Allegory is a literary device where characters, events, or settings symbolize deeper moral, political, or spiritual meanings beyond their literal sense. This technique enriches storytelling by conveying complex ideas through metaphorical narratives that engage the reader's imagination. Discover how allegory can deepen your understanding of texts and unlock hidden layers of meaning in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
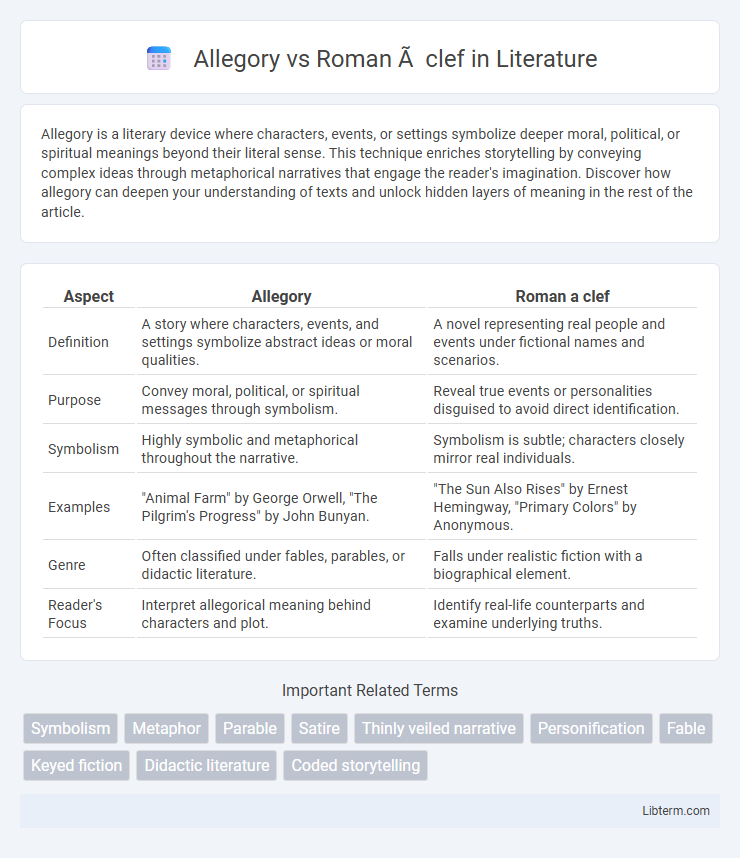
| Aspect | Allegory | Roman a clef |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A story where characters, events, and settings symbolize abstract ideas or moral qualities. | A novel representing real people and events under fictional names and scenarios. |
| Purpose | Convey moral, political, or spiritual messages through symbolism. | Reveal true events or personalities disguised to avoid direct identification. |
| Symbolism | Highly symbolic and metaphorical throughout the narrative. | Symbolism is subtle; characters closely mirror real individuals. |
| Examples | "Animal Farm" by George Orwell, "The Pilgrim's Progress" by John Bunyan. | "The Sun Also Rises" by Ernest Hemingway, "Primary Colors" by Anonymous. |
| Genre | Often classified under fables, parables, or didactic literature. | Falls under realistic fiction with a biographical element. |
| Reader's Focus | Interpret allegorical meaning behind characters and plot. | Identify real-life counterparts and examine underlying truths. |
Understanding Allegory: Definition and Key Features
Allegory is a literary device in which characters, events, and settings symbolically represent abstract ideas or moral qualities, creating a narrative with a deeper meaning beyond the surface story. Key features include a clear, consistent symbolic framework where every element corresponds to a particular concept, often used to convey ethical, religious, or political messages. Unlike a Roman a clef, which fictionalizes real people and events through disguised identities, allegory emphasizes universal truths and lessons through metaphorical representation.
Roman à Clef Explained: Characteristics and Purpose
Roman a clef is a literary genre where real-life events and people are depicted under the guise of fiction, allowing authors to explore sensitive or controversial topics without direct attribution. Characters and settings closely mirror actual figures and places, providing readers with a coded narrative that reveals truths through symbolism and recognizable traits. This technique serves to protect the author from political or social repercussions while engaging the audience in deciphering underlying realities behind the fictional facade.
Historical Origins of Allegory and Roman à Clef
Allegory traces back to ancient Greek literature, with foundational works like Plato's "Allegory of the Cave" illustrating abstract ideas through symbolic figures and narratives. Roman a clef emerged during the 17th century, particularly in France, where authors disguised real historical figures and events within fictional stories to bypass censorship. Both genres serve as literary tools for social and political commentary, but allegory relies on universal symbolism, while roman a clef uses direct historical references under fictional veneers.
Major Differences Between Allegory and Roman à Clef
Allegory uses symbolic characters and events to convey abstract ideas or moral lessons, while Roman a clef portrays real-life people and events disguised with fictional names and details. Allegory emphasizes universal themes and moral meanings, whereas Roman a clef revolves around specific, recognizable individuals and historical contexts. The major difference lies in allegory's broader symbolic narrative versus roman a clef's direct commentary on reality hidden beneath a fictional veneer.
Symbolism in Allegory: Interpreting Hidden Meanings
Allegory employs symbolism to convey deeper, often moral or political meanings through characters, events, and settings that represent abstract concepts. This symbolic framework invites readers to decipher hidden messages and universal truths embedded within the narrative. In contrast, Roman a clef disguises real-life individuals and events behind fictionalized versions, focusing less on abstract symbolism and more on revealing actual people through veiled representation.
Real-Life Inspiration in Roman à Clef: Fact Behind Fiction
Roman a clef uniquely blends fiction with real-life inspiration by embedding recognizable individuals, events, or settings beneath fictional names and plots. This literary technique allows authors to explore true occurrences or personalities while maintaining a narrative veil, offering readers the challenge of identifying the factual basis behind the story. Unlike allegory, which uses symbolic characters and themes to convey abstract ideas, roman a clef's power lies in revealing the fact behind fiction and providing insight into historical or personal realities.
Famous Examples of Allegory in Literature
Famous examples of allegory in literature include George Orwell's "Animal Farm," which uses a farm and its animal inhabitants to symbolize the Russian Revolution and the rise of totalitarianism. John Bunyan's "The Pilgrim's Progress" represents the spiritual journey of a Christian toward salvation through symbolic characters and settings. Nathaniel Hawthorne's "The Scarlet Letter" employs allegorical elements to explore themes of sin, guilt, and redemption in Puritan society.
Notable Roman à Clef Works and Their Real-World Parallels
Notable Roman a clef works include "The Devil Wears Prada" by Lauren Weisberger, which parallels the life of Vogue editor Anna Wintour, and "Animal Farm" by George Orwell, subtly representing the Russian Revolution and Soviet politics. These novels use fictionalized narratives to depict real-world figures and events, offering readers insight into historical or cultural contexts through disguised characters. Unlike allegories that rely on symbolic meaning throughout, Roman a clef novels maintain a one-to-one correlation between fictional characters and their actual counterparts, highlighting real-life intrigues within storytelling.
When to Use Allegory vs Roman à Clef in Creative Writing
Use allegory in creative writing when conveying universal themes through symbolic characters and events, allowing readers to interpret multiple layers of meaning beyond the surface narrative. Opt for a roman a clef to depict real-life individuals and situations under fictionalized names, providing a veiled, personalized critique or commentary. Choosing allegory enhances thematic depth and moral lessons, while roman a clef offers a direct, intimate exploration of actual experiences.
The Literary Impact of Allegory and Roman à Clef
Allegory and Roman a clef each have distinct literary impacts, with allegory using symbolic narrative to convey deeper moral, political, or spiritual meanings, enriching readers' interpretive engagement and fostering layered analysis. Roman a clef offers a unique form of storytelling by disguising real-life events and personalities within fictional frameworks, allowing authors to critique contemporary society and historical events subtly while preserving plausible deniability. Both forms challenge readers to decode hidden meanings, enhancing critical thinking and encouraging exploration of complex social and psychological themes.
Allegory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com