Optimize your website's loading speed by compressing images and minimizing code to enhance user experience and boost search engine rankings. Implementing efficient caching strategies and leveraging content delivery networks can significantly reduce page load times. Explore the full article to discover advanced techniques that will transform Your site's performance.
Table of Comparison
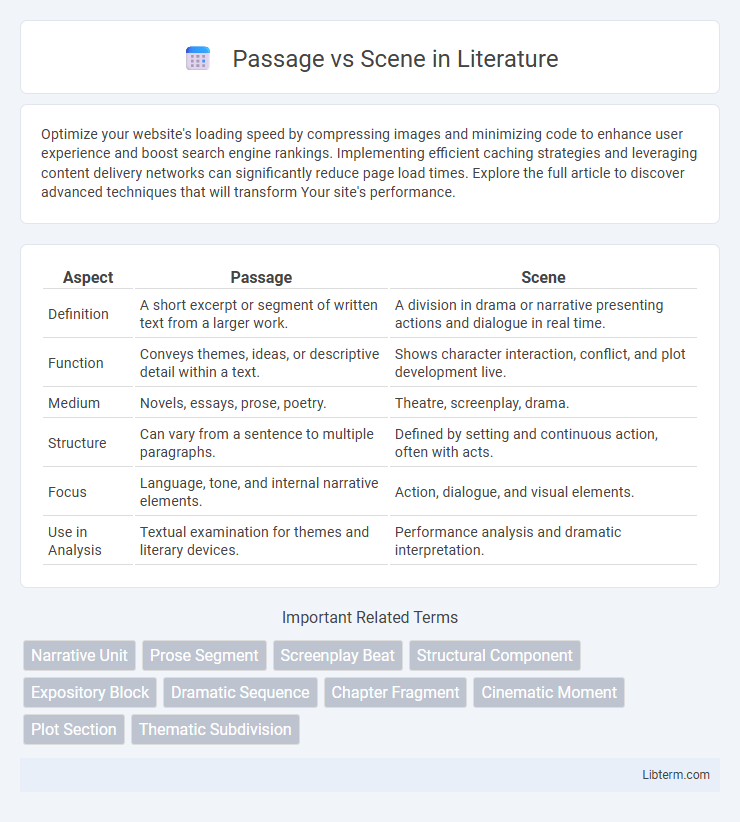
| Aspect | Passage | Scene |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A short excerpt or segment of written text from a larger work. | A division in drama or narrative presenting actions and dialogue in real time. |
| Function | Conveys themes, ideas, or descriptive detail within a text. | Shows character interaction, conflict, and plot development live. |
| Medium | Novels, essays, prose, poetry. | Theatre, screenplay, drama. |
| Structure | Can vary from a sentence to multiple paragraphs. | Defined by setting and continuous action, often with acts. |
| Focus | Language, tone, and internal narrative elements. | Action, dialogue, and visual elements. |
| Use in Analysis | Textual examination for themes and literary devices. | Performance analysis and dramatic interpretation. |
Understanding the Difference: Passage vs Scene
A passage is a broader section of text that can encompass various elements such as descriptions, dialogue, and narration, while a scene specifically depicts a continuous action or event occurring in a particular setting and time. Understanding the difference involves recognizing that scenes drive the plot forward through direct interaction and conflict, whereas passages provide context, background, or thematic depth. Writers use scenes to engage readers emotionally and passages to enhance comprehension and atmosphere within the narrative.
Definitions: What is a Passage?
A passage is a specific portion of text that contains a coherent unit of thought or information, typically spanning several sentences or paragraphs. It serves as a focused segment within a larger written work, emphasizing a particular idea, theme, or argument. Passages are often used to analyze or reference detailed content within books, articles, or speeches.
Definitions: What is a Scene?
A scene is a fundamental unit of storytelling in drama, film, and literature, defined by a continuous action occurring in a single location and time frame. It typically involves characters engaging in dialogue or activities that drive the plot forward, creating a focused moment within the larger narrative. Unlike a passage, which may encompass broader or varied content, a scene specifically captures a discrete segment of the story's progression.
Structural Role of Passages in Writing
Passages serve a crucial structural role in writing by organizing content into coherent units that develop themes, advance the plot, or elaborate on character traits. Unlike scenes, which are focused on specific moments of action or dialogue occurring in particular settings and timeframes, passages provide broader context and connect multiple scenes to create narrative flow. Effective use of passages enhances readability by segmenting complex ideas into manageable sections that guide the reader through the writer's intended message.
Structural Role of Scenes in Storytelling
Scenes serve as the fundamental structural units in storytelling, encapsulating specific moments of action, dialogue, or emotion that drive the narrative forward. Each scene establishes context, conflict, and character development, forming the building blocks that collectively shape the story's arc. While a passage can comprise multiple sentences or paragraphs conveying information or description, scenes focus on active, pivotal moments that advance plot and deepen audience engagement.
How Passages Advance Narrative Flow
Passages in literature function as cohesive units that consolidate multiple scenes to advance the narrative flow by providing context, emotional depth, and thematic continuity. Unlike individual scenes that depict specific moments or actions, passages synthesize these events to highlight character development and plot progression more fluidly. This seamless integration of scenes within passages enhances reader engagement by maintaining momentum and clarifying narrative arcs.
How Scenes Drive Plot and Action
Scenes are the building blocks of a narrative, each encapsulating specific moments where characters take decisive actions, conflicts escalate, or pivotal events unfold, directly driving the plot forward. By immersing readers in real-time interactions and sensory details, scenes create dynamic momentum and emotional engagement essential for plot development. Effective scene construction ensures that every dialogue, description, or character movement contributes to advancing the story's central conflict and objectives.
Key Elements: Passage vs Scene
Passages are larger sections in a narrative that encompass multiple scenes or thematic developments, emphasizing broader story arcs and character evolution. Scenes are smaller units within passages, defined by a specific setting, time, and action that propel the immediate plot forward with detailed interactions. Key elements distinguishing passages from scenes include scope, function, and temporal focus, where passages provide comprehensive context and scenes focus on precise moments.
When to Use a Passage vs When to Use a Scene
A passage is ideal for summarizing events or covering background information quickly to maintain narrative pace, while a scene is best used to show detailed, real-time interactions and significant character development. Use a scene when emotional depth, dialogue, and sensory details are crucial for immersing readers or advancing complex plot points. Choose a passage when you need to compress time, convey non-essential information efficiently, or transition between key scenes without interrupting narrative flow.
Tips for Balancing Passages and Scenes in Your Writing
Balancing passages and scenes in your writing enhances pacing and reader engagement by alternating detailed action scenes with informative passages. Use scenes to show character interactions and pivotal moments, while passages efficiently convey background information or internal thoughts without disrupting flow. Maintaining a clear purpose for each section ensures your narrative remains dynamic and cohesive, preventing overwhelming description or overextended scenes.
Passage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com