Circumlocution involves using excessive or indirect language to express an idea, often making communication less clear and more complex. This technique can sometimes obscure the intended message, leading to misunderstandings or confusion. Explore the rest of the article to learn how circumlocution impacts your communication and ways to avoid it.
Table of Comparison
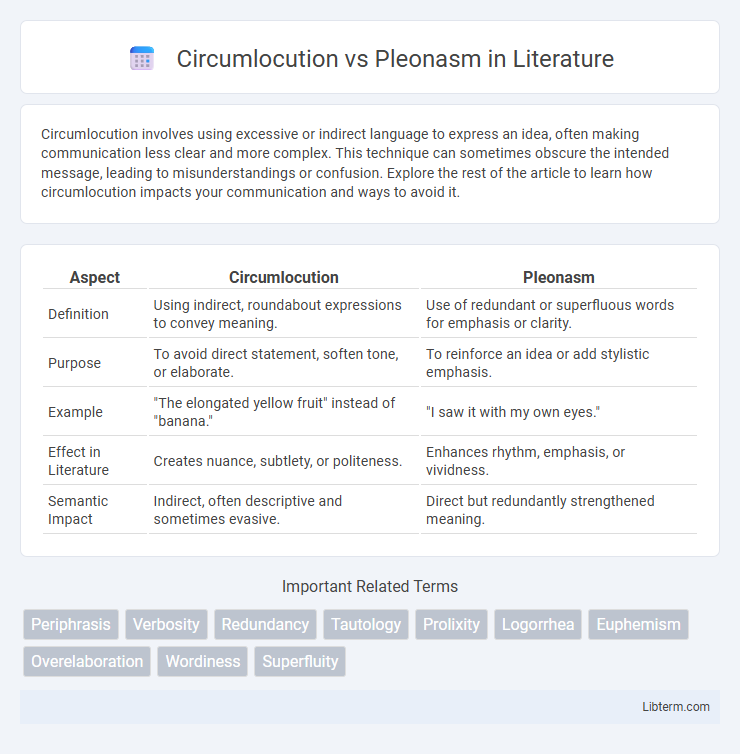
| Aspect | Circumlocution | Pleonasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using indirect, roundabout expressions to convey meaning. | Use of redundant or superfluous words for emphasis or clarity. |
| Purpose | To avoid direct statement, soften tone, or elaborate. | To reinforce an idea or add stylistic emphasis. |
| Example | "The elongated yellow fruit" instead of "banana." | "I saw it with my own eyes." |
| Effect in Literature | Creates nuance, subtlety, or politeness. | Enhances rhythm, emphasis, or vividness. |
| Semantic Impact | Indirect, often descriptive and sometimes evasive. | Direct but redundantly strengthened meaning. |
Introduction to Circumlocution and Pleonasm
Circumlocution involves using several words to express an idea that could be stated more concisely, often to avoid directly naming something or to be intentionally vague. Pleonasm refers to the use of redundant words or phrases that add no extra meaning, such as "free gift" or "end result." Both linguistic phenomena highlight different ways language can become verbose, either through indirect expression or unnecessary repetition.
Defining Circumlocution
Circumlocution is a rhetorical device involving the use of an unnecessarily wordy or indirect expression to convey a simple idea, often to avoid direct language or to add emphasis. It contrasts with pleonasm, which is the use of redundant or superfluous words to enhance clarity or style, rather than to evade straightforward communication. Circumlocution can function as a deliberate stylistic choice in literature or speech, creating a nuanced or evasive tone.
Understanding Pleonasm
Pleonasm involves the use of redundant words or phrases that do not add new meaning, often creating emphasis or stylistic effect, such as "free gift" or "past history." Understanding pleonasm requires recognizing its presence in everyday language where repetition is intentional for clarity or rhetorical impact rather than accidental verbosity. In contrast, circumlocution uses indirect and lengthy expressions to explain something simply stated, making pleonasm a specific type of redundancy focused on superfluous language.
Key Differences Between Circumlocution and Pleonasm
Circumlocution involves using many words to express an idea indirectly, often to be vague or evasive, whereas pleonasm entails the use of redundant or unnecessary words that add no new meaning. The key difference lies in circumlocution's purposeful roundabout expression versus pleonasm's unintentional redundancy. Understanding these distinctions helps identify when language is deliberately elaborate or simply tautological.
Common Examples of Circumlocution
Circumlocution involves using multiple words to express an idea that could be stated more simply, such as saying "a person who writes books" instead of "author," or "the period of time between lunch and dinner" instead of "afternoon." Common examples include phrases like "the man upstairs" for a landlord or "the vehicle of transportation" instead of simply "car." In contrast, pleonasm is the use of redundant words, such as "free gift" or "true fact," which adds unnecessary repetition rather than clarity.
Typical Instances of Pleonasm
Typical instances of pleonasm include redundant phrases such as "free gift," "advance planning," and "true fact," where extra words unnecessarily repeat the meaning for emphasis or clarity. Pleonasm often occurs in everyday speech and writing to add stylistic emphasis or reinforce ideas, contrasting with circumlocution which uses indirect or roundabout expressions to convey meaning. Recognizing pleonasm helps in refining language for conciseness, while its deliberate use can enhance rhetorical effect.
Effects on Writing and Communication
Circumlocution, characterized by indirect or roundabout expressions, often leads to vagueness and reduces clarity in writing, hindering effective communication by confusing readers or listeners. Pleonasm involves the use of redundant words that add emphasis or stylistic flair but can result in verbosity and weaken the impact of the message if overused. Both affect writing by either obscuring meaning or diluting conciseness, impacting the reader's comprehension and engagement.
Why Writers Use Circumlocution and Pleonasm
Writers use circumlocution to express ideas indirectly, often to soften statements or add nuance by avoiding blunt language, which enhances creativity and subtlety in communication. Pleonasm is employed to reinforce meaning, create emphasis, or achieve a rhythmic or poetic effect, despite occasionally introducing redundancy. Both techniques serve specific rhetorical purposes that enrich the texture and clarity of written and spoken language.
Strategies to Avoid Wordiness
Circumlocution involves using many words to express an idea that could be stated more concisely, while pleonasm is the redundant use of words that repeat the same meaning. Strategies to avoid wordiness include identifying and eliminating unnecessary phrases, simplifying complex expressions, and ensuring each word adds value to the sentence. Using precise vocabulary and restructuring sentences for clarity enhances communication efficiency and reduces redundancy.
Conclusion: Enhancing Clarity in Communication
Circumlocution involves using indirect or roundabout expressions, often leading to ambiguity, while pleonasm incorporates redundant words that can clutter the message but sometimes emphasize a point. Enhancing clarity in communication requires recognizing when circumlocution obscures meaning and when pleonasm unnecessarily inflates language. Effective speakers and writers prioritize concise, precise language that conveys ideas clearly without excessive verbosity or repetition.
Circumlocution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com