Fabula refers to the chronological sequence of events in a story, representing the raw, underlying narrative without any artistic structuring. It contrasts with "syuzhet," which is the way these events are organized and presented to the audience. Explore the full article to understand how mastering fabula enhances storytelling and narrative analysis.
Table of Comparison
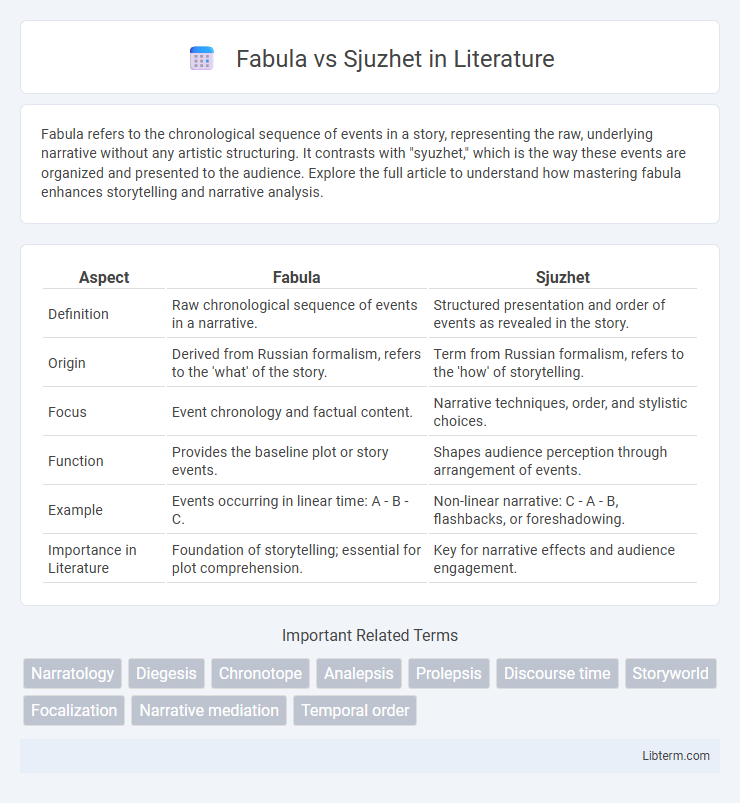
| Aspect | Fabula | Sjuzhet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw chronological sequence of events in a narrative. | Structured presentation and order of events as revealed in the story. |
| Origin | Derived from Russian formalism, refers to the 'what' of the story. | Term from Russian formalism, refers to the 'how' of storytelling. |
| Focus | Event chronology and factual content. | Narrative techniques, order, and stylistic choices. |
| Function | Provides the baseline plot or story events. | Shapes audience perception through arrangement of events. |
| Example | Events occurring in linear time: A - B - C. | Non-linear narrative: C - A - B, flashbacks, or foreshadowing. |
| Importance in Literature | Foundation of storytelling; essential for plot comprehension. | Key for narrative effects and audience engagement. |
Introduction to Fabula and Sjuzhet
Fabula represents the raw, chronological sequence of events in a narrative, forming the foundational storyline as it naturally occurs in time. Sjuzhet refers to the way these events are organized and presented by the narrator, often involving techniques like flashbacks, foreshadowing, and nonlinear arrangements. Understanding the distinction between Fabula and Sjuzhet is essential for analyzing narrative structure and the manipulation of time in storytelling.
Definitions: What are Fabula and Sjuzhet?
Fabula refers to the raw chronological sequence of events in a story, representing the actual timeline of happenings without any narrative manipulation. Sjuzhet is the structured presentation of these events as organized and revealed by the storyteller, shaping the order, emphasis, and perspective. Understanding the distinction between fabula and sjuzhet is essential for analyzing narrative techniques and how stories engage audiences through varied temporal arrangements.
Historical Origins and Theoretical Background
Fabula and Sjuzhet originate from Russian formalist theory in the early 20th century, specifically developed by scholars like Viktor Shklovsky and Boris Tomashevsky. Fabula refers to the raw chronological sequence of events in a story, while Sjuzhet represents the narrative structure or the way those events are presented to the audience. This distinction laid the groundwork for modern narratology by emphasizing the difference between story content and narrative form.
Key Differences Between Fabula and Sjuzhet
Fabula refers to the raw chronological sequence of events in a narrative, while sjuzhet denotes the way these events are organized and presented in the story structure. Fabula is concerned with the "what" of the narrative, encompassing the full timeline, whereas sjuzhet focuses on the "how," including narrative techniques like flashbacks, foreshadowing, and non-linear storytelling. The key difference lies in fabula representing the objective timeline and sjuzhet embodying the subjective arrangement that shapes audience perception and engagement.
Importance in Narrative Structure
Fabula represents the chronological series of events in a story, while Sjuzhet refers to the way these events are organized and presented to the audience. The importance of understanding Fabula versus Sjuzhet lies in how narrative tension, character development, and thematic depth are crafted through non-linear storytelling techniques. Mastery of this distinction allows writers to manipulate time, perspective, and information flow, enhancing engagement and emotional impact within the narrative structure.
Examples of Fabula in Literature and Film
Fabula represents the chronological sequence of events in a story, exemplified by the straightforward timeline found in Homer's "The Odyssey," where events unfold in their natural order. In film, "Memento" demonstrates fabula through its reconstructed timeline, as the actual events occur linearly but are revealed non-linearly to the audience. Understanding fabula aids in analyzing narrative structures by separating the raw story elements from their artistic presentation in the sjuzhet.
Examples of Sjuzhet in Literature and Film
Sjuzhet structures narratives non-linearly, manipulating chronological events to enhance thematic depth and suspense, as showcased in films like "Pulp Fiction" by Quentin Tarantino where scenes unfold out of sequence. In literature, William Faulkner's "The Sound and the Fury" employs sjuzhet through fragmented timelines and multiple perspectives that reveal characters' inner lives progressively. These examples demonstrate how sjuzhet transforms raw fabula--story events--into complex narrative experiences that engage audiences through temporal and causal reordering.
Influence on Reader Interpretation
Fabula refers to the raw chronological sequence of events in a narrative, while Sjuzhet represents the specific arrangement and presentation of these events by the author. The manipulation of Sjuzhet shapes the reader's interpretation by controlling the flow of information, creating suspense, or emphasizing particular themes. This deliberate structuring influences emotional responses and comprehension, highlighting the significance of narrative design in storytelling.
Fabula and Sjuzhet in Modern Storytelling
Fabula represents the raw chronological sequence of events in a narrative, while Sjuzhet refers to the structured presentation of these events by the storyteller, often manipulated for thematic impact or suspense. In modern storytelling, understanding the distinction allows creators to craft non-linear narratives that engage audiences through strategic reveals and temporal shifts. The interplay between Fabula and Sjuzhet enhances narrative depth, enabling complex character development and multifaceted plot constructions.
Conclusion: Fabula vs. Sjuzhet in Narrative Analysis
Fabula represents the raw chronological sequence of events in a narrative, while Sjuzhet refers to the structured presentation of these events as arranged by the narrator. The distinction between Fabula and Sjuzhet is crucial for understanding narrative techniques, including non-linear storytelling and temporal manipulation. Analyzing both elements reveals how narratives shape audience perception and create meaning through order, emphasis, and pacing.
Fabula Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com