Virtuality transforms how you experience digital environments, offering immersive and interactive experiences that blur the line between reality and simulation. This technology enhances training, entertainment, and communication by creating believable virtual spaces tailored to your needs. Explore the rest of the article to discover how virtuality can revolutionize your interaction with the digital world.
Table of Comparison
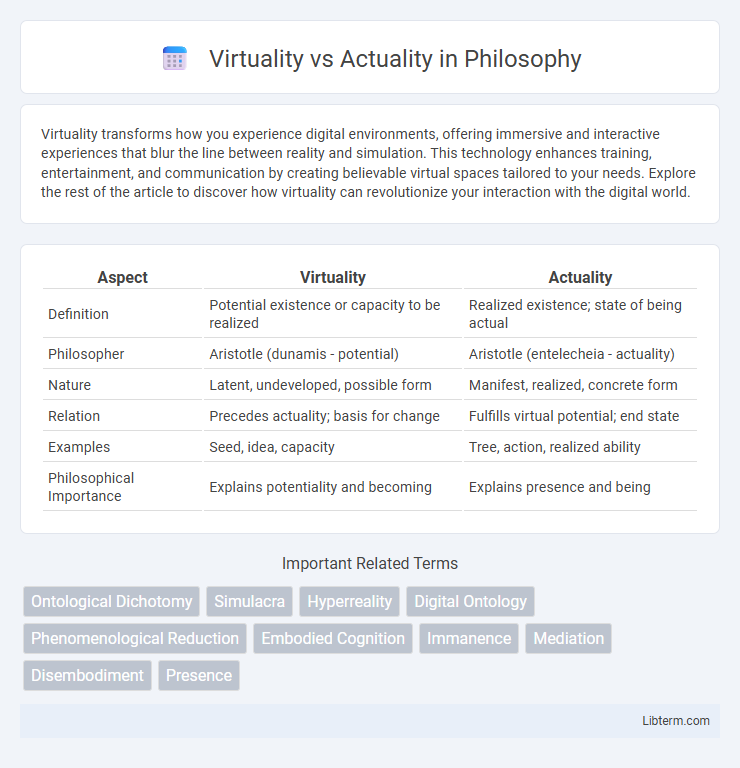
| Aspect | Virtuality | Actuality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Potential existence or capacity to be realized | Realized existence; state of being actual |
| Philosopher | Aristotle (dunamis - potential) | Aristotle (entelecheia - actuality) |
| Nature | Latent, undeveloped, possible form | Manifest, realized, concrete form |
| Relation | Precedes actuality; basis for change | Fulfills virtual potential; end state |
| Examples | Seed, idea, capacity | Tree, action, realized ability |
| Philosophical Importance | Explains potentiality and becoming | Explains presence and being |
Understanding Virtuality and Actuality
Virtuality refers to the state or quality of being virtual, representing something that exists in essence or effect but not in physical form, often experienced through digital or simulated environments. Actuality denotes the real, tangible existence of entities or events in the physical world, grounded in objective reality and observable phenomena. Understanding the distinction between virtuality and actuality is crucial for grasping how digital representations mimic or influence real-world experiences, emphasizing the interplay between simulated constructs and concrete existence.
Historical Perspectives on Reality
Historical perspectives on reality reveal an evolving understanding where Virtuality, as conceptualized in Plato's Allegory of the Cave, contrasts with Actuality by questioning the nature of perceived truth versus objective existence. Philosophers like Descartes emphasized doubt in physical reality, propelling the debate on whether sensory experience or rational thought constitutes actual reality. Contemporary discussions extend from 20th-century phenomenology to digital simulations, highlighting the enduring tension between virtual representations and tangible actuality in defining human experience.
Defining the Boundaries: Virtual vs Actual
Defining the boundaries between virtuality and actuality requires distinguishing immersive digital environments from tangible physical reality based on sensory perception, interactivity, and presence. Virtuality depends on computer-generated simulations and augmented reality overlays, allowing users to experience synthetic spaces without physical constraints. Actuality involves the objective, material world where entities exist independently of human mediation and are governed by natural laws.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Virtuality
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping virtuality by enabling immersive digital environments that simulate real-world experiences through advanced hardware and software innovations. Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies blur the lines between virtuality and actuality by enhancing sensory perception and real-time interaction within virtual spaces. The continuous evolution of computing power, artificial intelligence, and network connectivity drives the expansion of virtuality, transforming how individuals engage with digital content and redefining the boundaries of actual physical experience.
Psychological Impacts of Virtual and Actual Experiences
Virtual experiences can alter perception and cognitive processing, often leading to heightened sensory stimulation and immersion that impacts emotional responses and memory formation. Actual experiences engage multisensory inputs with real-world consequences, promoting stronger neural connections through direct physical interaction and social cues, which enhance psychological well-being and a sense of presence. The psychological impact of virtuality versus actuality influences empathy, stress levels, and identity construction, highlighting the importance of balancing both experiences for mental health.
The Philosophy Behind Virtuality and Actuality
The philosophy behind virtuality and actuality explores the distinction between potential existence and realized being, rooted in Aristotle's concept of potentiality and actuality. Virtuality refers to the intrinsic potential or capacity within an entity that has not yet been actualized, whereas actuality denotes the fulfilled, manifest state of that potential. This metaphysical framework informs contemporary debates in ontology, technology, and cognitive science regarding the nature of existence, reality, and the interplay between possibility and realization.
Real-World Applications of Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) transforms digital simulations into immersive experiences, bridging the gap between virtuality and actuality through realistic sensory interactions. Industries like healthcare utilize VR for surgical training and pain management, while architecture benefits from virtual walkthroughs to visualize designs before construction. In education, VR enhances experiential learning by enabling students to explore historical sites or complex scientific environments in a controlled, interactive setting.
Social Implications: Connecting and Dividing Worlds
Virtuality transforms social interactions by enabling global connectivity, fostering diverse online communities that transcend geographical barriers. Actuality remains crucial for face-to-face communication, providing tangible experiences and emotional depth often lacking in virtual environments. The tension between virtual and actual realms highlights significant social implications, where digital engagement can both unite disparate groups and create echo chambers that divide societies.
The Future of Virtuality in an Actual World
The future of virtuality in an actual world hinges on the seamless integration of immersive technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) into everyday life and industries. Advancements in 5G connectivity and AI-driven environments will enhance the realism and accessibility of virtual experiences, blurring the boundaries between digital and physical spaces. This convergence promises transformative impacts on education, healthcare, remote work, and entertainment by creating interactive, personalized, and efficient virtual-actual hybrid ecosystems.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating Virtuality and Actuality
Bridging the gap between virtuality and actuality involves seamlessly integrating digital simulations with real-world environments to enhance user experience and operational efficiency. Technologies such as augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and advanced sensors enable real-time interaction and data synchronization, allowing virtual objects to coexist and respond within physical spaces. This convergence supports industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and education by facilitating immersive training, remote collaboration, and precise decision-making through hyper-accurate digital twins and sensor-driven feedback loops.
Virtuality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com