Correction enhances accuracy and clarity, ensuring your communication is effective and professional. It involves identifying and rectifying errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, and style. Explore the article to understand the essential techniques and benefits of precise correction practices.
Table of Comparison
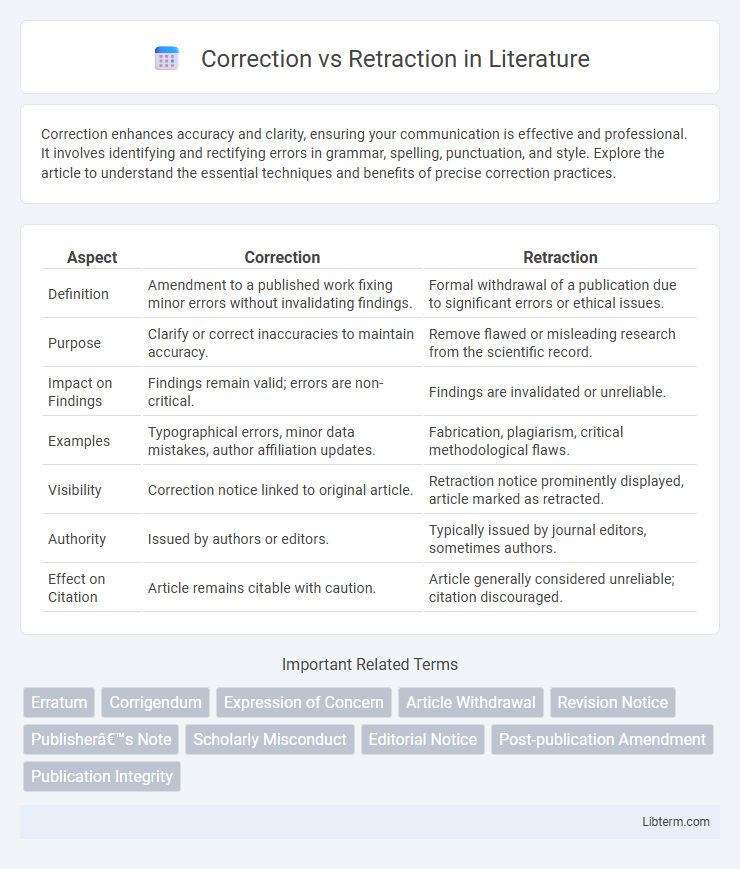
| Aspect | Correction | Retraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Amendment to a published work fixing minor errors without invalidating findings. | Formal withdrawal of a publication due to significant errors or ethical issues. |
| Purpose | Clarify or correct inaccuracies to maintain accuracy. | Remove flawed or misleading research from the scientific record. |
| Impact on Findings | Findings remain valid; errors are non-critical. | Findings are invalidated or unreliable. |
| Examples | Typographical errors, minor data mistakes, author affiliation updates. | Fabrication, plagiarism, critical methodological flaws. |
| Visibility | Correction notice linked to original article. | Retraction notice prominently displayed, article marked as retracted. |
| Authority | Issued by authors or editors. | Typically issued by journal editors, sometimes authors. |
| Effect on Citation | Article remains citable with caution. | Article generally considered unreliable; citation discouraged. |
Understanding Corrections and Retractions
Corrections address minor errors or clarifications in published research without invalidating the overall findings, ensuring the accuracy and integrity of the scientific record. Retractions occur when significant flaws, such as data fabrication or ethical violations, undermine the validity of the entire study, necessitating removal from the literature. Understanding these processes is crucial for maintaining trust in academic publishing and guiding researchers, editors, and readers in handling post-publication issues effectively.
Key Differences Between Correction and Retraction
Correction addresses minor errors in a published work, such as typographical mistakes or inaccuracies that do not affect the overall validity of the research, ensuring the integrity of the scientific record is maintained. Retraction occurs when the errors or misconduct significantly undermine the reliability or ethical standing of the entire study, often leading to withdrawal of the article from the journal. Corrections maintain the original publication with amendments, whereas retractions remove the publication from the formal literature to prevent the spread of invalid or fraudulent findings.
Common Reasons for Issuing Corrections
Common reasons for issuing corrections in academic publishing include errors in data presentation, misinterpretation of results, and typographical mistakes that affect the clarity or accuracy of the findings. Corrections address minor issues without invalidating the core conclusions, unlike retractions which involve fundamental flaws or ethical violations. Prompt issuance of corrections maintains the integrity of the scientific record and ensures transparency in research communication.
When is a Retraction Necessary?
A retraction is necessary when a published work contains critical errors or fraudulent data that invalidate the study's main findings, posing a risk to scientific integrity and public trust. Retractions address issues such as plagiarism, ethical violations, or irreproducible results, where mere corrections cannot resolve the underlying problems. Journals follow guidelines from organizations like COPE (Committee on Publication Ethics) to determine when retracting an article ensures the accuracy and reliability of the scientific record.
Impact of Corrections on Research Integrity
Corrections play a crucial role in maintaining research integrity by addressing errors without undermining the validity of the overall study, allowing scientific knowledge to evolve transparently. Retractions, in contrast, signify fundamental flaws or misconduct that invalidate the research findings, often leading to significant reputational damage and citation loss. Timely and clear corrections help preserve trust in the scientific record and ensure that subsequent research is built on accurate data.
Consequences of Retractions for Authors
Retractions can severely damage an author's professional reputation, often leading to loss of credibility and trust within the academic community. They may result in decreased citation rates, diminished future funding opportunities, and potential disciplinary actions from institutions or publishers. The long-term impact includes challenges in career advancement and collaboration due to perceived research integrity issues.
Procedures for Requesting a Correction
Procedures for requesting a correction typically involve submitting a formal notice to the journal or publisher, detailing the specific errors and providing accurate information to amend the original publication. This process requires clear identification of the article, precise description of the inaccuracies, and supporting documentation or evidence to justify the correction. Publishers often have established guidelines to ensure transparency and maintain the integrity of the scholarly record during the correction process.
Retraction Process: Step-by-Step Guide
The retraction process begins with identifying significant errors or ethical issues compromising the validity of a publication. Authors, editors, or institutions submit a formal request, which triggers an investigation to verify concerns and gather evidence. Once confirmed, the journal publishes a clear retraction notice stating the reasons, ensuring the article is labeled as retracted in databases and indexing services to maintain scientific integrity.
Preventing Errors in Scientific Publications
Correction and retraction are critical mechanisms for maintaining the integrity of scientific literature by addressing errors effectively. Corrections typically amend minor mistakes without undermining the overall validity of the research, while retractions remove flawed or fraudulent studies to prevent the dissemination of false information. Implementing rigorous peer review, data verification, and transparent reporting can significantly reduce the need for both corrections and retractions in scientific publications.
Best Practices for Journals and Researchers
Journals and researchers should implement transparent correction policies that clearly distinguish between corrections and retractions, emphasizing the severity and implications of each. Best practices include timely notification, detailed explanations for errors or misconduct, and maintaining accessibility of the original article with linked corrections or retraction notices. Adopting standardized guidelines from organizations like COPE enhances accountability, preserves scientific integrity, and fosters trust in published research.
Correction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com