Stream of consciousness is a narrative technique that captures the continuous flow of a character's thoughts and feelings, often without conventional punctuation or structure. This method immerses readers deeply into the character's inner experience, revealing emotions and memories in a raw, unfiltered manner. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this style enhances storytelling and its impact on your reading experience.
Table of Comparison
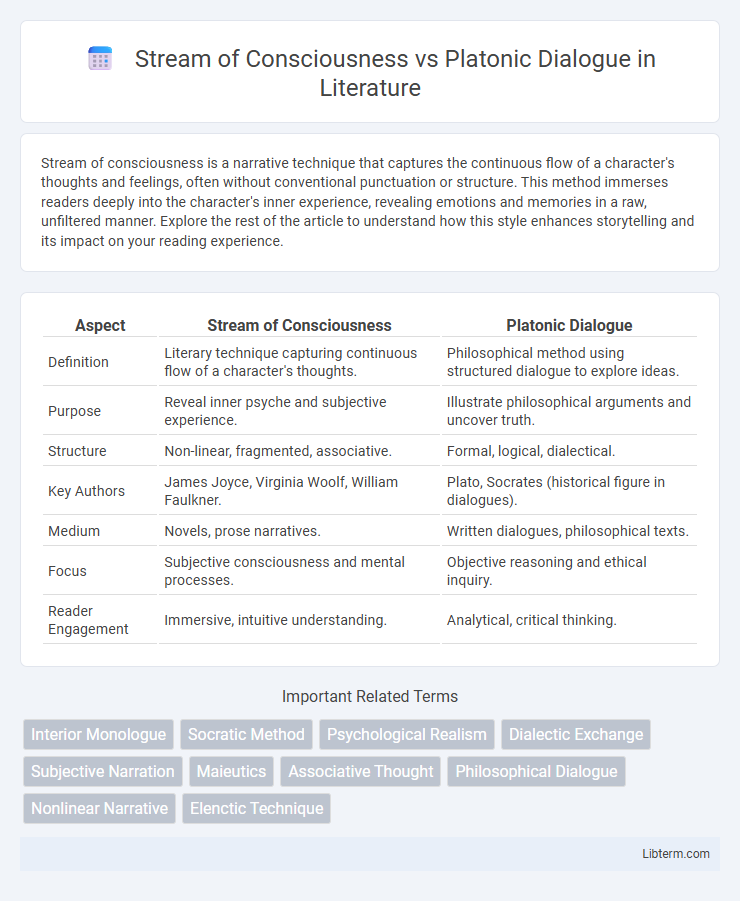
| Aspect | Stream of Consciousness | Platonic Dialogue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary technique capturing continuous flow of a character's thoughts. | Philosophical method using structured dialogue to explore ideas. |
| Purpose | Reveal inner psyche and subjective experience. | Illustrate philosophical arguments and uncover truth. |
| Structure | Non-linear, fragmented, associative. | Formal, logical, dialectical. |
| Key Authors | James Joyce, Virginia Woolf, William Faulkner. | Plato, Socrates (historical figure in dialogues). |
| Medium | Novels, prose narratives. | Written dialogues, philosophical texts. |
| Focus | Subjective consciousness and mental processes. | Objective reasoning and ethical inquiry. |
| Reader Engagement | Immersive, intuitive understanding. | Analytical, critical thinking. |
Introduction to Stream of Consciousness and Platonic Dialogue
Stream of consciousness is a literary technique that captures the continuous flow of a character's thoughts, emotions, and sensory experiences, often in an unstructured and nonlinear manner, reflecting the natural workings of the human mind. Platonic dialogue, rooted in the philosophical works of Plato, employs structured conversational exchanges to explore ideas, employing question-and-answer formats that reveal underlying truths through reasoned arguments. These two methods contrast in their focus: while stream of consciousness emphasizes subjective inner experience, Platonic dialogue prioritizes objective philosophical inquiry and logical clarity.
Historical Origins of Both Styles
Stream of consciousness emerged in the early 20th century, pioneered by writers such as James Joyce and Virginia Woolf, drawing from psychological theories on human perception and introspection. Platonic dialogue, rooted in ancient Greece around the 4th century BCE, originated with the philosopher Plato, who used dialectic conversations to explore philosophical ideas and achieve intellectual clarity. These distinct historical origins reflect their foundational purposes: the former to depict inner thoughts fluidly and the latter to reason through dialectical exchange.
Defining Stream of Consciousness
Stream of Consciousness is a narrative technique that captures the continuous flow of a character's thoughts, feelings, and sensory experiences, often presented in a fragmented or nonlinear style. This method emphasizes the interior monologue, revealing the subconscious mind without logical order or external dialogue constraints. In contrast, Platonic Dialogue is a structured form of philosophical discourse using reasoned arguments between interlocutors to explore ideas systematically.
Defining Platonic Dialogue
Platonic Dialogue is a dialectical method in which philosophical ideas are explored through structured conversations, often featuring Socratic questioning to uncover underlying truths. Unlike Stream of Consciousness, which captures the unfiltered flow of a character's thoughts and feelings, Platonic Dialogue emphasizes logical argumentation and critical examination. This form, rooted in Plato's works, aims to achieve clarity and philosophical insight by engaging participants in reasoned debate.
Narrative Structure: Flow vs. Framework
Stream of consciousness employs a fluid narrative structure that mimics natural thought processes, allowing readers to experience characters' unfiltered emotions and perceptions in real-time. Platonic dialogue follows a deliberate framework centered around structured argumentation and philosophical exploration, where ideas unfold methodically through question-and-answer exchanges. The contrast lies in stream of consciousness's emphasis on continuous mental flow versus Platonic dialogue's ordered progression of intellectual discourse.
Exploration of Inner Thought vs. Socratic Inquiry
Stream of Consciousness delves deeply into the spontaneous and unfiltered flow of a character's inner thoughts, capturing the raw, subjective experience of consciousness. Platonic Dialogue, by contrast, emphasizes structured Socratic inquiry through dialectical questioning to rigorously examine philosophical concepts and reach logical conclusions. While Stream of Consciousness prioritizes introspective exploration and emotional depth, Platonic Dialogue focuses on reasoned argumentation and critical thinking.
Language and Expression: Stylistic Differences
Stream of consciousness employs fragmented, free-flowing language that mimics the natural, often chaotic, inner thoughts of characters, emphasizing raw emotion and psychological depth. In contrast, Platonic dialogue utilizes structured, logical, and formal language aimed at clarity and philosophical argumentation through reasoned debate. The stylistic difference lies in stream of consciousness favoring subjective, associative expression, while Platonic dialogue prioritizes objective, systematic discourse.
Literary Impact and Notable Examples
Stream of consciousness revolutionized literary narrative by immersing readers in characters' raw, unfiltered thoughts, exemplified by James Joyce's *Ulysses* and Virginia Woolf's *Mrs Dalloway*. Platonic dialogue influenced philosophical literature through structured conversational exchanges that explore abstract ideas, notably in Plato's *Republic* and *Symposium*. Both techniques significantly shaped their genres, with stream of consciousness advancing modernist fiction and Platonic dialogue underpinning Western philosophical discourse.
Readers’ Experience and Interpretative Engagement
Stream of consciousness immerses readers in the unfiltered flow of a character's thoughts, creating an intimate and often nonlinear narrative experience that demands active interpretation to uncover underlying emotions and motivations. Platonic dialogue engages readers through structured philosophical exchanges, encouraging analytical thinking and direct engagement with ideas by presenting arguments and counterarguments in a clear, dialogic format. Both styles enhance interpretative engagement, with stream of consciousness fostering emotional empathy and subjective insight, while Platonic dialogue promotes critical reasoning and objective understanding.
Comparative Analysis: Strengths and Limitations
Stream of consciousness offers an immersive, unfiltered representation of a character's internal thoughts, revealing deep psychological complexity and emotional intensity, but its nonlinear, fragmented style can hinder clarity and reader comprehension. Platonic dialogue excels in presenting structured philosophical arguments through clear, logical exchanges between interlocutors, facilitating critical thinking and conceptual precision, yet it may lack emotional depth and accessibility for broader audiences. Both methods serve distinct literary and philosophical functions, with stream of consciousness emphasizing subjective experience and Platonic dialogue prioritizing rational discourse.
Stream of Consciousness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com