Mystical experiences often reveal hidden truths beyond ordinary perception, connecting You to deeper spiritual realities and universal energies. Exploring these phenomena can unlock transformative insights and elevate your consciousness to new heights. Discover how embracing mystical practices can enrich your life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
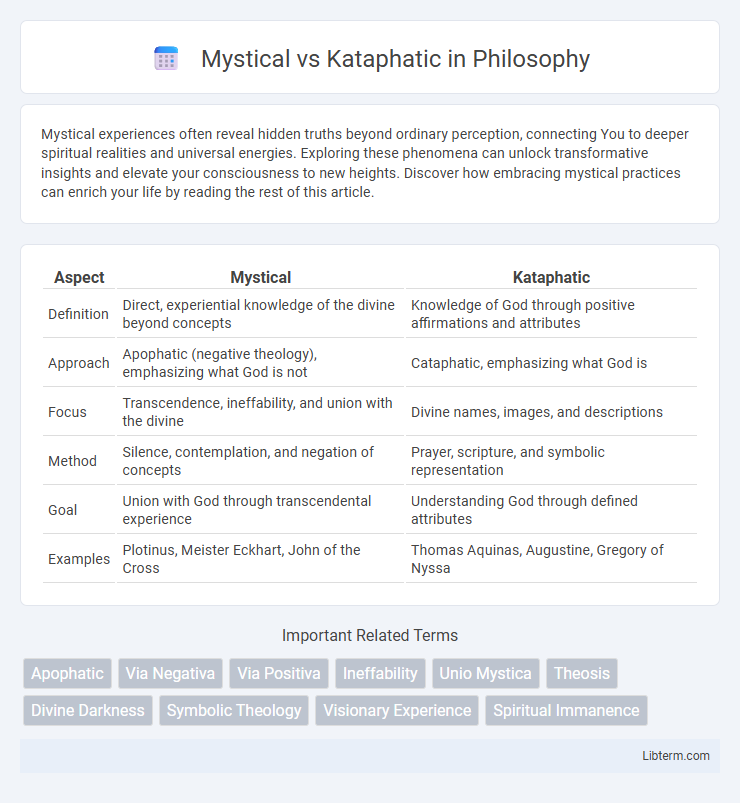
| Aspect | Mystical | Kataphatic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct, experiential knowledge of the divine beyond concepts | Knowledge of God through positive affirmations and attributes |
| Approach | Apophatic (negative theology), emphasizing what God is not | Cataphatic, emphasizing what God is |
| Focus | Transcendence, ineffability, and union with the divine | Divine names, images, and descriptions |
| Method | Silence, contemplation, and negation of concepts | Prayer, scripture, and symbolic representation |
| Goal | Union with God through transcendental experience | Understanding God through defined attributes |
| Examples | Plotinus, Meister Eckhart, John of the Cross | Thomas Aquinas, Augustine, Gregory of Nyssa |
Understanding Mystical and Kataphatic Approaches
Mystical approaches emphasize direct, experiential knowledge of the divine, often transcending language and conceptual thought to access spiritual truths. Kataphatic approaches focus on positive affirmations and descriptions of the divine, using imagery, symbols, and theological language to understand and relate to spiritual realities. Understanding the interplay between mystical silence and kataphatic expression enhances a deeper comprehension of varied spiritual practices and theological frameworks.
Defining Mystical Spirituality
Mystical spirituality centers on the direct, experiential union with the divine, transcending ordinary perception and rational understanding. It emphasizes inner transformation and the realization of ultimate reality through profound personal encounters or altered states of consciousness. In contrast, kataphatic spirituality relies on symbolic imagery, scripture, and positive affirmations to describe and relate to the divine within the limits of human language and thought.
The Essence of Kataphatic Tradition
The essence of the Kataphatic tradition lies in its use of positive affirmations to describe the divine through symbolic language, imagery, and attributes, enabling a tangible connection with the sacred. Unlike the Mystical or Apophatic tradition that emphasizes the ineffability and unknowability of God by negation, Kataphatic spirituality embraces concrete expressions and doctrines to experience and articulate the divine presence. This approach fosters a relational and experiential understanding of God, making spirituality accessible through sacred texts, ritual, and iconography.
Historical Roots of Mystical and Kataphatic Practices
Mystical and kataphatic practices have distinct historical roots that shaped their development within religious traditions. Mystical practices trace back to ancient contemplative traditions in early Christianity, Neoplatonism, and Eastern philosophies, emphasizing direct, ineffable union with the divine. Kataphatic practices evolved from structured liturgical worship and biblical symbolism in Judaism and Christianity, focusing on positive affirmation and descriptive representations of God.
Key Differences: Mystical vs. Kataphatic
Mystical spirituality emphasizes direct, experiential knowledge of the divine beyond intellectual comprehension, focusing on inner transformation and union with the transcendent. Kataphatic spirituality employs positive affirmations, images, and symbols to describe and approach God, relying on scripture and doctrine to guide understanding. The key difference lies in Mystical spirituality's apophatic approach of negation and silence versus Kataphatic spirituality's use of concrete language and conceptual frameworks.
Influential Thinkers and Practitioners
Influential thinkers in mystical traditions, such as Meister Eckhart and Rumi, emphasize direct experiential knowledge of the divine beyond conceptualization, while kataphatic practitioners like St. Thomas Aquinas and John of the Cross focus on positive affirmations and symbolic language to describe God. Mystical approaches prioritize transcendence and ineffability, relying on silence and negation (apophatic) to express the divine mystery. Kataphatic theology uses scripture, doctrine, and prayer to engage the divine presence through affirming attributes, making it central to many Christian contemplative practices.
Core Methods in Mystical Spirituality
Mystical spirituality centers on direct, experiential union with the divine through practices such as meditation, contemplation, and silence that transcend rational thought. Core methods involve surrendering the ego and embracing inner stillness to access deeper states of consciousness beyond verbal expression. These approaches contrast with kataphatic spirituality, which relies on affirmations, imagery, and positive descriptions to engage with the divine.
Kataphatic Imagery and Language
Kataphatic imagery and language employ positive, concrete descriptions to convey the divine, using sensory and symbolic elements that evoke a tangible experience of the sacred. This approach emphasizes affirmations and visualizations, often utilizing metaphor, metaphorical imagery, and vivid detail to articulate spiritual truths in a relatable, comprehensible form. Kataphatic expression contrasts with mystical apophatic methods by embracing articulated depictions that shape the believer's understanding through direct and imaginative engagement with divine attributes.
Contemporary Relevance and Applications
Mystical approaches emphasize direct, ineffable experiences of the divine, influencing contemporary spirituality through practices like meditation and contemplative prayer that foster personal transformation and mental well-being. Kataphatic methods rely on positive affirmations and symbolic language, shaping modern worship and therapeutic techniques by providing structured pathways for understanding and connecting with sacred concepts. Both approaches inform current interfaith dialogues, psychological therapy, and holistic health by integrating experiential and conceptual dimensions of spirituality.
Choosing Between Mystical and Kataphatic Paths
Choosing between mystical and kataphatic paths depends on one's spiritual goals and personal disposition; mystical approaches emphasize direct, experiential union with the divine through silence and contemplation, while kataphatic methods utilize imagery, symbols, and structured prayer to engage with the sacred. Mystical traditions such as Sufism or Christian mysticism prioritize inner transformation beyond conceptual frameworks, contrasting with kataphatic spirituality found in liturgical practices that invoke God through affirmations and sensory expressions. Evaluating one's inner openness to mystery versus desire for concrete representation informs the optimal path for deepening spiritual insight and connection.
Mystical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com