Understanding the difference between actual and ideal performance is crucial for setting realistic goals and measuring progress effectively. Actual performance refers to what is currently being achieved, while ideal performance represents the optimal standard or target. Explore the rest of this article to discover how aligning your actual efforts with ideal outcomes can drive success.
Table of Comparison
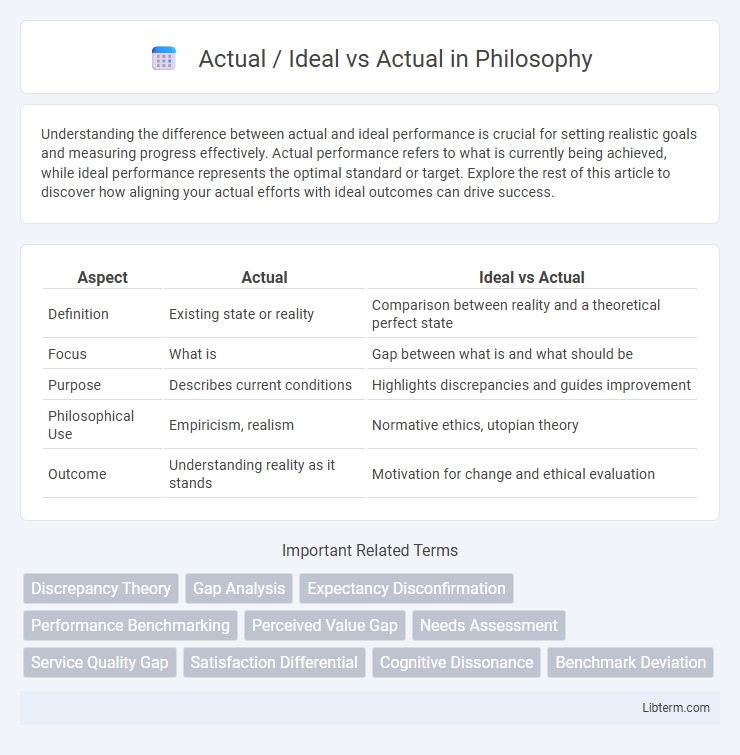
| Aspect | Actual | Ideal vs Actual |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Existing state or reality | Comparison between reality and a theoretical perfect state |
| Focus | What is | Gap between what is and what should be |
| Purpose | Describes current conditions | Highlights discrepancies and guides improvement |
| Philosophical Use | Empiricism, realism | Normative ethics, utopian theory |
| Outcome | Understanding reality as it stands | Motivation for change and ethical evaluation |
Understanding the Concept: Actual vs Ideal
Understanding the concept of Actual vs Ideal involves comparing current states or performances with desired or perfect standards, highlighting gaps and areas for improvement. The "Actual" represents real-world outcomes measured by data or experience, while the "Ideal" reflects theoretical goals based on optimal conditions or values. This comparison is crucial in fields like quality management, decision-making, and performance analysis to identify discrepancies and drive progress toward desired objectives.
Key Differences Between Actual and Ideal
Actual refers to the real, observed state of a system or situation, while ideal represents the perfect or desired condition. Key differences include measurability, as actual data reflects tangible outcomes, whereas ideal serves as a theoretical benchmark. The actual state often includes imperfections and constraints, contrasting with the ideal's focus on optimal performance and best-case scenarios.
Real-World Examples of Actual vs Ideal
In the automotive industry, customer expectations often contrast with actual vehicle performance, where ideal fuel efficiency metrics are not always met due to real-world driving conditions. In software development, ideal project timelines frequently differ from actual completion dates, influenced by unforeseen technical challenges or scope changes. Retail businesses experience discrepancies between ideal inventory levels and actual stock, impacted by supply chain disruptions and fluctuating demand patterns.
Why the Ideal Differs from the Actual
The ideal differs from the actual due to constraints such as resource limitations, environmental factors, and imperfect information influencing decision-making processes. Human error, unforeseen external variables, and evolving circumstances prevent the attainment of ideal outcomes in practical scenarios. These discrepancies highlight the gap between theoretical models and real-world implementations across various fields.
Measuring Performance: Actual Output vs Ideal Output
Measuring performance involves comparing actual output against ideal output to identify efficiency gaps and operational bottlenecks. The actual output reflects real production levels, while the ideal output represents maximum achievable performance under optimal conditions. Analyzing the variance between these metrics enables businesses to implement targeted improvements and enhance productivity.
Causes of Variance: Bridging Actual and Ideal
Causes of variance between Actual / Ideal vs Actual often stem from discrepancies in expected performance standards, resource allocation, and operational inefficiencies. Root causes include inaccurate forecasting, process bottlenecks, and environmental factors impacting execution. Addressing these variances requires aligning strategic objectives with real-time data, improving communication channels, and implementing agile corrective measures to bridge the gap between ideal and actual outcomes.
The Role of Perception in Ideal vs Actual
Perception plays a critical role in distinguishing the ideal self from the actual self, as individuals evaluate their real attributes against personal or societal standards. Discrepancies between perceived actual traits and the ideal can lead to varying degrees of self-esteem and motivation, influencing behavior and emotional well-being. Understanding the cognitive processes behind perception helps clarify how people construct their self-image and respond to gaps between reality and aspiration.
Impact on Decision-Making: Actual Metrics vs Ideal Targets
Comparing actual metrics to ideal targets reveals critical gaps that influence decision-making by highlighting performance shortfalls and opportunities for improvement. Decision-makers rely on actual data to diagnose real-world outcomes, while ideal targets provide benchmarks to set strategic goals and prioritize actions. The contrast between actual results and ideal expectations drives more informed, data-driven decisions that enhance operational efficiency and business growth.
Strategies to Minimize the Gap Between Actual and Ideal
Implementing continuous performance monitoring systems enables organizations to identify discrepancies between actual and ideal outcomes swiftly. Leveraging data-driven decision-making and adaptive feedback loops ensures real-time adjustments align operations closer to ideal standards. Employee training programs combined with clear goal-setting frameworks foster skill development that directly minimizes the gap between actual performance and ideal benchmarks.
Lessons Learned: Embracing Actual Over Ideal
Focusing on actual outcomes instead of ideal expectations encourages realistic goal-setting and practical problem-solving in project management. Embracing actual data allows teams to identify true challenges, adapt strategies effectively, and foster continuous improvement. Lessons learned from prioritizing real-world results enhance decision-making accuracy and drive sustainable success.
Actual / Ideal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com