Chorus is a powerful musical element that reinforces the main theme of a song through repeated lines or phrases, creating emotional impact and memorability. It serves as the centerpiece where the key message resonates, often making the song instantly recognizable. Discover how mastering the chorus can elevate your music by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
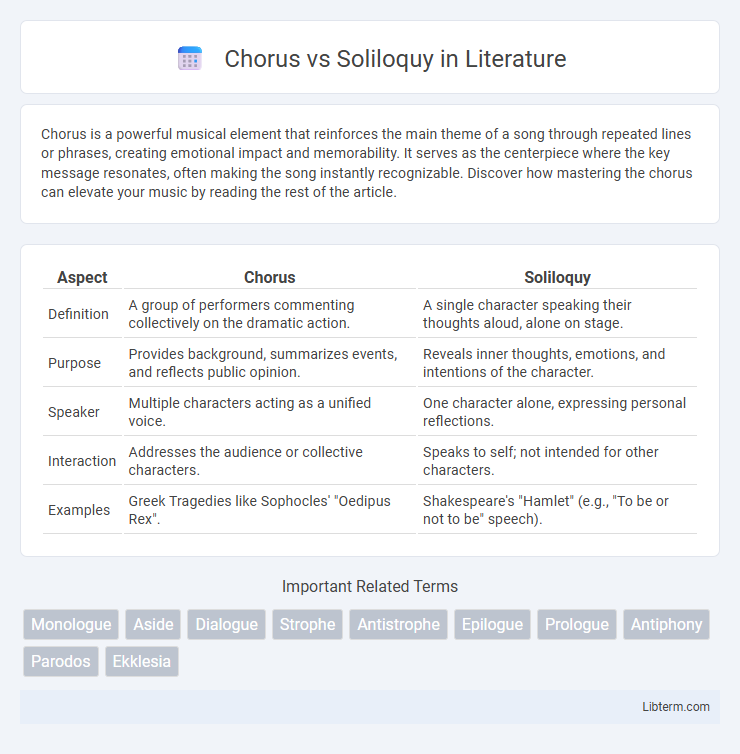
| Aspect | Chorus | Soliloquy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A group of performers commenting collectively on the dramatic action. | A single character speaking their thoughts aloud, alone on stage. |
| Purpose | Provides background, summarizes events, and reflects public opinion. | Reveals inner thoughts, emotions, and intentions of the character. |
| Speaker | Multiple characters acting as a unified voice. | One character alone, expressing personal reflections. |
| Interaction | Addresses the audience or collective characters. | Speaks to self; not intended for other characters. |
| Examples | Greek Tragedies like Sophocles' "Oedipus Rex". | Shakespeare's "Hamlet" (e.g., "To be or not to be" speech). |
Introduction to Chorus and Soliloquy
Chorus in classical Greek drama functions as a collective voice representing the broader community's perspective, often providing background information, commentary, and reflections on the play's events. Soliloquy, by contrast, is a dramatic device where a single character speaks their innermost thoughts aloud, revealing personal motivations and emotions directly to the audience. Both techniques enhance narrative depth, with the Chorus offering societal context and the soliloquy delivering intimate psychological insight.
Defining Chorus: Purpose and Function
The chorus in classical drama serves as a collective voice that comments on the action and provides background information, helping the audience interpret the unfolding events. Its primary function is to reflect the public opinion or societal norms, often guiding the moral perspective of the narrative and enhancing emotional resonance. Unlike a soliloquy, which reveals an individual character's inner thoughts, the chorus operates externally, offering a unified, communal viewpoint essential to the structure of Greek tragedies.
Understanding Soliloquy: Meaning and Role
A soliloquy is a dramatic device where a character speaks their thoughts aloud while alone on stage, revealing inner feelings and motivations to the audience. This technique offers deep psychological insight, allowing viewers to understand the character's dilemmas and intentions without external influence. Unlike the chorus, which comments on the action from an external perspective, the soliloquy provides a direct window into the character's mind.
Origins and Historical Context
The chorus originates from ancient Greek theatre, serving as a collective voice that provided commentary, background information, and reflections on the play's action, often representing societal or communal views. Soliloquy, primarily rooted in Elizabethan drama, especially in Shakespearean plays, allows a single character to express inner thoughts and emotions directly to the audience, revealing personal conflicts and motivations. While the chorus was integral to classical theatrical conventions emphasizing communal experience, the soliloquy emphasizes individual introspection characteristic of Renaissance humanism.
Structural Differences Between Chorus and Soliloquy
The chorus in classical drama functions as a collective voice that comments on the action and interacts with the audience, often serving as a narrative bridge between scenes, while a soliloquy is a single character's extended speech revealing inner thoughts and emotions directly to the audience. Structurally, the chorus typically appears as a group, delivering choral odes or songs that reflect communal perspectives, whereas soliloquies are monologues embedded within the play's dialogue, providing intimate insight into the protagonist's mindset. The chorus's presence is external and interpretative, contrasting with the soliloquy's introspective and personal nature within the dramatic structure.
Impact on Audience Engagement
Chorus and soliloquy each uniquely shape audience engagement through their distinct narrative roles. A chorus offers collective commentary, providing context and influencing the audience's emotional and intellectual response by articulating communal values or societal norms. Soliloquies, in contrast, grant intimate access to a character's internal thoughts, fostering a deep personal connection and enhancing empathy by revealing motivations and conflicts otherwise hidden from the audience.
Usage in Classical and Modern Drama
In classical drama, the chorus functions as a collective voice providing background information, commentary, and reflections on the play's events, as seen in Greek tragedies like Sophocles' "Oedipus Rex." Soliloquies are predominantly individual speeches expressing a character's inner thoughts and emotions, famously utilized by Shakespeare in plays such as "Hamlet." Modern drama often reduces the chorus to symbolic or atmospheric roles, while soliloquies remain vital for character development and psychological insight, adapting to contemporary narrative styles.
Examples from Famous Plays
In Shakespeare's *Julius Caesar*, the Chorus delivers collective commentary that guides the audience's understanding of the unfolding events, contrasting sharply with Hamlet's soliloquies, such as the famous "To be or not to be," which reveal the protagonist's inner turmoil. Sophocles' *Oedipus Rex* uses the Chorus to reflect societal norms and moral lessons, while the soliloquies in *Macbeth* provide intimate insights into Macbeth's ambition and guilt, exemplified by the "Tomorrow, and tomorrow, and tomorrow" speech. These examples highlight how choruses serve a communal narrative function, whereas soliloquies offer direct access to a single character's private thoughts.
Thematic Significance
Choruses in classical drama often represent the collective voice of society, providing thematic commentary on moral and social issues. Soliloquies reveal the intimate, internal struggles of individual characters, highlighting themes of personal conflict and introspection. Together, they explore the tension between public perception and private reality, deepening the audience's understanding of the narrative's core themes.
Conclusion: Comparing Dramatic Techniques
Chorus and soliloquy serve distinct dramatic functions, with the chorus offering collective commentary and context, enhancing the audience's understanding of the plot and themes. Soliloquies provide deep insight into a single character's inner thoughts and emotions, creating intimacy and personal connection. Comparing these techniques highlights the chorus as a communal narrative device, while soliloquy emphasizes individual psychological depth in drama.
Chorus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com