De nunc marks the precise moment from which a new situation or rule begins to apply, often used in legal and formal contexts to indicate changes effective immediately. Understanding de nunc helps clarify how current actions or decisions impact your rights and obligations moving forward. Explore the rest of the article to fully grasp how de nunc influences legal and contractual scenarios.
Table of Comparison
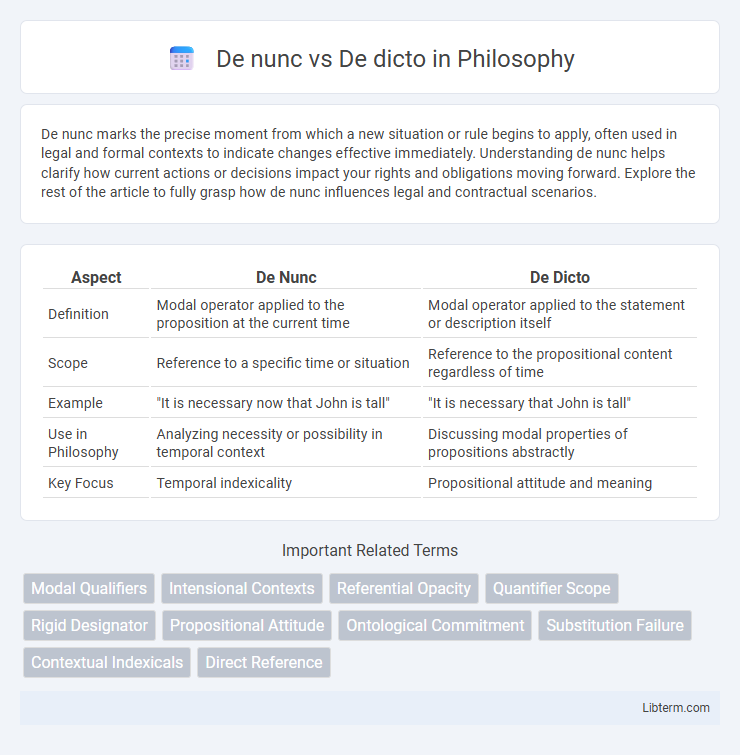
| Aspect | De Nunc | De Dicto |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modal operator applied to the proposition at the current time | Modal operator applied to the statement or description itself |
| Scope | Reference to a specific time or situation | Reference to the propositional content regardless of time |
| Example | "It is necessary now that John is tall" | "It is necessary that John is tall" |
| Use in Philosophy | Analyzing necessity or possibility in temporal context | Discussing modal properties of propositions abstractly |
| Key Focus | Temporal indexicality | Propositional attitude and meaning |
Introduction to De Nunc and De Dicto
De nunc and de dicto represent two distinct modes of propositional attitude ascription in philosophy of language and logic. De dicto refers to the attribution of a belief or statement about a proposition as a whole, emphasizing the content regardless of time or context, whereas de nunc focuses on the evaluation of a statement relative to the current time or situation, highlighting temporal aspects of belief or knowledge. Understanding the difference between de nunc and de dicto is essential for analyzing modalities and intensional contexts in semantics and epistemology.
Defining De Nunc: Meaning and Usage
De nunc refers to the interpretation of statements or beliefs that are assessed from the present moment, emphasizing what is true or valid now rather than at the time it was originally expressed. It is used in philosophy and linguistics to analyze the temporal aspects of knowledge, belief, and truth, distinguishing current understanding from past or hypothetical scenarios. This contrasts with de dicto, which focuses on the content of the expression regardless of temporal context, making de nunc crucial for discussions about evolving truths and beliefs.
Understanding De Dicto: Core Concepts
De dicto refers to the interpretation of statements where the proposition itself is the focus, emphasizing the meaning or belief expressed rather than its specific reference or context. Understanding de dicto involves recognizing how beliefs or desires relate to the entire proposition, often contrasted with de nunc interpretations that anchor meaning to a particular time or situation. This concept is crucial in epistemology and philosophy of language for analyzing belief reports and modal statements accurately.
Historical Context: Origins of De Nunc and De Dicto
The origins of De nunc and De dicto trace back to medieval scholastic philosophy, where logicians sought to distinguish between statements about beliefs as they stand (de dicto) and beliefs held at a specific time (de nunc). These concepts were essential in developing theories of modality and propositional attitudes, influencing later philosophical debates on the interpretation of temporal and intentional statements. Key figures such as William of Ockham and John Buridan contributed significantly to formalizing these distinctions within the framework of medieval logic.
Key Differences Between De Nunc and De Dicto
De nunc and de dicto represent distinct modes of proposition interpretation in philosophy, primarily concerning the timing of beliefs or statements. De nunc refers to beliefs or statements evaluated with respect to the current time or context, emphasizing the actual truth value at the moment of utterance. De dicto involves considering the content of the belief or statement as a propositional attitude, focusing on the general or timeless meaning rather than the specific temporal circumstances.
Practical Examples in Linguistics
De nunc and de dicto distinction plays a crucial role in interpreting belief reports and modal statements in semantics. For example, in the sentence "John believes that the winner of the race is tall," the de dicto reading focuses on the proposition about "the winner," while the de nunc reading concerns John's belief about a specific individual currently considered the winner. Analyzing such examples helps linguists understand scope ambiguities and reference in natural language, improving models of meaning representation.
Applications in Philosophy and Logic
De nunc and de dicto distinctions play a crucial role in philosophy and logic, particularly in the analysis of propositional attitudes and modal contexts. De dicto interpretations concern the truth of a statement under the interpretation of the entire proposition, while de nunc focuses on the truth relative to a specific time or situation. Applications include clarifying the semantics of belief reports, resolving ambiguities in modal logic, and refining theories of time-sensitive statements in epistemology and metaphysics.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
De nunc and de dicto represent distinct approaches in propositional attitude reports, where de nunc refers to beliefs about a proposition at a specific time, while de dicto captures beliefs about the proposition's content regardless of time. A common misconception is confusing de dicto with de re attitudes, leading to errors in attributing belief persistence or change over time. Pitfalls often arise when failing to recognize temporal indexicals in de nunc interpretations, causing misanalysis of belief dynamics and theoretical inconsistencies in modal contexts.
Importance in Contemporary Semantic Analysis
The distinction between De nunc and De dicto is crucial in contemporary semantic analysis as it clarifies how meaning shifts based on temporal perspectives and belief attribution. De nunc interpretations capture the truth of statements relative to the present context, while De dicto interpretations preserve the original propositional content regardless of time. This differentiation enhances the precision of natural language understanding systems and informs advanced models of modality, belief, and intensionality.
Conclusion: Implications and Future Directions
De nunc and de dicto distinctions shape the interpretation of belief reports, impacting linguistic theory and philosophy of language by clarifying how context influences meaning. Understanding these modalities enhances computational semantics and natural language processing, enabling more accurate modeling of speaker intentions and belief attribution. Future research may explore cross-linguistic applications and dynamic context integration to refine semantic frameworks and improve human-computer interaction.
De nunc Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com