An oxymoron combines contradictory terms to create a unique and thought-provoking expression, such as "bittersweet" or "deafening silence." These linguistic pairs add depth and complexity to language by highlighting paradoxes in everyday experiences. Explore the rest of the article to discover how oxymorons enrich your communication and creative writing.
Table of Comparison
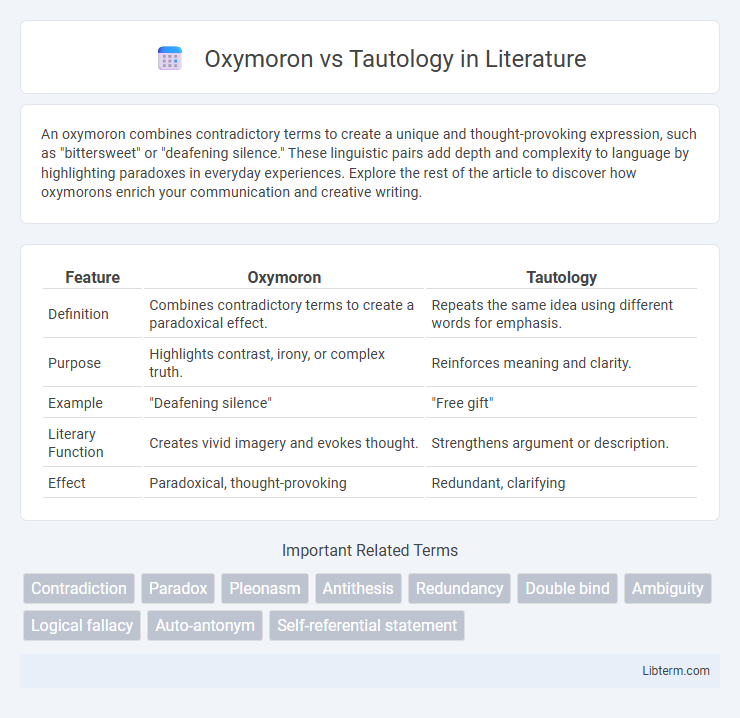
| Feature | Oxymoron | Tautology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines contradictory terms to create a paradoxical effect. | Repeats the same idea using different words for emphasis. |
| Purpose | Highlights contrast, irony, or complex truth. | Reinforces meaning and clarity. |
| Example | "Deafening silence" | "Free gift" |
| Literary Function | Creates vivid imagery and evokes thought. | Strengthens argument or description. |
| Effect | Paradoxical, thought-provoking | Redundant, clarifying |
Understanding Oxymoron vs Tautology
Oxymoron combines contradictory terms like "bittersweet" to create a paradoxical effect, enriching language with nuanced meaning. Tautology redundantly repeats the same idea using different words, such as "free gift," often emphasizing a point or clarifying meaning. Understanding oxymoron versus tautology involves recognizing oxymoron's juxtaposition of opposing concepts versus tautology's unnecessary repetition.
Definition of Oxymoron
An oxymoron is a figure of speech that combines two contradictory or opposing terms to create a paradoxical effect, such as "deafening silence" or "bittersweet." This literary device conveys complex or nuanced meanings by juxtaposing words that typically do not belong together. Unlike tautology, which involves redundant repetition of the same idea, oxymoron highlights the contrast between conflicting concepts within a concise phrase.
Definition of Tautology
A tautology is a statement that is true by necessity or by logical form, often repeating the same idea using different words to reinforce a concept, such as "free gift" or "true fact." Unlike an oxymoron, which combines contradictory terms like "bittersweet," a tautology emphasizes redundancy to create clarity or emphasis without introducing contradiction. This linguistic device is commonly employed in everyday language, rhetoric, and logic to underline truth or certainty.
Key Differences Between Oxymoron and Tautology
Oxymoron combines contradictory terms, such as "bittersweet" or "deafening silence," creating a paradoxical phrase that reveals complex meanings. Tautology, on the other hand, involves redundant repetition of the same idea using different words, like "free gift" or "advance planning," emphasizing the unnecessary duplication. The key difference lies in oxymoron's fusion of opposing concepts versus tautology's reiteration of identical or similar ideas for emphasis or clarity.
Common Examples of Oxymoron
Common examples of oxymoron include phrases like "jumbo shrimp," "deafening silence," and "bittersweet." These expressions combine contradictory terms to create a unique, thought-provoking effect that emphasizes complexity or irony. Unlike tautologies, which repeat the same idea using different words, oxymorons highlight paradoxical relationships between concepts.
Common Examples of Tautology
Common examples of tautology include phrases like "free gift," "advance warning," and "true fact," where the repetition of meaning adds unnecessary redundancy. Tautologies reinforce the same idea using different words, which can be useful for emphasis but often leads to wordiness. Understanding tautology helps distinguish it from oxymorons, where contradictory terms are combined, such as "deafening silence" or "bittersweet.
Purpose and Usage in Language
Oxymorons combine contradictory terms like "bittersweet" to create a dramatic or thought-provoking effect, enhancing literary expression by highlighting complex or paradoxical ideas. Tautologies use redundant or repetitive language such as "free gift" to emphasize a point, clarify meaning, or maintain rhythm in speech and writing. Both serve distinct rhetorical purposes: oxymorons evoke emotional depth and irony, while tautologies reinforce information and aid comprehension.
Effect on Communication and Expression
Oxymorons enhance communication by juxtaposing contradictory terms, creating a striking effect that provokes thought and highlights complexity in expression. Tautologies, on the other hand, reinforce an idea through redundancy, ensuring clarity and emphasis but risking monotony or verbosity. Both devices influence the recipient's understanding, with oxymorons sparking intrigue and tautologies providing reassurance or emphasis.
Oxymoron and Tautology in Literature
Oxymoron in literature creates a striking effect by combining contradictory terms, such as "bittersweet" or "deafening silence," to reveal complex emotions or paradoxes. Tautology, on the other hand, involves redundant expressions that repeat the same idea in different words, like "free gift" or "safe haven," often emphasizing a point or reinforcing meaning. Both devices enhance literary depth by manipulating language, but oxymorons provoke thought through contrast, while tautologies clarify or intensify meaning through repetition.
How to Identify Oxymoron and Tautology
Oxymorons combine contradictory terms such as "bittersweet" or "deafening silence," creating a paradoxical effect that emphasizes contrast within a single phrase. Tautologies involve redundant expressions where the same idea is repeated using different words, like "free gift" or "safe haven," which adds unnecessary emphasis but lacks contradiction. Identifying oxymorons requires spotting opposing or incompatible words joined together, whereas tautologies are recognized by the repetition of meaning without logical conflict.
Oxymoron Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com