Marginalia refers to the notes, comments, or doodles written in the margins of a book or manuscript, offering personal insights or reflections from the reader. These annotations provide a unique glimpse into the reader's thought process and enhance the textual experience by adding depth and context. Explore the rest of the article to discover how marginalia can transform your reading habits and enrich your understanding of literature.
Table of Comparison
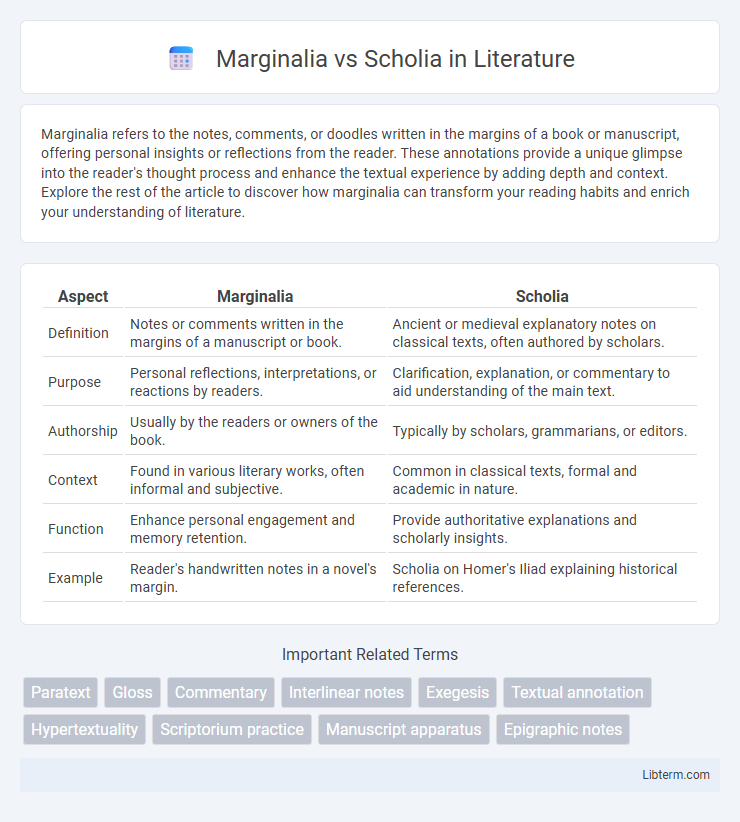
| Aspect | Marginalia | Scholia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Notes or comments written in the margins of a manuscript or book. | Ancient or medieval explanatory notes on classical texts, often authored by scholars. |
| Purpose | Personal reflections, interpretations, or reactions by readers. | Clarification, explanation, or commentary to aid understanding of the main text. |
| Authorship | Usually by the readers or owners of the book. | Typically by scholars, grammarians, or editors. |
| Context | Found in various literary works, often informal and subjective. | Common in classical texts, formal and academic in nature. |
| Function | Enhance personal engagement and memory retention. | Provide authoritative explanations and scholarly insights. |
| Example | Reader's handwritten notes in a novel's margin. | Scholia on Homer's Iliad explaining historical references. |
Introduction to Marginalia and Scholia
Marginalia are handwritten notes, comments, or annotations placed in the margins of a text, often reflecting the reader's personal insights or interpretations. Scholia are explanatory notes or critical comments added by ancient or medieval scholars to clarify, interpret, or expand on literary or scholarly works. Both marginalia and scholia serve to enhance understanding, but marginalia tend to be informal and personal, whereas scholia are more formal, scholarly, and authoritative.
Defining Marginalia: Notes in the Margins
Marginalia refers to handwritten notes, comments, or annotations made in the margins of a text, often reflecting a reader's personal insights or interpretations. These notes provide immediate, contextual responses to the main text, enhancing understanding or emphasizing key points without interrupting the flow of reading. Unlike scholia, which are formal, scholarly explanations or critical glosses typically added by experts, marginalia embody informal, spontaneous engagement with the material.
Understanding Scholia: Ancient Scholarly Commentary
Scholia are ancient scholarly comments or annotations written in the margins of classical manuscripts, providing critical explanations, interpretations, and context for the main text. Unlike marginalia, which often contain personal notes or reactions, scholia serve as formal academic commentary crafted by experts to enhance understanding and preserve historical knowledge. These annotations illuminate linguistic nuances, historical references, and cultural insights essential for deeper comprehension of ancient literature and philosophy.
Historical Origins of Marginalia and Scholia
Marginalia, originating in ancient manuscripts, consists of handwritten notes or comments found in the margins, serving to clarify or expand on the main text. Scholia, dating back to classical antiquity, are scholarly annotations or explanations traditionally added by commentators to elucidate complex passages, often appearing alongside Greek and Latin texts. Both originated as tools to aid understanding but differ in their formality and purpose, with marginalia being more informal and personal, and scholia more formal and academic.
Functions and Purposes: Marginalia vs Scholia
Marginalia serve as personal annotations, highlighting key points, clarifications, or reactions directly in the margins of a text to aid individual comprehension and memory. Scholia function as scholarly explanations or critical commentary attached to specific passages, providing historical context, linguistic analysis, or interpretive insights intended to enhance collective academic understanding. Both marginalia and scholia enrich the reading experience but differ in scope, with marginalia focusing on personal interaction and scholia aiming for educational exposition.
Key Differences Between Marginalia and Scholia
Marginalia are handwritten notes or annotations in the margins of a manuscript or book, often personal reflections, clarifications, or explanations made by readers. Scholia consist of ancient or scholarly comments written alongside classical texts, providing critical interpretations, historical context, or linguistic analysis. Key differences include marginalia's informal, reader-driven nature versus scholia's formal, academic purpose for enhancing textual understanding.
Famous Examples in Literary History
Marginalia, often seen in the handwritten notes of Leonardo da Vinci and Virginia Woolf, reveal personal reflections and analytical insights alongside texts, enriching the reader's engagement with literary works. Scholia, found prominently in ancient manuscripts like those accompanying Homeric epics, provide scholarly commentary and elucidation to clarify difficult passages or cultural references. These annotations serve distinct purposes: while marginalia offer individual interpretation, scholia function as authoritative guides preserving classical knowledge and critical traditions.
The Role in Textual Interpretation
Marginalia serve as personal annotations that provide insight into a reader's immediate reactions, enabling a subjective understanding of the text, while scholia offer more formal, scholarly commentary that contextualizes and explicates the content through historical and linguistic analysis. The interplay between marginalia and scholia enriches textual interpretation by combining individual perspectives with authoritative explanations, enhancing comprehension and critical engagement. These annotations collectively support the dynamic interaction between readers and texts, facilitating deeper exploration of meaning and textual nuances.
Evolution in Modern and Digital Contexts
Marginalia and scholia have evolved from handwritten annotations in medieval manuscripts to dynamic digital commentaries, enhancing textual interaction through hyperlinked notes and collaborative platforms. Modern digital tools integrate semantic tagging and AI-driven analysis, transforming marginalia into accessible scholarly resources that support multifaceted interpretations. This evolution underscores the shift toward interactive, networked knowledge systems, merging traditional exegesis with contemporary digital humanities methodologies.
Importance in Literary and Academic Research
Marginalia provide invaluable insights by revealing readers' personal interpretations and contextual reactions to texts, enriching literary analysis and historical understanding. Scholia, as ancient or scholarly annotations, offer authoritative explanations and critical commentary that clarify complex passages and preserve interpretative traditions. Both marginalia and scholia play crucial roles in academic research by illuminating textual nuances and enhancing the depth of literary scholarship.
Marginalia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com