Consonance is a literary device characterized by the repetition of consonant sounds within or at the end of words placed close together, enhancing the rhythm and musicality of a text. This technique is often used in poetry and prose to create mood, emphasize particular words, and connect ideas through sound patterns. Explore the rest of the article to discover how consonance can enrich your writing and reading experience.
Table of Comparison
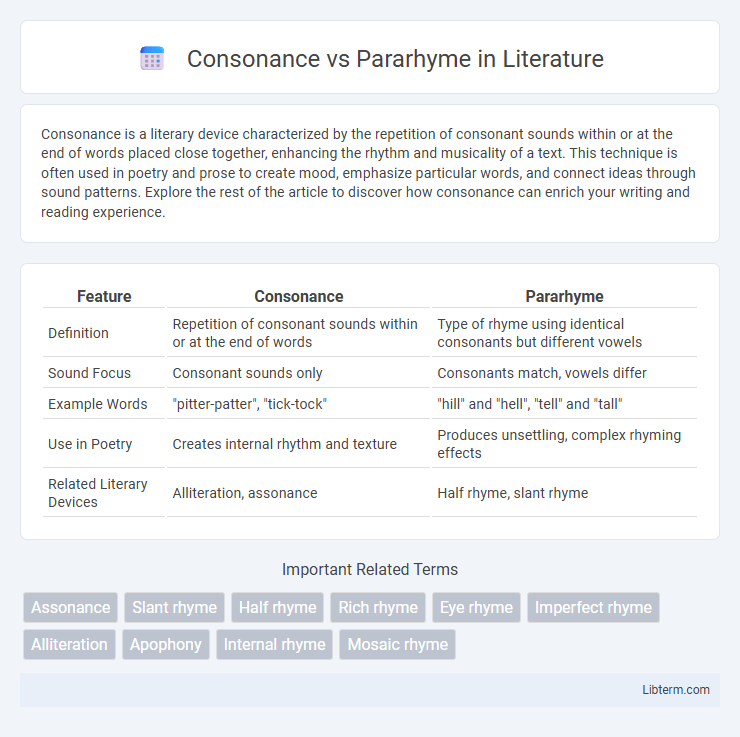
| Feature | Consonance | Pararhyme |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetition of consonant sounds within or at the end of words | Type of rhyme using identical consonants but different vowels |
| Sound Focus | Consonant sounds only | Consonants match, vowels differ |
| Example Words | "pitter-patter", "tick-tock" | "hill" and "hell", "tell" and "tall" |
| Use in Poetry | Creates internal rhythm and texture | Produces unsettling, complex rhyming effects |
| Related Literary Devices | Alliteration, assonance | Half rhyme, slant rhyme |
Understanding Consonance: Definition and Examples
Consonance is the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end or middle of words, creating a harmonious effect in poetry and prose. Examples include phrases like "pitter-patter" or "all mammals named Sam are clammy," where the consonant sounds 't' and 'm' respectively repeat. This literary device enhances the rhythm and mood without relying on full rhyme, distinguishing it from pararhyme which involves consonant sounds with varied vowel sounds.
What is Pararhyme? Key Features Explained
Pararhyme is a poetic device where consonant sounds match while vowel sounds differ, creating a subtle internal rhyme often found in modern and war poetry. Key features include identical consonant patterns at the beginnings and ends of words, with deliberate vowel variation to produce a tension between similarity and difference. This technique enhances phonetic texture and emotional nuance, distinguishing it from traditional consonance, which simply involves repetition of consonant sounds regardless of vowel changes.
Historical Origins of Consonance and Pararhyme
Consonance traces back to Old English poetry where repeated consonant sounds reinforced rhythm without rhyme, prevalent in works like "Beowulf." Pararhyme, a more modern concept popularized by poet Wilfred Owen in the early 20th century, involves matching consonants while varying vowels to create an unsettling or haunting effect. Historically, consonance embedded oral tradition's musicality, whereas pararhyme evolved to convey psychological depth and complexity in modernist literature.
How Consonance Shapes Poetry
Consonance, the repetition of consonant sounds, shapes poetry by enhancing its musicality and rhythm, creating a subtle harmony within lines that engages readers' auditory senses. Unlike pararhyme, which involves closely matched consonants with differing vowels to produce an imperfect rhyme, consonance provides a smoother, more resonant sound pattern that underpins the poem's emotional tone and mood. This technique strengthens thematic cohesion and imagination through sound symbolism, making consonance a vital tool in poetic expression.
Pararhyme in Modern Literature
Pararhyme, a form of consonance characterized by matching consonants with varying vowel sounds, plays a significant role in modern literature by creating subtle auditory effects that enhance thematic complexity and emotional depth. This technique diverges from traditional rhyme by emphasizing consonantal echo rather than vowel harmony, often found in works of poets like Wilfred Owen and T.S. Eliot, who utilize pararhyme to convey tension and fragmentation. Its strategic use in contemporary poetry and prose enriches the texture of language, fostering nuanced interpretations and engaging readers through imperfect, yet resonant sound patterns.
Phonetic Differences: Consonance vs Pararhyme
Consonance involves the repetition of identical consonant sounds, typically at the end or middle of words, creating harmonious phonetic patterns without matching vowels. Pararhyme specifically features identical consonant sounds at the beginning and end of words, while the vowel sounds differ, producing a more subtle and dissonant effect. The key phonetic difference lies in consonance's consistent consonant repetition across positions versus pararhyme's strict consonantal framing with vowel variation.
Effects on Tone and Mood
Consonance creates a harmonious and soothing tone by repeating consonant sounds, enhancing the overall musicality and emotional resonance of a poem. Pararhyme introduces tension and unrest through near-rhymes with matching consonants but differing vowels, generating a dissonant mood that can evoke unease or complexity. Both techniques manipulate sound patterns to influence the reader's perception and emotional response, with consonance fostering comfort and pararhyme provoking intrigue or discomfort.
Famous Poets Who Used Consonance and Pararhyme
Famous poets like Wilfred Owen extensively used pararhyme to create unsettling effects in their war poetry, exemplified in his poem "Dulce et Decorum Est." Consonance, characterized by the repetition of consonant sounds, is notably employed by Emily Dickinson, who used it to add musicality and emphasis within her concise verses. Both devices enhance the auditory experience, with pararhyme building tension through near rhymes and consonance reinforcing rhythm and mood.
Tips for Employing Consonance and Pararhyme in Writing
Consonance involves repeating consonant sounds to create rhythm and mood, while pararhyme pairs similar but not identical consonant sounds for a subtle, tense effect. Use consonance to enhance musicality and emphasize key phrases without overwhelming the reader, especially in poetry and prose. Employ pararhyme when aiming for an eerie or dissonant tone, ensuring the consonant sounds align closely enough to suggest rhyme but maintain a deliberate imperfection.
Choosing the Right Device: When to Use Consonance or Pararhyme
Choosing between consonance and pararhyme depends on the desired sound effect and emotional tone in poetry or prose. Consonance, the repetition of consonant sounds within or at the end of words, is ideal for creating harmony and subtle reinforcement of themes. Pararhyme, involving consonant sounds that nearly rhyme but differ in vowels, produces tension and unease, making it effective for darker or more complex moods.
Consonance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com