Narratology explores the structure and function of narrative across various media, analyzing elements like plot, character, and time to uncover how stories shape human experience. Understanding narratology can enhance your ability to interpret and craft compelling narratives in literature, film, and beyond. Dive into the article to discover the key concepts and applications of narratology.
Table of Comparison
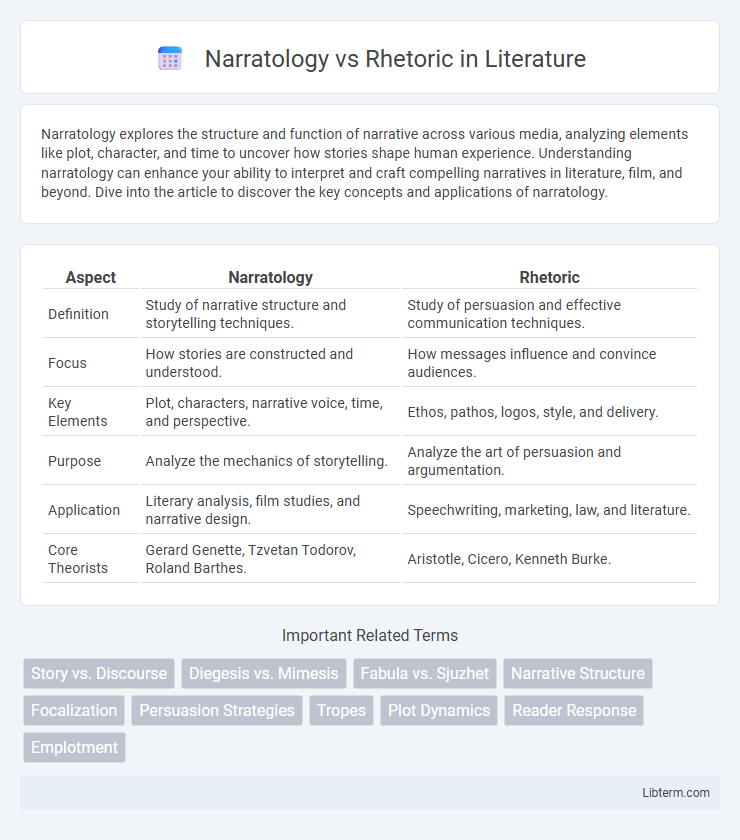
| Aspect | Narratology | Rhetoric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of narrative structure and storytelling techniques. | Study of persuasion and effective communication techniques. |
| Focus | How stories are constructed and understood. | How messages influence and convince audiences. |
| Key Elements | Plot, characters, narrative voice, time, and perspective. | Ethos, pathos, logos, style, and delivery. |
| Purpose | Analyze the mechanics of storytelling. | Analyze the art of persuasion and argumentation. |
| Application | Literary analysis, film studies, and narrative design. | Speechwriting, marketing, law, and literature. |
| Core Theorists | Gerard Genette, Tzvetan Todorov, Roland Barthes. | Aristotle, Cicero, Kenneth Burke. |
Introduction to Narratology and Rhetoric
Narratology studies the structure and function of narrative and storytelling, analyzing plot, characters, and narrative techniques to understand how stories are constructed and interpreted. Rhetoric focuses on the art of persuasion, examining how language and stylistic devices influence audiences and convey meaning in various contexts. Both disciplines intersect in their analysis of language use but differ in their primary goals: narratology centers on storytelling mechanics, while rhetoric emphasizes persuasive communication.
Defining Narratology: Key Concepts
Narratology is the systematic study of narrative structures and how stories are told, focusing on elements such as plot, characters, and narrative time. Key concepts include the distinction between story (fabula) and discourse (sjuzhet), narrative voice, and focalization, which analyze how events are organized and perceived. This contrasts with rhetoric, which centers on persuasion and the effective use of language to influence an audience rather than on narrative construction.
Understanding Rhetoric: Core Principles
Rhetoric centers on persuasive communication strategies, emphasizing ethos, pathos, and logos to influence audiences effectively. It involves structuring arguments, choosing precise language, and adapting messages to context and audience expectations. Mastery of rhetoric enhances the impact of discourse by aligning form and content with persuasive intent.
Historical Origins of Narratology and Rhetoric
Narratology originated in the mid-20th century as a formal study of narrative structures, drawing heavily on the works of scholars like Vladimir Propp and Gerard Genette, while rhetoric dates back to classical antiquity, with roots in ancient Greece and Rome, influenced by figures such as Aristotle, Cicero, and Quintilian who formalized the art of persuasive communication. The historical development of narratology is intertwined with structuralism and semiotics, emphasizing narrative forms and functions, whereas rhetoric evolved as a practical discipline focused on effective speech and writing techniques for persuasion and public discourse. These distinct historical trajectories highlight narratology's analytical approach to storytelling and rhetoric's prescriptive strategies for argumentation and influence.
Methodological Approaches: Narratology vs Rhetoric
Narratology employs a structuralist approach, analyzing narrative elements such as plot, characters, and temporal sequences to uncover underlying story frameworks. Rhetoric focuses on persuasive techniques, emphasizing ethos, pathos, and logos to understand how messages influence audience perception and response. Methodologically, narratology deconstructs narrative form and function, while rhetoric dissects argumentation strategies and stylistic devices.
Story Structure vs Persuasive Technique
Narratology explores the fundamental components of story structure, such as plot, characters, and narrative arcs, to analyze how stories are constructed and understood. Rhetoric emphasizes persuasive techniques, including ethos, pathos, and logos, to influence audience attitudes and behaviors through effective communication. While narratology dissects the framework of storytelling, rhetoric focuses on the strategic deployment of language to achieve persuasion.
Narratology and Rhetoric in Literary Analysis
Narratology examines the structure and function of narrative elements, such as plot, character, and temporality, to understand how stories convey meaning and shape readers' interpretations. Rhetoric centers on the strategic use of language and persuasive techniques to influence audience perception and elicit emotional or intellectual responses. In literary analysis, narratology provides tools for dissecting narrative frameworks, while rhetoric analyzes stylistic devices and argumentation, together enriching comprehension of textual effects and authorial intent.
Points of Intersection and Divergence
Narratology analyzes the structure and function of narrative elements such as plot, character, and temporality, while rhetoric examines strategies of persuasion through language and discourse. Both disciplines intersect in their focus on how stories influence audience perception and meaning-making, yet they diverge as narratology emphasizes storytelling mechanics and rhetoric centers on argumentation and communicative effect. Understanding their points of convergence and divergence enhances insights into narrative persuasion and the construction of meaning in texts.
Contemporary Debates in Narrative and Rhetorical Studies
Contemporary debates in narrative and rhetorical studies focus on the intersection of narratology's structural analysis of story elements and rhetoric's emphasis on persuasive strategies in communication. Scholars examine how narrative techniques function as rhetorical tools to shape audience interpretation and influence ideology within diverse media contexts. This interdisciplinary approach highlights the dynamic interplay between narrative form and rhetorical effect, advancing theoretical frameworks in both fields.
Implications for Future Research and Criticism
Narratology and rhetoric both contribute essential frameworks for analyzing narrative structures but emphasize different aspects: narratology centers on the mechanics of story construction, while rhetoric focuses on persuasive communication and audience effect. Future research can explore their intersection to develop more nuanced models that account for both narrative form and rhetorical impact, improving interpretive depth and critical methodologies. Integrating cognitive science and digital humanities tools may further enhance interdisciplinary approaches to narrative analysis and rhetorical criticism.
Narratology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com