Alliteration enhances your writing by repeating initial consonant sounds, creating rhythm and musicality that captivate readers. This literary device emphasizes key phrases, making your message more memorable and engaging. Discover how to effectively use alliteration in your writing by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
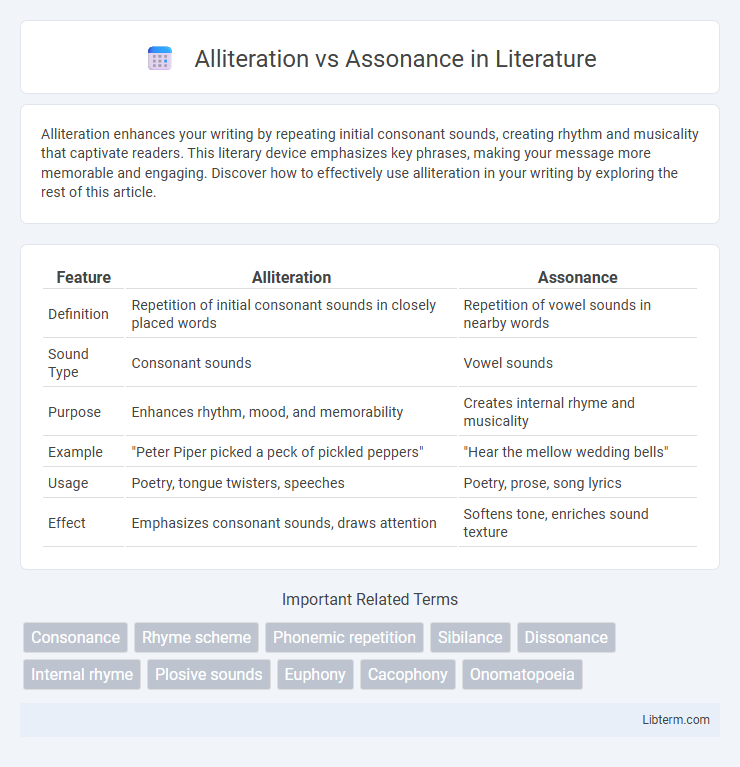
| Feature | Alliteration | Assonance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetition of initial consonant sounds in closely placed words | Repetition of vowel sounds in nearby words |
| Sound Type | Consonant sounds | Vowel sounds |
| Purpose | Enhances rhythm, mood, and memorability | Creates internal rhyme and musicality |
| Example | "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers" | "Hear the mellow wedding bells" |
| Usage | Poetry, tongue twisters, speeches | Poetry, prose, song lyrics |
| Effect | Emphasizes consonant sounds, draws attention | Softens tone, enriches sound texture |
Understanding Alliteration: Definition and Examples
Alliteration is a literary device characterized by the repetition of the same consonant sound at the beginning of closely connected words, enhancing rhythm and mood in poetry and prose. Common examples include phrases like "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers" and "wild and woolly," where the initial consonant sounds create a musical quality that emphasizes particular words or themes. Understanding alliteration involves recognizing its role in drawing attention to specific lines or ideas through sound patterns, which differs from assonance that repeats vowel sounds within words.
What is Assonance? Meaning and Usage
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words to create internal rhyming and enhance musicality in poetry and prose. It differs from alliteration, which focuses on consonant sounds at the beginning of words, while assonance emphasizes vowel sound patterns regardless of consonants. Writers use assonance to evoke mood, emphasize key themes, and improve the flow and rhythm of language in literary compositions.
Key Differences Between Alliteration and Assonance
Alliteration involves the repetition of initial consonant sounds in closely positioned words, enhancing rhythm and emphasis in poetry or prose. Assonance, in contrast, is the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, creating internal rhyming and musicality without relying on consonants. The key difference lies in alliteration focusing on consonant sounds at word beginnings, while assonance emphasizes vowel sounds within or at the beginning of words.
The Role of Sound in Literary Devices
Alliteration emphasizes the repetition of initial consonant sounds, creating a rhythmic and memorable effect that enhances the mood and tone in poetry and prose. Assonance focuses on the repetition of vowel sounds within words, contributing to musicality and emotional resonance by linking lines and ideas through sound patterns. Both literary devices harness the power of phonetic elements to engage readers and reinforce thematic connections in literature.
Alliteration in Poetry and Prose
Alliteration in poetry and prose enhances rhythm and musicality by repeating initial consonant sounds, creating memorable and engaging text that draws readers' attention. This stylistic device often emphasizes mood and tone, making phrases more vivid and impactful. Unlike assonance, which relies on vowel sounds, alliteration's consonant repetition distinctively shapes the auditory experience of literary works.
Assonance’s Impact on Rhythm and Mood
Assonance, the repetition of vowel sounds within closely placed words, significantly shapes the rhythm and mood of a text by creating a musical quality that enhances emotional resonance. This sonic pattern influences the pacing, making the reading experience either smooth and harmonious or tense and dissonant, depending on the vowel sounds used. Its strategic use in poetry and prose deepens atmospheric layering, guiding the audience's emotional response and engagement.
Techniques for Identifying Alliteration
Alliteration involves the repetition of initial consonant sounds in closely placed words, whereas assonance focuses on repeated vowel sounds within words. Techniques for identifying alliteration include listening for repeated consonant sounds at the beginning of words in a phrase or line and analyzing phonetic patterns rather than relying solely on spelling. Recognizing stressed syllables with identical consonant sounds enhances the detection of alliteration in poetry and prose.
Spotting Assonance in Sentences
Spotting assonance in sentences involves identifying the repetition of vowel sounds within closely placed words, enhancing the musicality and mood of the text. Unlike alliteration, which focuses on consonant sounds at the beginning of words, assonance creates internal rhyme by emphasizing vowels, such as the long "o" in "mold old gold." Recognizing patterns like "the rain in Spain stays mainly in the plain" helps distinguish assonance, crucial for literary analysis and poetic composition.
Creative Uses: Combining Alliteration and Assonance
Combining alliteration and assonance creates a rich auditory tapestry that enhances the rhythm and mood of poetry or prose, making the language more memorable and engaging. Writers skillfully blend repetition of consonant sounds (alliteration) with vowel sound echoes (assonance) to intensify emotional impact and emphasize key themes. This creative interplay amplifies sonic texture, driving deeper reader connection and elevating poetic sophistication.
Enhancing Writing Style with Sound Devices
Alliteration emphasizes the repetition of initial consonant sounds in closely placed words, creating rhythm and musicality that enhance memorability and engagement. Assonance involves repeating vowel sounds within words, adding a lyrical quality that enriches the tone and mood of the text. Both sound devices contribute to a dynamic writing style by reinforcing meaning and evoking emotional responses through auditory patterns.
Alliteration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com