Surrealism revolutionized art and literature by exploring the unconscious mind through dreamlike imagery and unexpected juxtapositions. This movement challenged traditional perceptions of reality, encouraging deeper reflection on imagination and desire. Discover how surrealism can transform your perspective by diving into the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
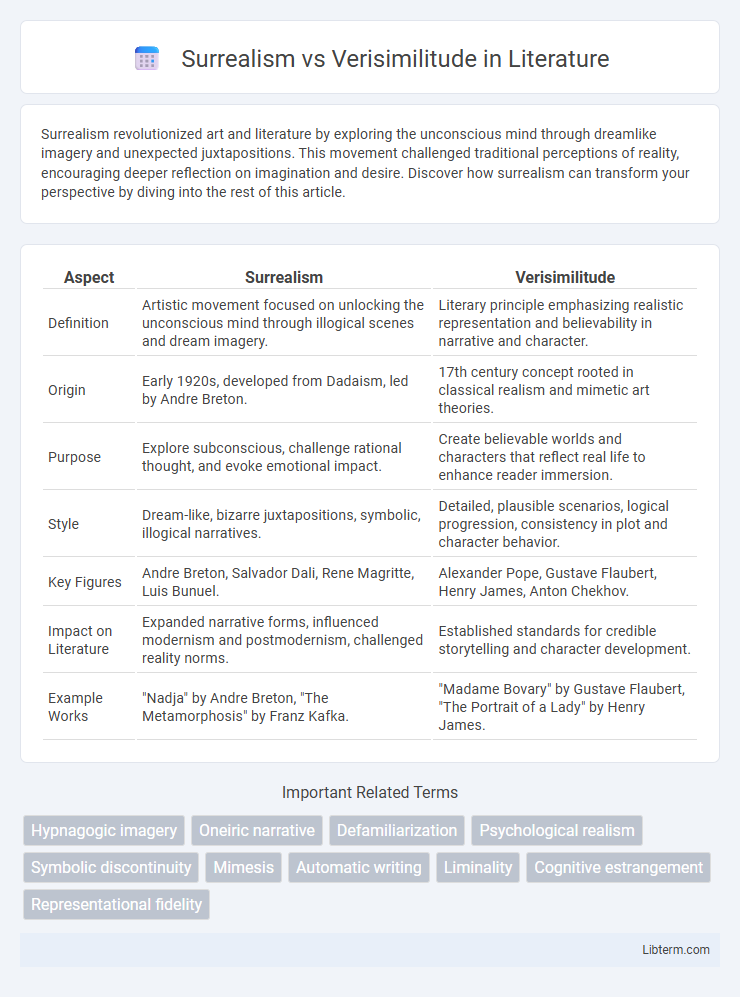
| Aspect | Surrealism | Verisimilitude |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic movement focused on unlocking the unconscious mind through illogical scenes and dream imagery. | Literary principle emphasizing realistic representation and believability in narrative and character. |
| Origin | Early 1920s, developed from Dadaism, led by Andre Breton. | 17th century concept rooted in classical realism and mimetic art theories. |
| Purpose | Explore subconscious, challenge rational thought, and evoke emotional impact. | Create believable worlds and characters that reflect real life to enhance reader immersion. |
| Style | Dream-like, bizarre juxtapositions, symbolic, illogical narratives. | Detailed, plausible scenarios, logical progression, consistency in plot and character behavior. |
| Key Figures | Andre Breton, Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Luis Bunuel. | Alexander Pope, Gustave Flaubert, Henry James, Anton Chekhov. |
| Impact on Literature | Expanded narrative forms, influenced modernism and postmodernism, challenged reality norms. | Established standards for credible storytelling and character development. |
| Example Works | "Nadja" by Andre Breton, "The Metamorphosis" by Franz Kafka. | "Madame Bovary" by Gustave Flaubert, "The Portrait of a Lady" by Henry James. |
Defining Surrealism and Verisimilitude
Surrealism is an artistic and literary movement that emphasizes the irrational, dream-like, and fantastical elements beyond conventional reality, often blending unexpected juxtapositions to unlock the unconscious mind. Verisimilitude refers to the appearance of being true or real, prioritizing realistic depiction and internal consistency within a narrative or artwork to foster believability. While surrealism challenges logical representation through imaginative abstraction, verisimilitude seeks to mirror life's authenticity and plausible experiences.
Historical Origins of Both Movements
Surrealism emerged in the early 1920s as a cultural movement founded by Andre Breton, rooted in the Dada movement and inspired by the psychoanalytic theories of Sigmund Freud, emphasizing the unconscious mind and dream imagery. Verisimilitude, traced back to classical antiquity, gained prominence during the Renaissance as a principle in literature and art, focused on creating lifelike representations and believable narratives based on observable reality. Both movements reflect distinct responses to their socio-cultural contexts: Surrealism challenges rationality through fantastical abstraction, while Verisimilitude upholds realistic depiction and narrative coherence.
Key Philosophical Differences
Surrealism emphasizes the exploration of the unconscious mind, dreams, and irrational juxtapositions to reveal deeper truths beyond logical reality, challenging traditional perceptions of existence. Verisimilitude prioritizes the faithful representation of reality through plausibility and coherence, aiming to create a credible and relatable depiction of the external world. The key philosophical divergence lies in surrealism's pursuit of transcending objective truth versus verisimilitude's commitment to mimicking observable truth.
Prominent Artists and Works
Surrealism, championed by artists such as Salvador Dali and Rene Magritte, emphasizes dreamlike, illogical scenes in works like Dali's "The Persistence of Memory" and Magritte's "The Son of Man," exploring the unconscious mind through bizarre imagery. Verisimilitude, focused on lifelike representation and realism, is exemplified by artists like Gustave Courbet with paintings such as "The Stone Breakers" and Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot, capturing everyday life and nature with meticulous detail. These contrasting approaches highlight Surrealism's distortion of reality versus Verisimilitude's faithful depiction of the observable world.
Techniques and Artistic Styles
Surrealism employs techniques such as automatism, dream imagery, and unexpected juxtapositions to evoke the subconscious and challenge reality, often using distorted forms and exaggerated perspectives to create fantastical, irrational scenes. Verisimilitude emphasizes meticulous details, realistic lighting, and accurate proportions to convincingly imitate real life, prioritizing naturalism and faithful representation over abstraction or fantasy. While surrealism breaks conventional artistic rules to explore imagination and subconscious truths, verisimilitude seeks to faithfully depict the visible world through precision and lifelike visual cues.
The Role of Imagination vs. Realism
Surrealism prioritizes imagination by exploring dreamlike, fantastical imagery that transcends logical reality, emphasizing subconscious creativity and emotional expression. Verisimilitude, rooted in realism, demands accurate representation and adherence to observable truth, aiming to create narratives or art that closely mirror real life. The tension between these approaches highlights the balance between imaginative freedom and faithful depiction of reality in artistic and literary works.
Surrealism in Modern Art and Media
Surrealism in modern art and media challenges conventional representations by embracing dreamlike imagery and illogical scenes that evoke the subconscious mind. This movement prioritizes symbolic, fantastical elements over realistic accuracy, creating a visual language that disrupts verisimilitude's focus on lifelike detail and coherence. Contemporary artists and filmmakers frequently integrate surrealist techniques to explore themes of identity, reality, and the unconscious, pushing the boundaries of narrative and perception.
Verisimilitude’s Impact on Visual Storytelling
Verisimilitude enhances visual storytelling by creating a believable world that engages viewers through accurate details and logical consistency. This technique fosters emotional investment and deeper immersion, making characters and narratives more relatable and impactful. By prioritizing realism, filmmakers and artists effectively communicate complex themes and authentic experiences.
Audience Perception and Emotional Response
Surrealism challenges audience perception by presenting dreamlike, illogical visuals that evoke subconscious emotions and provoke introspection. Verisimilitude fosters believability through realistic representation, enabling viewers to emotionally relate to familiar scenarios and characters. The emotional response in surrealism often involves intrigue and discomfort, while verisimilitude encourages empathy and understanding.
The Ongoing Dialogue: Surrealism vs Verisimilitude
Surrealism challenges conventional reality by embracing dream-like, irrational imagery that disrupts logical coherence, while verisimilitude strives for a lifelike representation with faithful attention to detail and plausibility. The ongoing dialogue between these two artistic approaches centers on the tension between imaginative freedom and credible realism, influencing literature, visual arts, and cinema in unique ways. This dynamic interplay prompts continual reevaluation of authenticity, perception, and the boundaries of artistic expression.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com