Syntax governs the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences, ensuring clarity and coherence in communication. Mastering syntax enhances your ability to convey complex ideas effectively and engage readers with fluid, meaningful language. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of syntax and its crucial role in writing.
Table of Comparison
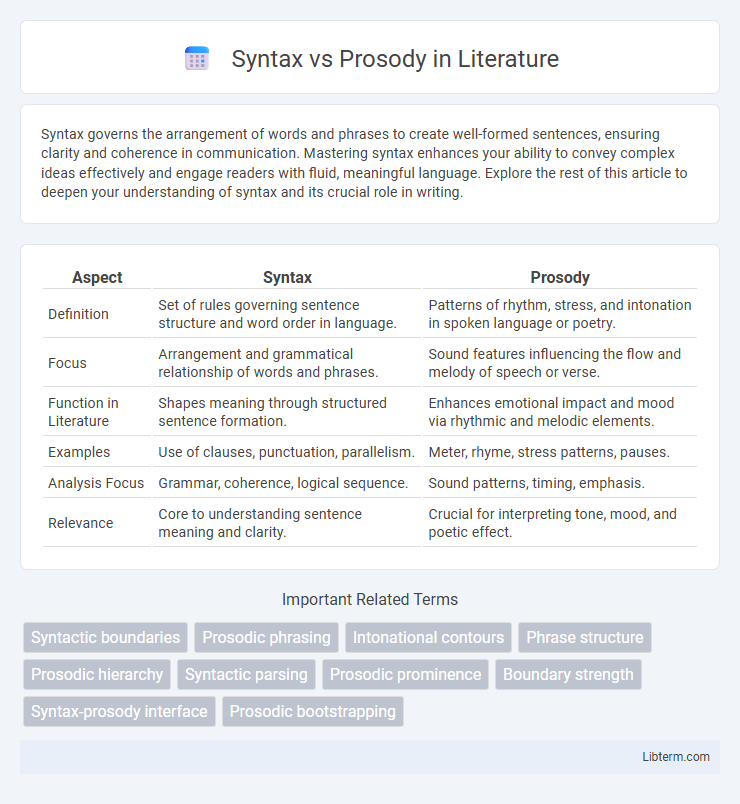
| Aspect | Syntax | Prosody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of rules governing sentence structure and word order in language. | Patterns of rhythm, stress, and intonation in spoken language or poetry. |
| Focus | Arrangement and grammatical relationship of words and phrases. | Sound features influencing the flow and melody of speech or verse. |
| Function in Literature | Shapes meaning through structured sentence formation. | Enhances emotional impact and mood via rhythmic and melodic elements. |
| Examples | Use of clauses, punctuation, parallelism. | Meter, rhyme, stress patterns, pauses. |
| Analysis Focus | Grammar, coherence, logical sequence. | Sound patterns, timing, emphasis. |
| Relevance | Core to understanding sentence meaning and clarity. | Crucial for interpreting tone, mood, and poetic effect. |
Introduction to Syntax and Prosody
Syntax governs the structural arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language, enabling clear communication of meaning. Prosody involves the rhythm, stress, and intonation patterns in spoken language, which influence how syntactic structures are interpreted and understood. Together, syntax and prosody interact to enhance linguistic comprehension and convey subtle nuances beyond the literal semantic content.
Defining Syntax: Structure and Rules
Syntax defines the structured set of rules governing the arrangement of words and phrases to create meaningful sentences in a language. It establishes the hierarchical relationships between sentence components such as subjects, verbs, and objects, ensuring grammatical coherence. Understanding syntax is essential for parsing sentence construction and enabling clear communication through consistent linguistic patterns.
What is Prosody? Rhythm and Intonation
Prosody refers to the patterns of rhythm, stress, and intonation in spoken language, playing a crucial role in conveying meaning beyond the literal words. It influences how sentences are understood by signaling questions, statements, emotions, and emphasis through variations in pitch, duration, and intensity. Unlike syntax, which deals with sentence structure and grammatical rules, prosody focuses on the melodic and temporal qualities of speech that shape communication and listener interpretation.
Core Differences Between Syntax and Prosody
Syntax governs the structure and order of words in sentences, defining grammatical relationships and rules essential for meaningful communication. Prosody involves the rhythm, stress, and intonation patterns in spoken language, which convey emotion, emphasis, and speaker intent beyond word choice. Core differences lie in syntax's focus on sentence construction and grammatical correctness, while prosody shapes speech modulation and expressive nuance.
The Role of Syntax in Sentence Construction
Syntax governs the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences, ensuring clarity and coherence in communication. It defines grammatical structures such as subject-verb agreement, phrase hierarchy, and sentence types, essential for interpreting meaning accurately. Proper syntactic construction supports semantic precision, enabling speakers and writers to convey complex ideas effectively.
How Prosody Influences Meaning
Prosody influences meaning by shaping the rhythm, stress, and intonation patterns that modulate how syntax is interpreted in spoken language. Variations in pitch and timing can clarify questions, commands, or emotions, altering the listener's understanding without changing the underlying syntactic structure. For example, rising intonation may indicate a question, while stress placement can emphasize particular words, guiding semantic focus beyond the fixed word order of syntax.
Syntax vs Prosody in Language Comprehension
Syntax structures sentences by organizing words into grammatical patterns, enabling the interpretation of complex ideas and relationships within language. Prosody, characterized by intonation, stress, and rhythm, provides cues that influence sentence meaning and disambiguate syntactic structures during spoken language comprehension. Effective language understanding relies on integrating syntactic rules with prosodic features to accurately interpret speaker intent and contextual nuances.
Interaction of Syntax and Prosody in Communication
Syntax structures the arrangement of words into sentences, defining grammatical relationships and meaning, while prosody conveys rhythm, intonation, and stress patterns, impacting how messages are interpreted. Their interaction enhances communication by clarifying ambiguities, signaling sentence boundaries, and emphasizing specific information to guide listener understanding. Prosodic cues often reflect syntactic structures, enabling efficient parsing and emotional nuance in spoken language.
Studying Syntax and Prosody: Methods and Tools
Studying syntax and prosody involves analyzing sentence structure and speech patterns using diverse methods such as syntactic tree parsing and acoustic signal processing. Tools like syntactic parsers enable detailed examination of grammatical relationships, while software such as Praat facilitates the analysis of intonation, rhythm, and stress in spoken language. Combining these approaches provides insights into how syntactic structures influence prosodic features, enhancing understanding of spoken communication.
Implications for Language Learning and Linguistics
Syntax governs the structural rules of sentence formation, while prosody involves the rhythm, stress, and intonation patterns in speech; their interaction significantly impacts language acquisition and linguistic analysis. Variations in prosodic features can alter syntactic parsing, affecting comprehension and fluency in second-language learners. Understanding the synergy between syntax and prosody enhances models of natural language processing and informs effective teaching strategies in linguistics.
Syntax Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com