Chrony is a versatile network time synchronization tool designed for accuracy and reliability in various environments, including virtual machines and intermittent network connections. It efficiently synchronizes system clocks with remote NTP servers, ensuring minimal time drift and improved performance for time-sensitive applications. Explore the rest of the article to learn how Chrony can optimize your system's time management.
Table of Comparison
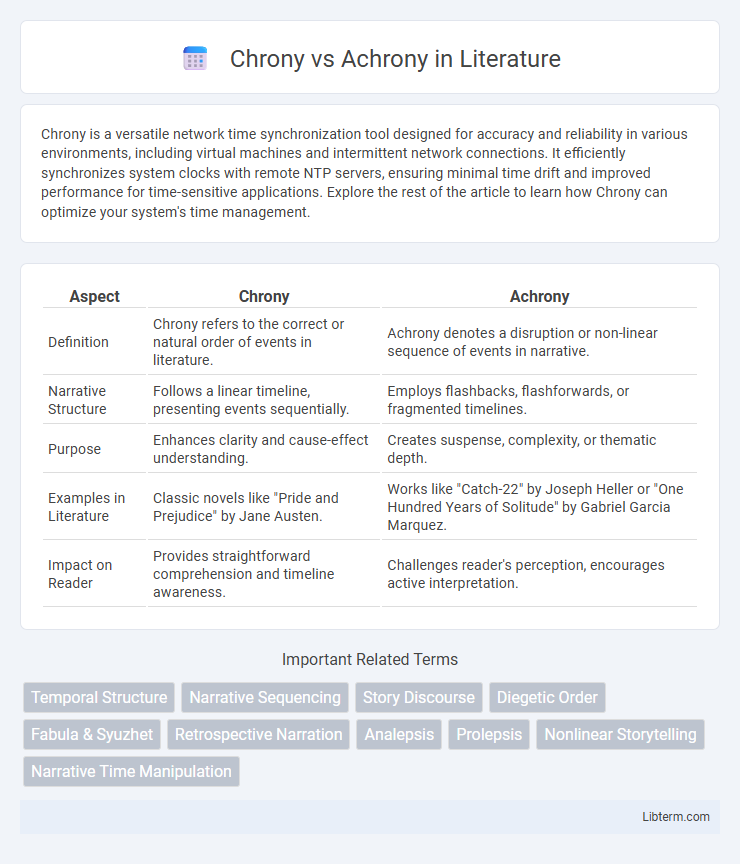
| Aspect | Chrony | Achrony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chrony refers to the correct or natural order of events in literature. | Achrony denotes a disruption or non-linear sequence of events in narrative. |
| Narrative Structure | Follows a linear timeline, presenting events sequentially. | Employs flashbacks, flashforwards, or fragmented timelines. |
| Purpose | Enhances clarity and cause-effect understanding. | Creates suspense, complexity, or thematic depth. |
| Examples in Literature | Classic novels like "Pride and Prejudice" by Jane Austen. | Works like "Catch-22" by Joseph Heller or "One Hundred Years of Solitude" by Gabriel Garcia Marquez. |
| Impact on Reader | Provides straightforward comprehension and timeline awareness. | Challenges reader's perception, encourages active interpretation. |
Introduction to Chrony and Achrony
Chrony is a versatile and efficient network time synchronization tool designed to maintain accurate system clocks by continuously adjusting for drift and latency, especially useful in environments with intermittent connectivity. Achrony serves as an experimental or less commonly used alternative, focusing on different synchronization algorithms or applications with specific timekeeping requirements. Both tools aim to improve time accuracy but differ in their implementation approaches and target use cases within network time synchronization.
Defining Chrony: Meaning and Examples
Chrony refers to events or conditions occurring in proper chronological order, maintaining a clear and logical sequence of time. Examples include historical records that follow a timeline, such as biographies detailing life events year by year or project schedules organized by deadlines. This semantic focus on temporal accuracy distinguishes Chrony as essential for coherent storytelling, data analysis, and systematic documentation.
Understanding Achrony: Meaning and Examples
Achrony refers to the absence or disruption of chronological order, where events or narratives are presented non-linearly or without a fixed temporal sequence. It is commonly used in literature, film, and cognitive studies to explore time perception and narrative structures that challenge conventional timelines. Examples of achrony include nonlinear storytelling in novels like "Cloud Atlas" and films such as "Memento," where events unfold out of chronological sequence to enhance thematic depth and audience engagement.
Key Differences Between Chrony and Achrony
Chrony and Achrony differ primarily in time synchronization accuracy and use cases; Chrony excels in maintaining precise time in unstable network conditions, making it ideal for servers and virtual machines. Achrony, on the other hand, is less common and emphasizes simplicity, often used in smaller or less time-critical environments. Key differences include Chrony's support for both hardware timestamping and dynamic adjustments, whereas Achrony lacks advanced synchronization features and extensive configuration options.
Use Cases for Chrony in Narrative Structures
Chrony excels in narrative structures requiring precise time synchronization, such as distributed storytelling platforms and real-time collaborative editing environments where consistent event order is crucial. Its efficient adjustment algorithm supports asynchronous data fusion and event logging in multimedia projects, ensuring temporal coherence. Chrony's adaptability to varying network conditions makes it ideal for interactive narratives spanning multiple devices or locations.
Use Cases for Achrony in Storytelling
Achrony excels in storytelling by enabling narrative structures that defy linear time, allowing authors to explore memories, dreams, or parallel events uniquely. Its non-chronological framework supports fragmented timelines and multiple perspectives, enhancing thematic depth and emotional resonance in complex stories. This flexibility makes Achrony ideal for genres like mystery, literary fiction, and experimental narratives where temporal disruption drives suspense and audience engagement.
Effects on Reader Perception and Engagement
Chrony, emphasizing chronological storytelling, enhances reader perception by providing clear, linear progression that aids comprehension and emotional investment. In contrast, Achrony disrupts traditional timeline order, challenging readers to piece together events, which can increase engagement through active interpretation but may risk confusion. The choice between Chrony and Achrony significantly influences narrative clarity and reader immersion, impacting cognitive processing and memory retention.
Chrony and Achrony in Modern Literature
Chrony in modern literature often explores the chronological sequencing of events, emphasizing linear narrative structures that enhance clarity and cause-effect relationships. Achrony, by contrast, disrupts temporal order through non-linear storytelling, flashbacks, and fragmented timelines to evoke complexity and reflect psychological or thematic depth. Contemporary authors use chrony to ground readers in time while achrony challenges traditional narrative conventions, fostering experimental literary forms.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Chrony offers high accuracy and fast synchronization in systems with intermittent network connections, making it ideal for virtual machines and mobile devices but may consume more resources compared to simpler time synchronization tools. Achrony provides lower resource usage and simpler implementation, suitable for environments with stable network connectivity, but it may lack the advanced features and rapid correction capabilities found in Chrony. Both approaches balance precision and resource efficiency differently, requiring selection based on specific network stability and performance requirements.
Choosing Between Chrony and Achrony
Choosing between Chrony and Achrony hinges on your synchronization requirements and system environment. Chrony excels in environments with intermittent network connectivity or virtual machines due to its rapid synchronization and resilience to network changes. Achrony is better suited for systems requiring continuous time adjustments with minimal latency, emphasizing precision over adaptability.
Chrony Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com