Antithesis highlights contrasting ideas within a sentence to create emphasis and clarity, making your message more impactful and memorable. This rhetorical device is commonly used in literature, speeches, and everyday communication to showcase opposing concepts effectively. Explore the article to learn how to use antithesis to enhance your writing and speaking skills.
Table of Comparison
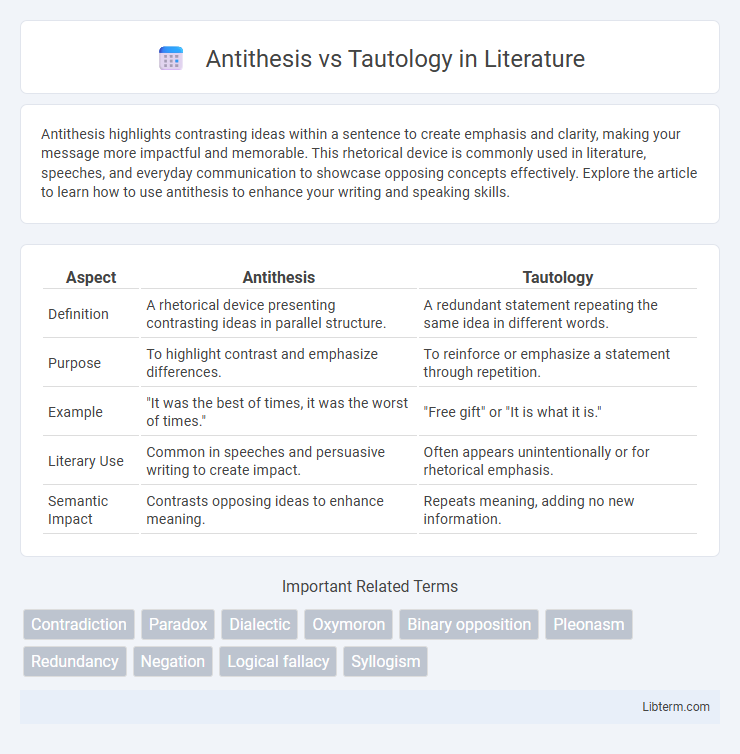
| Aspect | Antithesis | Tautology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A rhetorical device presenting contrasting ideas in parallel structure. | A redundant statement repeating the same idea in different words. |
| Purpose | To highlight contrast and emphasize differences. | To reinforce or emphasize a statement through repetition. |
| Example | "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times." | "Free gift" or "It is what it is." |
| Literary Use | Common in speeches and persuasive writing to create impact. | Often appears unintentionally or for rhetorical emphasis. |
| Semantic Impact | Contrasts opposing ideas to enhance meaning. | Repeats meaning, adding no new information. |
Introduction to Antithesis and Tautology
Antithesis contrasts two opposing ideas within a sentence to create emphasis and highlight differences, often using parallel structure for clarity and impact. Tautology involves the unnecessary repetition of the same idea using different words, which can weaken the statement's effectiveness by redundancy. Both rhetorical devices influence the persuasiveness and style of communication by manipulating semantic relationships.
Defining Antithesis: Meaning and Examples
Antithesis is a rhetorical device that contrasts two opposing ideas within a balanced structure, enhancing clarity and emphasis in communication. Examples include phrases like "love and hate" or "speech is silver, but silence is golden," which juxtapose contradictory concepts to highlight differences. This technique is widely used in literature, speeches, and everyday language to create memorable and impactful statements.
Understanding Tautology: Meaning and Examples
Tautology refers to the redundant repetition of an idea using different words that convey the same meaning, often considered a logical fault in arguments. Common examples include phrases like "free gift" or "advance planning," where the second term is inherently included in the first. Understanding tautology helps in identifying unnecessary wordiness and clarifies communication by eliminating repetitive expressions.
Origins and Etymology of Both Terms
The term "antithesis" originates from the Greek word "antithesis," meaning "opposition" or "contrast," derived from "anti-" (against) and "thesis" (position). "Tautology" comes from the Greek "tautologia," rooted in "tauto-" (the same) and "logia" (speech or saying), signifying redundant or repetitive expression. Both terms have classical origins reflecting their core conceptual meanings in rhetoric and logic.
Structural Differences Between Antithesis and Tautology
Antithesis employs a structural framework that juxtaposes contrasting ideas in parallel grammatical forms to highlight differences, often using balanced clauses or phrases. Tautology, by contrast, repeats the same idea or meaning using redundant expressions within similar or identical syntactic constructions, emphasizing redundancy rather than contradiction. The key structural difference lies in antithesis's use of oppositional elements arranged symmetrically, whereas tautology relies on repetition without introducing conceptual opposition.
Functions in Rhetoric and Literature
Antithesis functions in rhetoric and literature by creating contrast between opposing ideas to highlight differences and enhance the impact of the message, often emphasizing conflict or complexity. Tautology serves to reinforce an idea through repetition or redundancy, intensifying clarity and emphasis by restating the same concept in different words. Both devices manipulate language to influence audience perception, with antithesis promoting critical reflection and tautology ensuring memorable reinforcement.
Common Misconceptions and Confusions
Antithesis is a rhetorical device contrasting two opposing ideas to highlight differences, while tautology involves redundant repetition of the same idea using different words, often seen as a logical fallacy. Common misconceptions arise when antithesis is mistakenly identified as tautology due to both involving the juxtaposition of ideas, but antithesis emphasizes contradiction and balance rather than redundancy. Confusions also occur when tautological expressions are perceived as stylistic emphasis rather than illogical repetition, blurring the distinct purposes of these concepts in language and argumentation.
Importance of Context in Usage
Antithesis and tautology serve distinct rhetorical functions that rely heavily on context for effective usage. Antithesis juxtaposes contrasting ideas to emphasize differences and create impact, while tautology involves redundant repetition that may clarify or emphasize a point depending on the audience. Understanding the situational context ensures that antithesis enhances argumentative clarity and that tautology avoids unnecessary redundancy, optimizing communication precision.
Practical Applications in Writing and Speech
Antithesis enhances clarity and impact in writing and speech by juxtaposing contrasting ideas, making arguments more persuasive and memorable. Tautology, often used for emphasis or reinforcement, can highlight key points but risks redundancy if overused. Effective communication balances antithesis to engage audiences with clear contrasts and tautology to underscore important messages without diluting content.
Summary: Choosing Between Antithesis and Tautology
Antithesis effectively highlights contrast by juxtaposing opposing ideas, enhancing clarity and impact in persuasive writing or speeches. Tautology, often redundant, emphasizes a point by repeating similar concepts, which can reinforce meaning but may reduce conciseness if overused. Selecting between antithesis and tautology depends on whether the goal is to create dramatic contrast or to stress an idea through reiteration for emphasis.
Antithesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com