Crafting a compelling introduction is essential for engaging readers and setting the tone of your content. It should capture attention quickly, outline the main topic, and invite curiosity to encourage further reading. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for writing introductions that captivate your audience.
Table of Comparison
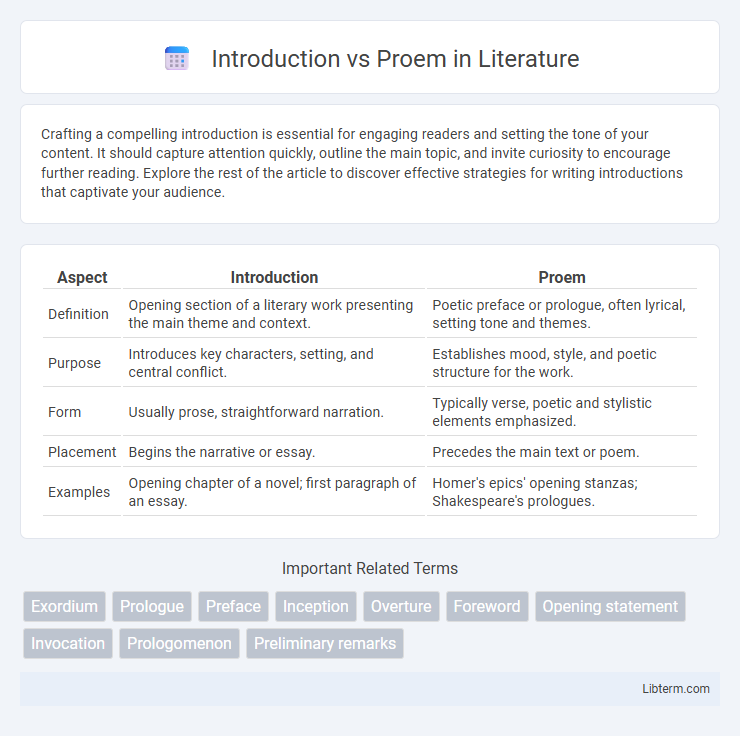
| Aspect | Introduction | Proem |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Opening section of a literary work presenting the main theme and context. | Poetic preface or prologue, often lyrical, setting tone and themes. |
| Purpose | Introduces key characters, setting, and central conflict. | Establishes mood, style, and poetic structure for the work. |
| Form | Usually prose, straightforward narration. | Typically verse, poetic and stylistic elements emphasized. |
| Placement | Begins the narrative or essay. | Precedes the main text or poem. |
| Examples | Opening chapter of a novel; first paragraph of an essay. | Homer's epics' opening stanzas; Shakespeare's prologues. |
Understanding the Concept of Introduction
The introduction serves as the initial section of a text, designed to present the main topic and outline the purpose, setting the stage for the reader. A proem, often used interchangeably with introduction, specifically refers to a preliminary or preface-like segment that introduces themes more poetically or broadly. Understanding the concept of introduction involves recognizing its role in guiding the audience's expectations and providing essential context for the ensuing content.
Defining Proem: A Literary Perspective
Proem, in literary terms, refers to a brief introductory section or preface that sets the tone and purpose of a work, often distinct from a straightforward introduction. It serves as a thematic gateway, encapsulating the essence and mood to engage readers before the main content begins. Unlike a typical introduction, a proem emphasizes stylistic expression and poetic nuance, enriching the reader's anticipation and understanding of the text.
Historical Origins of Introductions and Proems
Introductions and proems both serve as preliminary texts but differ substantially in historical usage and purpose. Introductions historically emerged in the medieval and Renaissance periods as explanatory or guiding sections preceding the main content, often used in academic and literary works to prepare readers. Proems, deriving from the Greek "prooimion," were classical literary openings designed to establish tone and thematic context, especially prevalent in ancient epic poetry and philosophical treatises.
Structural Differences: Introduction vs Proem
The Introduction typically serves as a formal opening that outlines the main topics and objectives of a text, establishing a clear roadmap for the reader. The Proem, by contrast, is a more poetic or rhetorical prelude often found in classical literature, aiming to engage the audience emotionally and thematically rather than providing explicit content structure. Structurally, the Introduction is concise and straightforward, while the Proem employs figurative language and thematic hints to set the tone and invite contemplation.
Purpose and Functions in Texts
The introduction establishes the overall context and purpose of a text, guiding readers into the main subject and outlining key themes or arguments. The proem serves a more specialized function, often employed in classical or literary works to set the tonal or stylistic framework, engaging readers emotionally or rhetorically before the main content begins. Both elements enhance reader comprehension but differ in scope; the introduction is broad and informational, while the proem is concise and evocative.
Usage in Various Literary Genres
Introductions serve as the opening section in essays, reports, and academic papers, providing context, thesis statements, and guiding readers into the subject matter. Proems appear predominantly in poetry, epic narratives, and classical literature, functioning as prefatory passages that establish thematic tone, invoke muses or inspiration, and frame the ensuing story. While introductions prioritize clarity and direct exposition across various genres, proems emphasize artistic expression and thematic resonance, reflecting their distinct literary purposes.
Stylistic Approaches: Analytical vs Artistic
Introduction typically employs an analytical stylistic approach, focusing on clear, concise presentation of key themes and objectives to guide the reader's understanding. Proem adopts an artistic style, rich in metaphor and imagery, designed to evoke emotion and set a tonal atmosphere rather than deliver straightforward information. This contrast highlights the Introduction's function as an explanatory framework versus the Proem's role as a literary or poetic overture.
Notable Examples in Literature
Notable examples in literature highlight the distinction between introduction and proem, where the introduction typically sets the scene or tone of the work, as seen in Charles Dickens' "A Tale of Two Cities," which begins with the famous line, "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times." In contrast, the proem serves as a poetic preamble or invocation, exemplified by Homer's "Iliad," where the opening lines directly call upon the Muse to inspire the epic, establishing both theme and authority. This differentiation underscores the proem's more artistic and formal role compared to the often straightforward narrative function of the introduction.
Relevance in Modern Writing
In modern writing, the Introduction establishes the context and purpose, providing readers with a clear overview of the content to follow. The Proem, often used in classical poetry and formal prose, serves as a thematic prelude that sets the tone and invites readers into the narrative or argument. While the Introduction prioritizes clarity and directness, the Proem emphasizes stylistic engagement, making both elements relevant depending on the writer's intent and audience expectations.
Choosing the Right Opening: When to Use Introduction or Proem
Choosing between an introduction and a proem depends on the purpose and structure of the text; an introduction typically provides a clear overview and sets the stage for formal content, while a proem offers a poetic or thematic preamble that establishes mood or tone. Use an introduction in academic papers, reports, or essays requiring clarity and directness to guide readers through the subject matter. Opt for a proem in literary works, speeches, or narratives where evoking emotion or atmosphere enhances engagement before the main content begins.
Introduction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com