Hyperbole is a figure of speech that involves deliberate exaggeration to create emphasis or effect, often used in everyday language, literature, and advertising to make descriptions more vivid and memorable. It is not meant to be taken literally but to convey strong feelings or highlight the importance of a subject. Explore the article to discover how hyperbole can enhance your communication and storytelling skills.
Table of Comparison
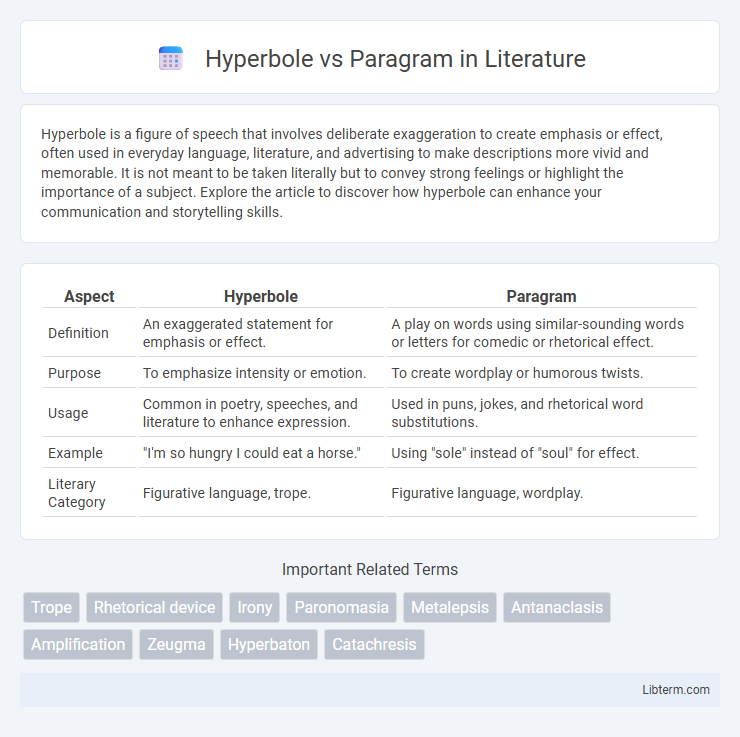
| Aspect | Hyperbole | Paragram |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An exaggerated statement for emphasis or effect. | A play on words using similar-sounding words or letters for comedic or rhetorical effect. |
| Purpose | To emphasize intensity or emotion. | To create wordplay or humorous twists. |
| Usage | Common in poetry, speeches, and literature to enhance expression. | Used in puns, jokes, and rhetorical word substitutions. |
| Example | "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." | Using "sole" instead of "soul" for effect. |
| Literary Category | Figurative language, trope. | Figurative language, wordplay. |
Understanding Hyperbole: Definition and Examples
Hyperbole is a rhetorical device characterized by deliberate and obvious exaggeration used to create emphasis or effect. Examples include phrases like "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse" or "This bag weighs a ton," which intensify the expression beyond literal truth. Understanding hyperbole helps clarify its role in literature and everyday language as a tool for dramatic or humorous impact.
Introduction to Paragram: Meaning and Usage
Paragram is a rhetorical device involving the deliberate substitution of one word for another with a similar sound but a different meaning, often used to create puns or humorous effects. Unlike hyperbole, which relies on exaggerated statements to emphasize a point, paragram plays with language intricacies to engage the audience through wordplay. This technique enhances literary creativity by highlighting unexpected connections between words, making it a distinctive tool in poetry and prose for stylistic expression.
Key Differences Between Hyperbole and Paragram
Hyperbole involves deliberate exaggeration used to emphasize a point or evoke strong feelings, often seen in phrases like "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." Paragram refers to a type of wordplay involving a deliberate misspelling or pun that alters meaning for humorous or rhetorical effect. The key difference lies in hyperbole exaggerating reality for emphasis, while paragram manipulates language structure to create irony or wit.
Historical Origins of Hyperbole and Paragram
Hyperbole, rooted in ancient Greek rhetoric, emerged as a deliberate exaggeration technique to evoke strong emotions and emphasize points in classical literature and speeches dating back to Aristotle's works. Paragram, originating from the Greek term "paragramma," refers to a playful or intentional alteration of words and gained prominence in medieval and Renaissance literature as a form of linguistic wit and wordplay. Both rhetorical devices highlight the evolution of language manipulation techniques with hyperbole focusing on amplified expression and paragram emphasizing phonetic or semantic word substitutions.
Functions of Hyperbole in Language and Literature
Hyperbole serves as a powerful linguistic tool to emphasize emotions and create vivid imagery by deliberate exaggeration, enhancing the expressive quality of language and engaging readers' imaginations. It functions to intensify feelings, underscore the importance of a subject, and evoke humor or irony in literary works. Hyperbole contrasts with a paragram, which involves playful word substitution and punning, focusing more on linguistic creativity than emotional amplification.
How Paragrams Enhance Wordplay
Paragrams enhance wordplay by creating clever substitutions and puns through slight alterations of letters within words, enriching textual complexity and humor. Unlike hyperbole, which amplifies meaning through exaggeration, paragrams rely on phonetic and graphical similarities to engage readers in linguistic puzzles. This technique deepens semantic layers and invites active interpretation, making communication both playful and intellectually stimulating.
Common Mistakes: Mixing Up Hyperbole and Paragram
Confusing hyperbole with paragram often occurs because both involve creative language use, yet hyperbole means deliberate exaggeration for emphasis, while a paragram involves wordplay or a pun through deliberate misspelling or alteration. A common mistake is interpreting a paragram's playful twist as an exaggerated statement typical of hyperbole, leading to misunderstanding the writer's intent. Clear differentiation hinges on recognizing hyperbole's focus on extreme emphasis versus paragram's linguistic substitution or punning effect.
Hyperbole in Modern Media and Advertising
Hyperbole dominates modern media and advertising as a persuasive tool that exaggerates product benefits to capture consumer attention and evoke strong emotional responses. Brands frequently employ hyperbolic claims, such as "the best coffee in the world" or "unmatched performance," to create memorable messaging and differentiate from competitors. This strategic use of hyperbole amplifies brand identity and drives engagement by appealing to desires for superiority and excellence.
Paragrams in Poetry and Creative Writing
Paragrams in poetry and creative writing serve as a poetic device that involves the deliberate alteration of a word's letters or structure to create a pun, evoke multiple meanings, or generate playful ambiguity. Unlike hyperbole, which relies on exaggerated statements to emphasize emotions or concepts, paragrams hinge on linguistic creativity through wordplay, enriching the text with layered interpretations and subtle humor. This technique enhances the reader's engagement by inviting exploration of nuanced meanings and phonetic similarities, thereby expanding the expressive potential of language in literary works.
Choosing the Right Device: Hyperbole or Paragram?
Choosing between hyperbole and paragram depends on the intended impact and context of communication. Hyperbole exaggerates for emphasis, creating dramatic or humorous effects, while paragram involves a deliberate word substitution or pun to challenge expectations and evoke wit. Selecting the right device enhances clarity and engages the audience by matching the tone and purpose of the message.
Hyperbole Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com