Epistrophe is a powerful rhetorical device that involves the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences, creating emphasis and rhythm. This technique enhances the emotional impact of writing or speech, making messages more memorable and persuasive. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can effectively use epistrophe in your communication.
Table of Comparison
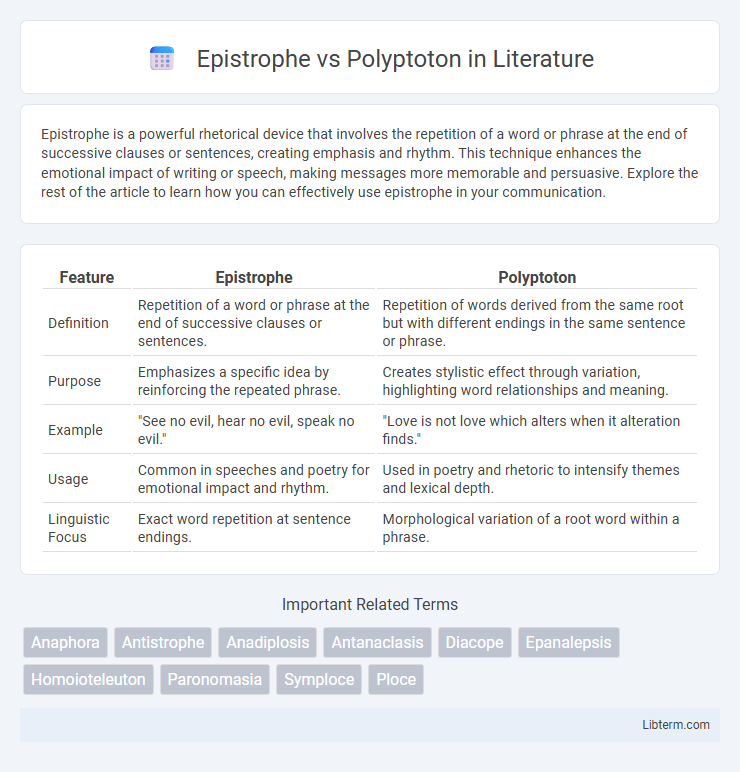
| Feature | Epistrophe | Polyptoton |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences. | Repetition of words derived from the same root but with different endings in the same sentence or phrase. |
| Purpose | Emphasizes a specific idea by reinforcing the repeated phrase. | Creates stylistic effect through variation, highlighting word relationships and meaning. |
| Example | "See no evil, hear no evil, speak no evil." | "Love is not love which alters when it alteration finds." |
| Usage | Common in speeches and poetry for emotional impact and rhythm. | Used in poetry and rhetoric to intensify themes and lexical depth. |
| Linguistic Focus | Exact word repetition at sentence endings. | Morphological variation of a root word within a phrase. |
Introduction to Epistrophe and Polyptoton
Epistrophe is a rhetorical device characterized by the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences, creating emphasis and rhythm. Polyptoton involves the repetition of a root word in different grammatical forms within the same sentence or passage, enhancing meaning through variation and contrast. Both techniques serve to intensify expression and reinforce key concepts in literary and oratory contexts.
Defining Epistrophe: Meaning and Usage
Epistrophe is a rhetorical device characterized by the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences, enhancing emphasis and rhythm in speech or writing. It is commonly used in literature, speeches, and persuasive texts to reinforce a particular idea or emotional appeal. Unlike polyptoton, which involves repeating words derived from the same root, epistrophe strictly focuses on the recurring terminal phrase for impact.
Understanding Polyptoton: Definition and Examples
Polyptoton is a rhetorical device involving the repetition of words derived from the same root but with different endings, such as "strong" and "strength," to create emphasis and enhance meaning. This figure of speech frequently appears in literature and speeches to evoke emotional resonance and reinforce key themes, exemplified in phrases like "Choosy mothers choose Jif." Understanding polyptoton helps to appreciate the nuanced use of language that intensifies persuasion and literary impact.
Historical Origins of Both Rhetorical Devices
Epistrophe, with roots in Ancient Greek rhetoric, was a favored device among classical orators like Demosthenes to emphasize repeated endings for persuasive effect. Polyptoton originated from Latin literary traditions, extensively used by Roman poets such as Virgil to create stylistic repetition through variations of the same root word. Both devices evolved during antiquity, embedding themselves in Western rhetorical theory and practices of speech and poetry.
Key Differences: Epistrophe vs Polyptoton
Epistrophe is the rhetorical device characterized by the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences, creating emphasis through consistent closure. Polyptoton involves repeating the same root word in different forms within a sentence or phrase, highlighting variations in meaning and grammatical function. The key difference lies in epistrophe's repetition at clause endings versus polyptoton's morphological variations of words within a single expression.
The Effect of Epistrophe in Persuasive Writing
Epistrophe, the repetition of words at the end of successive clauses, enhances persuasive writing by reinforcing key ideas and creating a memorable rhythm that appeals to readers' emotions. This technique amplifies emphasis on central themes, aiding in argument retention and strengthening the writer's call to action. Unlike polyptoton, which involves repetition of words derived from the same root, epistrophe directly anchors the audience's focus through strategic word placement.
The Impact of Polyptoton on Language and Style
Polyptoton enhances language by repeating words derived from the same root, creating rhythmic emphasis and intensifying meaning through variation, as seen in literature and rhetoric. This stylistic device deepens thematic resonance by reinforcing ideas with nuanced repetition, engaging readers emotionally and intellectually. Its impact on style lies in promoting eloquence and memorability, distinguishing texts through sophisticated wordplay.
Famous Literary Examples of Epistrophe
Epistrophe, a rhetorical device featuring the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses, is famously exemplified in Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address with the repeated phrase "of the people, by the people, for the people." Shakespeare also utilized epistrophe in his plays, such as the line "I'll have my bond!" in *The Merchant of Venice*, emphasizing the final repeated terms. Unlike polyptoton, which involves the repetition of a root word in different forms, epistrophe strictly repeats the ending phrase to create emphasis and rhythm.
Notable Instances of Polyptoton in Literature
Polyptoton, a rhetorical device involving the repetition of words derived from the same root, appears prominently in Shakespeare's works, such as "Love is not love which alters when it alteration finds" in Sonnet 116. Classical literature also features polyptoton, with Cicero employing it to emphasize ideas through variations like "virtue" and "virtuous." These notable instances highlight polyptoton's power to create emphasis and rhythm by exploiting the morphological variations of key terms.
Choosing Between Epistrophe and Polyptoton in Writing
Choosing between epistrophe and polyptoton depends on the desired emphasis and rhythmic effect in writing. Epistrophe, the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses, creates a strong, memorable cadence that reinforces key ideas. Polyptoton involves the repetition of a root word in different grammatical forms, adding complexity and depth by highlighting contrasts or nuances in meaning.
Epistrophe Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com