Characterization reveals the depth and complexity of characters through their actions, dialogue, and inner thoughts, shaping the reader's understanding of their motivations and growth. Effective characterization enhances the story's emotional impact and provides insight into human nature. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to master this essential literary technique and elevate your writing.
Table of Comparison
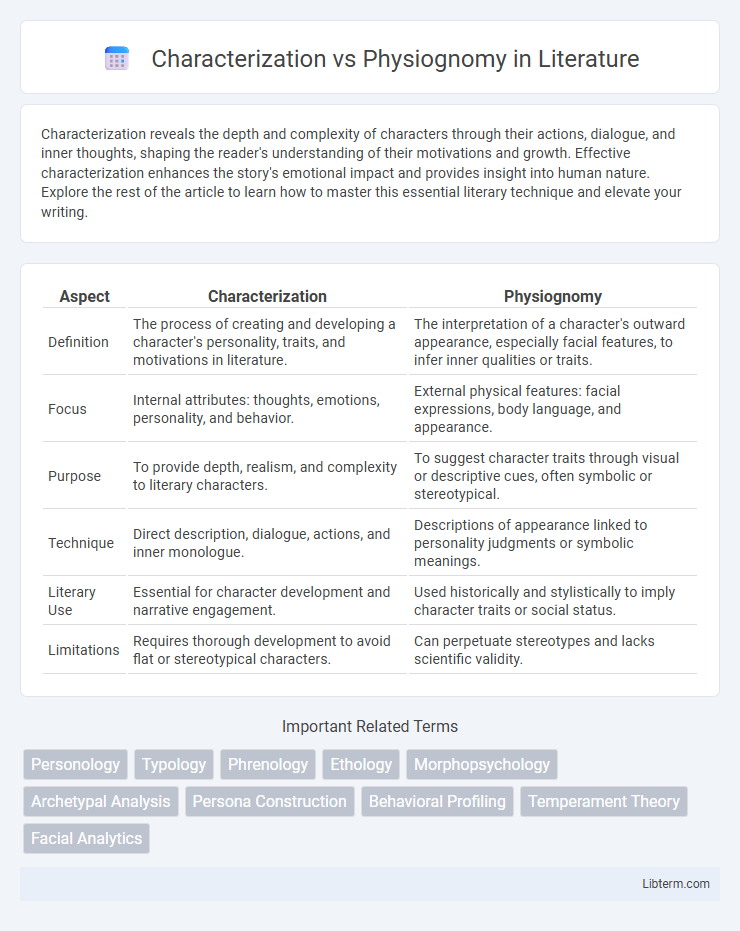
| Aspect | Characterization | Physiognomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of creating and developing a character's personality, traits, and motivations in literature. | The interpretation of a character's outward appearance, especially facial features, to infer inner qualities or traits. |
| Focus | Internal attributes: thoughts, emotions, personality, and behavior. | External physical features: facial expressions, body language, and appearance. |
| Purpose | To provide depth, realism, and complexity to literary characters. | To suggest character traits through visual or descriptive cues, often symbolic or stereotypical. |
| Technique | Direct description, dialogue, actions, and inner monologue. | Descriptions of appearance linked to personality judgments or symbolic meanings. |
| Literary Use | Essential for character development and narrative engagement. | Used historically and stylistically to imply character traits or social status. |
| Limitations | Requires thorough development to avoid flat or stereotypical characters. | Can perpetuate stereotypes and lacks scientific validity. |
Understanding Characterization: Definition and Purpose
Characterization is the literary technique used to create and develop a character's personality, motivations, and traits through direct description, dialogue, actions, and thoughts. It serves to provide depth, making characters believable and relatable to readers by revealing their inner complexities and driving forces. Unlike physiognomy, which judges character based on external appearance, characterization builds understanding through narrative elements and psychological insight.
The Concept of Physiognomy: Historical Background
Physiognomy, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy and widely practiced through the Renaissance, asserts that a person's character and personality traits can be discerned from facial features and outward appearance. This concept historically influenced literature, psychology, and criminology, promoting the belief that physical characteristics reveal moral and intellectual qualities. Despite its longstanding impact, modern science has largely discredited physiognomy due to its lack of empirical support and potential for reinforcing stereotypes.
Key Differences between Characterization and Physiognomy
Characterization involves the development of a character's personality, motivations, and inner qualities through dialogue, actions, and narrative details, providing depth and complexity. Physiognomy focuses on interpreting a character's outer appearance, especially facial features, to infer personality traits or moral qualities, often relying on stereotypes and visual cues. While characterization offers a multidimensional view of a character's inner life, physiognomy emphasizes external looks to suggest or symbolize their nature.
Literary Approaches to Characterization
Literary characterization explores the depth of a character through their actions, dialogue, and inner thoughts, creating a complex and realistic portrayal. Physiognomy, often considered a superficial technique, interprets a character's personality through physical appearance or facial features, reflecting historical biases rather than nuanced development. Modern literary approaches prioritize psychological complexity and motivation over physiognomic stereotypes to enhance narrative authenticity.
Physiognomy in Literature and Art
Physiognomy in literature and art involves the representation of characters' facial features and expressions to convey personality traits and emotions, often shaping audience perceptions without explicit narrative description. This technique draws on historical and cultural associations with specific facial attributes, enabling creators to visually communicate inner qualities or moral alignments. Artists and authors utilize physiognomic cues to deepen character development, influence thematic interpretations, and enhance emotional impact in storytelling.
Ethical Implications of Physiognomy
Physiognomy, the practice of assessing a person's character based on facial features, raises significant ethical concerns due to its potential for reinforcing stereotypes and justifying discrimination. This pseudoscientific method lacks empirical support and can perpetuate biases that affect social justice and human rights. In contrast, characterization in literature evaluates personality through behavior and choices, avoiding the ethical pitfalls associated with physiognomy's reductive judgments.
Characterization Techniques Beyond Physical Appearance
Characterization techniques extend beyond physiognomy by exploring personality traits, psychological motivations, and social interactions to create a multidimensional character. Writers employ dialogue, internal monologue, and behavior patterns to reveal complex emotions and ethical dilemmas, enriching narrative depth. Symbolism and relationships further develop characters, offering insights into their values and growth throughout the story.
Misconceptions: When Physiognomy Influences Characterization
Misconceptions arise when physiognomy--the assessment of character based on facial features--unduly influences characterization, leading to stereotypes and biased interpretations. This conflation falsely assumes that external appearance directly reveals internal traits, ignoring the complexity of personality development. Effective characterization requires nuanced psychological insight beyond superficial physiognomic judgments to avoid reinforcing prejudiced or simplistic narratives.
Contemporary Views on Characterization and Physiognomy
Contemporary views on characterization emphasize the psychological depth, motivations, and development of fictional characters, moving beyond surface-level descriptions to explore complex human behaviors and emotions. In contrast, modern perspectives largely reject physiognomy--the assessment of character based on physical appearance--as unscientific and ethically problematic, recognizing its historical use in reinforcing stereotypes and biases. Current literary and psychological analysis prioritize internal traits and narrative context, distancing from outdated physiognomic theories.
Impact on Readers: Perceiving Character Traits and Morality
Characterization provides readers with a deep understanding of characters' motivations, emotions, and ethical complexities, enabling nuanced judgment of their morality. Physiognomy relies on physical appearance to imply character traits, often leading readers to form immediate but superficial impressions. This contrast influences how readers engage with moral ambiguity, as characterization encourages empathy and critical thinking, while physiognomy may reinforce stereotypes and bias.
Characterization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com