Griots are West African storytellers, historians, and musicians who preserve oral traditions through generations. They play a vital role in maintaining cultural heritage by recounting history, genealogy, and folklore with music and poetry. Discover more about the rich legacy of griots and how their art continues to shape communities in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
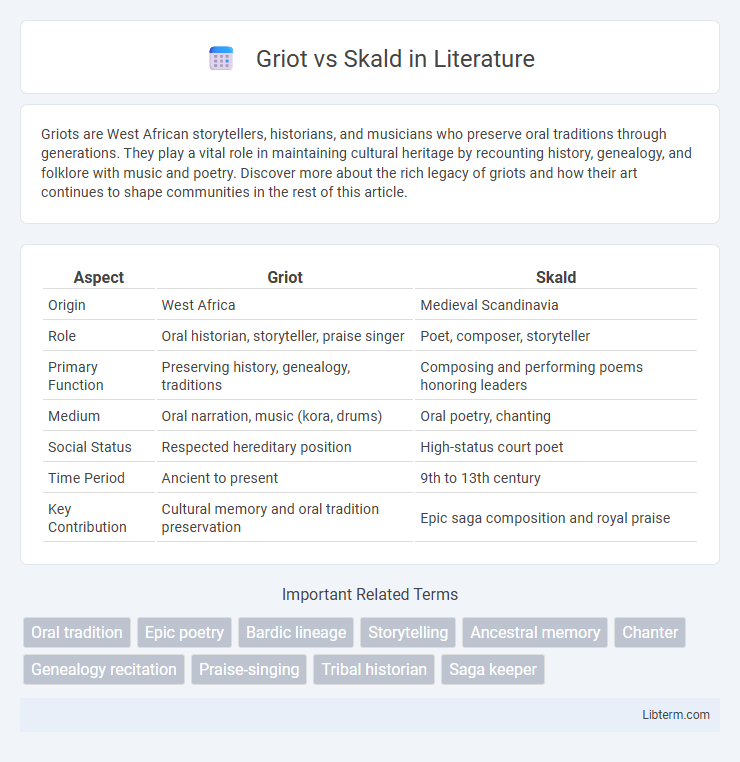
| Aspect | Griot | Skald |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | West Africa | Medieval Scandinavia |
| Role | Oral historian, storyteller, praise singer | Poet, composer, storyteller |
| Primary Function | Preserving history, genealogy, traditions | Composing and performing poems honoring leaders |
| Medium | Oral narration, music (kora, drums) | Oral poetry, chanting |
| Social Status | Respected hereditary position | High-status court poet |
| Time Period | Ancient to present | 9th to 13th century |
| Key Contribution | Cultural memory and oral tradition preservation | Epic saga composition and royal praise |
Introduction to Griots and Skalds
Griots are West African storytellers, poets, and musicians who preserve oral history and culture through generations, serving as living repositories of tradition. Skalds, in contrast, were medieval Scandinavian poets who composed intricate verses celebrating heroes and gods, often performing in royal courts to immortalize legendary deeds. Both roles function as cultural historians, using oral art forms to maintain societal memory and identity.
Historical Origins of Griots and Skalds
Griots originated in West Africa, serving as oral historians, storytellers, and musicians who preserved the genealogies and traditions of Mande societies for centuries. Skalds emerged in medieval Scandinavia as poet-historians who composed and recited epic verses celebrating Viking heroes and Norse mythology. Both roles were crucial in preserving cultural heritage, with griots deeply embedded in the oral traditions of African kingdoms and skalds tied to the courtly and warrior culture of Norse societies.
Cultural Roles in African and Norse Societies
Griots in African societies serve as oral historians, storytellers, musicians, and cultural custodians, preserving ancestral knowledge and societal values through generations. In contrast, Skalds in Norse culture function as court poets and historians, composing intricate verses that celebrate heroic deeds and maintain the legacy of Viking clans and kings. Both roles are pivotal in reinforcing cultural identity, social cohesion, and historical continuity within their respective African and Norse communities.
Storytelling Techniques: Griot vs Skald
Griots employ oral tradition techniques such as call-and-response, repetition, and musical accompaniment to preserve and transmit African history, genealogy, and cultural values. Skalds, rooted in Norse culture, utilize intricate poetic forms like drottkvaett with alliteration, kennings, and complex meter to chronicle heroic deeds and maintain communal memory. Both emphasize mnemonic devices, yet griots integrate performance and audience interaction, while skalds focus on structured verse and metaphorical language.
Musical Traditions and Instruments
Griots are West African storytellers and musicians known for playing instruments like the kora, balafon, and djembe, integral to oral history and praise singing in Mande culture. Skalds were medieval Scandinavian poets and musicians who performed using the harp or lyre, composing complex verses that preserved Norse history and mythology. Both traditions emphasize musical accompaniment to storytelling, but Griots use a broader range of stringed and percussion instruments tied to communal ceremonies, while Skalds employed simpler instruments suited to royal courts and Viking gatherings.
Oral Tradition and Preservation of History
Griots of West Africa and Skalds of medieval Scandinavia served as vital custodians of oral tradition, preserving history through storytelling, poetry, and song. Griots maintained genealogies, historical events, and cultural lore within their communities, often using instruments like the kora to enhance their narratives. Skalds composed complex, structured verses known as skaldic poetry, which chronicled heroic deeds, royal lineages, and societal values, ensuring the transmission of Norse heritage across generations.
Griots in Modern West Africa
Griots in modern West Africa serve as vital cultural historians, musicians, and storytellers, preserving oral traditions and genealogies through generations. Their performances combine music, poetry, and historical narrative, fostering social cohesion and transmitting collective memory in countries like Senegal, Mali, and Guinea. Unlike Skalds who were Norse poets focused on mythology and heroic tales, West African Griots maintain an active role in community leadership and cultural education today.
The Legacy of Skalds in Scandinavian Culture
Skalds were revered poets in medieval Scandinavian culture, serving as court historians, storytellers, and preservers of Norse mythology through intricate oral poetry known as skaldic verse. Their compositions not only celebrated the deeds of kings and warriors but also reinforced social values and historical continuity within Viking Age societies. The legacy of skalds endures in the preservation of Old Norse literature, profoundly influencing modern understanding of Scandinavian heritage and linguistic tradition.
Influence on Contemporary Literature and Media
Griots, West African oral historians and storytellers, infuse contemporary literature and media with rich cultural narratives, emphasizing communal memory and historical continuity. Skalds, Norse poets, contribute influence through vivid mythological themes and heroic motifs, shaping modern fantasy genres and epic storytelling structures. Both traditions enhance contemporary literary arts by preserving heritage and inspiring innovative narrative techniques.
Conclusion: Comparing the Enduring Impact
Griots and Skalds each shaped cultural memory through distinct oral traditions, with Griots preserving West African history and values, while Skalds chronicled Norse legends and heroic tales. Both roles ensured the transmission of identity and societal norms across generations, influencing literature, music, and communal cohesion. Their enduring impact reflects the power of oral storytelling as a vessel for cultural preservation and historical continuity.
Griot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com