Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and social norms to maintain societal stability and continuity. It advocates for gradual change rather than radical reform, valuing experience and established practices. Explore the rest of the article to understand how conservatism shapes political and cultural landscapes today.
Table of Comparison
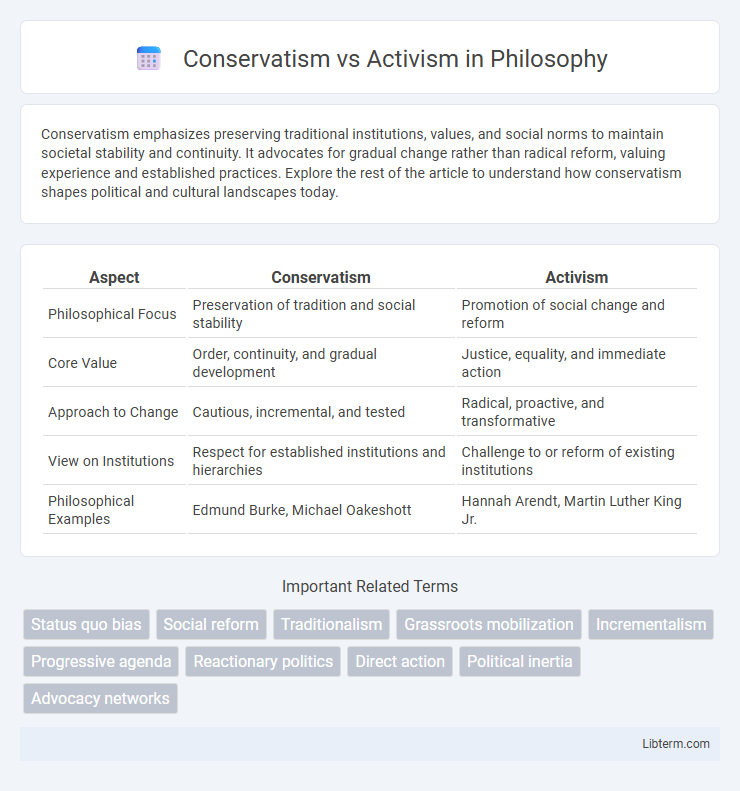
| Aspect | Conservatism | Activism |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophical Focus | Preservation of tradition and social stability | Promotion of social change and reform |
| Core Value | Order, continuity, and gradual development | Justice, equality, and immediate action |
| Approach to Change | Cautious, incremental, and tested | Radical, proactive, and transformative |
| View on Institutions | Respect for established institutions and hierarchies | Challenge to or reform of existing institutions |
| Philosophical Examples | Edmund Burke, Michael Oakeshott | Hannah Arendt, Martin Luther King Jr. |
Introduction to Conservatism and Activism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional values, institutions, and social stability, advocating gradual change to maintain societal order. Activism involves proactive efforts to promote or resist social, political, or environmental reforms, often seeking immediate and significant transformation. These contrasting approaches shape debates on policy-making, cultural norms, and governance strategies worldwide.
Defining Conservatism: Core Principles
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and social norms as essential for stability and continuity within society. It advocates limited government intervention, individual responsibility, and respect for established customs and cultural heritage. Core principles include a commitment to gradual change, skepticism of radical reforms, and the protection of property rights and personal liberties.
Understanding Activism: Key Motivations
Activism is driven by a commitment to social change, motivated by addressing injustices and advocating for marginalized communities. Key motivations include demands for equality, environmental sustainability, and human rights, often fueled by personal experiences or ethical convictions. This drive for reform contrasts with conservatism's emphasis on preserving tradition and resisting rapid societal shifts.
Historical Roots of Conservatism and Activism
Conservatism traces its historical roots to the 18th-century reaction against the French Revolution, emphasizing tradition, social stability, and gradual change to preserve established institutions. Activism emerged prominently in the 19th and 20th centuries, rooted in social reform movements and the push for civil rights, labor rights, and political change through collective action. These divergent origins highlight conservatism's commitment to continuity and activism's drive for progress and systemic transformation.
Ideological Differences Between Conservatism and Activism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional values, social structures, and institutions to maintain stability and continuity, often advocating gradual change through established processes. Activism prioritizes proactive efforts to challenge and reform existing systems, promoting social justice and equity through direct action and rapid change. The ideological divide lies in conservatism's preference for order and skepticism toward radical shifts, while activism embraces transformation to address perceived injustices and systemic inequalities.
Social Change: Conservative vs. Activist Perspectives
Conservative perspectives on social change emphasize gradual evolution, valuing tradition, social stability, and preserving established institutions. Activist viewpoints prioritize rapid reform, challenging systemic inequalities and advocating for immediate action to achieve social justice. These contrasting approaches reflect fundamental differences in beliefs about the pace and legitimacy of societal transformation.
Political Influence: Comparative Impacts
Conservatism emphasizes maintaining established traditions and institutions, resulting in political influence through gradual reform and stability-focused policies. Activism drives rapid political change by mobilizing grassroots movements and challenging existing power structures to address social injustices. The comparative impact shows conservatism often sustains long-term governance frameworks, while activism accelerates policy innovation and societal transformation.
Conservatism and Activism in Modern Society
Conservatism in modern society emphasizes preserving traditional values, social institutions, and cultural continuity, advocating for gradual change rather than sudden reform. Activism, by contrast, drives social and political progress through proactive efforts to challenge and transform existing systems, often addressing issues like climate change, social justice, and human rights. The tension between conservatism and activism shapes contemporary debates on governance, policy-making, and cultural evolution worldwide.
Prominent Figures and Movements
Conservatism prominently features figures like Edmund Burke and Ronald Reagan, who emphasize tradition, limited government, and gradual societal change, with movements such as the Tea Party advocating for fiscal restraint and constitutional originalism. Activism is driven by leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. and Gloria Steinem, spearheading civil rights and feminist movements that demand social justice, equality, and systemic reform. Both ideologies shape political landscapes through distinct approaches to governance, policy, and public engagement.
Reconciling Conservatism and Activism: Is Balance Possible?
Reconciling conservatism and activism involves finding a balance between preserving established traditions and advocating for progressive change. Emphasizing adaptive conservatism can harmonize respect for historical values with the need for social reform, allowing incremental activism without undermining foundational principles. This balance fosters sustainable progress by integrating cautious innovation within a stable societal framework.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com