dialogism: Key Concepts
Dialogism centers on interactive meaning-making through multiple voices, perspectives, and interpretations within a text or communication, contrasting with monophony's singular, authoritative voice. Key concepts include heteroglossia, which highlights the coexistence of diverse linguistic styles and social voices, and the ongoing dialogue between these differing viewpoints that shape understanding. This dynamic interplay fosters a richer, multidimensional narrative structure compared to monophonic expressions that emphasize uniformity and singularity.
Understanding Monophony in Discourse
Monophony in discourse refers to a single, unified voice or perspective dominating communication without interaction or acknowledgment of alternative viewpoints. This concept contrasts with dialogism, where multiple voices and perspectives engage in a dynamic exchange, creating meaning through interaction. Understanding monophony emphasizes the limitations of one-sided discourse in fostering comprehensive meaning and the importance of recognizing diverse voices for richer communication.
Historical Background: Dialogism vs Monophony
Dialogism emerged from the literary theories of Mikhail Bakhtin in the early 20th century, emphasizing the coexistence of multiple voices and perspectives within a text. Monophony, rooted in medieval musicology and applied metaphorically to literature, represents a single, unified voice or perspective dominating a narrative. The historical development of these concepts highlights a shift from singular authoritative discourse toward recognition of diverse, interacting voices in storytelling and analysis.
Bakhtin’s Theory of Dialogism
Bakhtin's Theory of Dialogism emphasizes the multiplicity of voices and perspectives within a text, contrasting with monophony, which represents a single, unified voice or viewpoint. Dialogism highlights the interaction, conflict, and coexistence of diverse consciousnesses, shaping meaning through ongoing dialogue. This theoretical framework underscores that meaning emerges dynamically from the interplay of different social and ideological utterances rather than from an isolated narrative voice.
Characteristics of Monophonic Narratives
Monophonic narratives feature a single, unified voice or perspective, emphasizing clarity and cohesion without overlapping voices or conflicting viewpoints. The focus remains on a linear, straightforward progression that lacks internal dialogue or multiple layers of interpretation. This singular narrative stream facilitates a direct and unambiguous delivery of a story or message.
Dialogism in Literature and Communication
Dialogism in literature and communication emphasizes the interaction of multiple voices, perspectives, and meanings, creating a rich, polyphonic discourse that challenges singular interpretations. It fosters dynamic exchanges where characters, narrators, or communicators engage in an ongoing dialogue, reflecting social, cultural, and ideological diversity. This concept, rooted in Mikhail Bakhtin's theories, contrasts with monophony by promoting relational understanding and complex narrative structures rather than isolated, authoritative voices.
Monophony in Media and Rhetoric
Monophony in media and rhetoric emphasizes a single, unified voice or perspective, creating a clear and direct communication style that prioritizes authority and coherence. This approach often appeals to audiences seeking straightforward narratives or messages, reducing complexity by avoiding multiple, competing viewpoints. In contrast to dialogism, monophony's univocal structure reinforces singular interpretations, making it a powerful tool for persuasive media campaigns and rhetorical strategies.
Comparative Analysis: Dialogic and Monophonic Approaches
Dialogism fosters a dynamic interplay of multiple voices and perspectives, enhancing textual complexity and reader engagement through a polyphonic structure, whereas monophony emphasizes a single, unified narrative voice that conveys a clear, authoritative message. Dialogic texts thrive on contradiction, interaction, and the coexistence of diverse viewpoints, promoting interpretative richness, while monophonic approaches prioritize coherence, stability, and a singular ideological position. Comparative analysis reveals that dialogism supports heteroglossia and promotes cognitive multiplicity, contrasting sharply with monophony's focus on singularity and narrative uniformity.
Implications and Applications in Contemporary Studies
Dialogism emphasizes the interplay of multiple voices and perspectives within a text, fostering a richer, dynamic understanding relevant to literary theory, sociolinguistics, and cultural studies. Monophony, characterized by a single, unified voice, offers clarity and directness, often applied in fields requiring authoritative discourse or focused narrative analysis. Contemporary studies leverage dialogism to explore diversity and hybridity in identity and communication, while monophony aids in analyzing ideological structures and power dynamics through singular perspectives.
Dialogism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com