Self-consciousness often leads to overthinking and heightened sensitivity to how others perceive you, impacting your confidence and social interactions. Understanding its psychological roots and coping strategies can help you manage these feelings more effectively. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips and insights for overcoming self-consciousness.
Table of Comparison
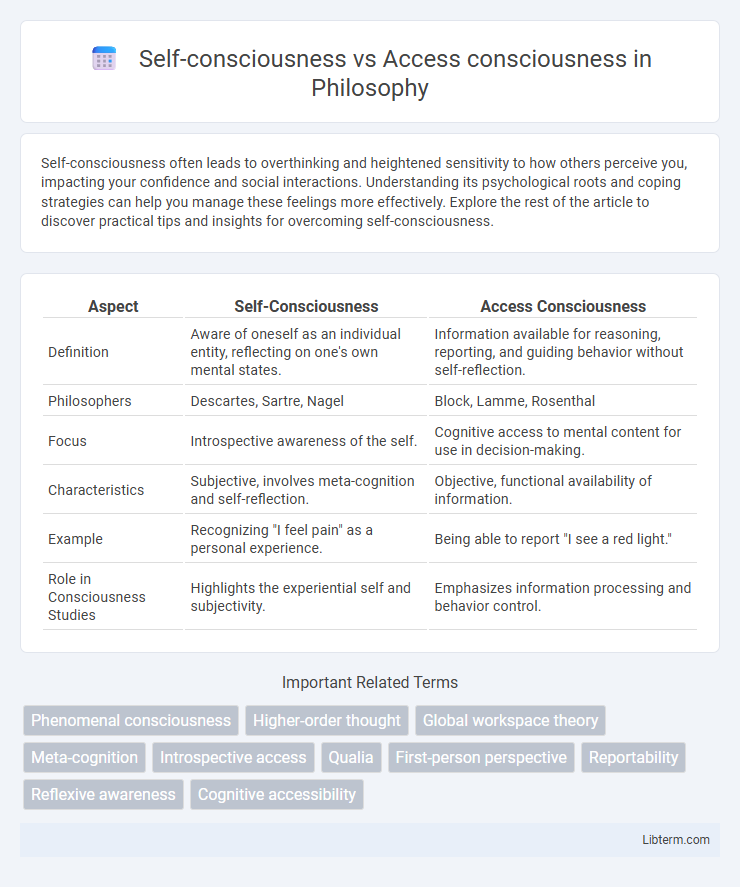
| Aspect | Self-Consciousness | Access Consciousness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aware of oneself as an individual entity, reflecting on one's own mental states. | Information available for reasoning, reporting, and guiding behavior without self-reflection. |
| Philosophers | Descartes, Sartre, Nagel | Block, Lamme, Rosenthal |
| Focus | Introspective awareness of the self. | Cognitive access to mental content for use in decision-making. |
| Characteristics | Subjective, involves meta-cognition and self-reflection. | Objective, functional availability of information. |
| Example | Recognizing "I feel pain" as a personal experience. | Being able to report "I see a red light." |
| Role in Consciousness Studies | Highlights the experiential self and subjectivity. | Emphasizes information processing and behavior control. |
Defining Self-Consciousness
Self-consciousness refers to the capacity of an individual to be aware of themselves as distinct entities, encompassing self-reflection, self-recognition, and an understanding of one's own identity. It involves meta-cognition, where the mind is aware of its own states, thoughts, and experiences, contrasting with access consciousness which denotes the availability of information for reasoning and action without self-referential awareness. Defining self-consciousness emphasizes the subjective experience and the explicit knowledge of oneself as an enduring being through time.
Understanding Access Consciousness
Access consciousness refers to the aspect of consciousness that enables information to be globally available for reasoning, decision-making, and verbal report. It involves the cognitive processes that allow a person to access and utilize stored information for guiding behavior without necessarily being aware of the content itself. Understanding access consciousness highlights its role in the integration of perceptual inputs and higher-order cognitive functions crucial for intentional actions and problem-solving.
Historical Perspectives on Consciousness
Historical perspectives on consciousness distinguish self-consciousness as the awareness of oneself as a distinct entity capable of reflection, whereas access consciousness refers to the availability of information for verbal report and rational decision-making. Philosophers like John Locke emphasized self-consciousness in personal identity, while cognitive scientists including Ned Block delineated access consciousness in functional cognitive processes. This distinction has shaped contemporary debates by linking self-consciousness to higher-order thought theories and access consciousness to global workspace models of mental representation.
Key Differences Between Self- and Access Consciousness
Self-consciousness involves awareness of oneself as a distinct entity with reflective thought, while access consciousness refers to information in the mind that is available for reasoning and guiding behavior without necessarily being self-reflective. Key differences include self-consciousness's emphasis on meta-awareness and personal identity, whereas access consciousness centers on the accessibility of mental content for cognitive processing. Self-consciousness typically enables introspective experiences, whereas access consciousness facilitates decision-making and verbal reportability.
Neuroscientific Insights and Mechanisms
Self-consciousness involves the brain's higher-order regions, such as the prefrontal cortex, enabling reflective awareness of oneself as an entity over time, while access consciousness relates to information processing that enters working memory and guides behavior without necessarily involving self-reflective thought. Neuroscientific studies using fMRI and EEG reveal that access consciousness is associated with activation in sensory and attentional networks, whereas self-consciousness engages additional meta-cognitive circuits, including the default mode network. Mechanistically, the integration of global neuronal workspace theory explains access consciousness through widespread cortical broadcasting, whereas self-consciousness relies on recurrent processing loops facilitating introspective and autobiographical representations.
The Role of Language in Conscious Experiences
Self-consciousness involves awareness of oneself as a distinct entity, often requiring complex linguistic structures that facilitate reflection and self-reporting. Access consciousness refers to the availability of information in mental processing accessible for reasoning and verbal expression, highlighting language's role in articulating conscious experiences. The interplay between language and consciousness enables individuals to conceptualize and communicate internal states, enhancing metacognitive abilities and self-awareness.
Self-Reflection vs Information Processing
Self-consciousness involves self-reflection, enabling individuals to recognize and evaluate their own thoughts and experiences, fostering personal identity and introspection. Access consciousness pertains to the ability to process and report information, allowing cognitive functions such as decision-making, verbal communication, and behavioral control. The interplay between self-reflection and information processing highlights how awareness not only includes internal monitoring but also the manipulation and use of data within cognitive systems.
Implications for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Minds
Self-consciousness involves an entity's awareness of itself as distinct and capable of self-reflection, whereas access consciousness refers to the availability of information for reasoning and guiding behavior without subjective experience. In artificial intelligence, access consciousness aligns with current models processing and utilizing data, but self-consciousness remains elusive, challenging machines' ability to possess true self-awareness or reflective thought. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for developing machine minds that not only perform tasks effectively but also exhibit adaptive, context-aware behaviors linked to a form of self-referential cognition.
Philosophical Debates and Thought Experiments
Philosophical debates on self-consciousness versus access consciousness critically analyze the distinction between subjective awareness of one's own mental states and the cognitive accessibility of those states for reasoning and behavior. Thought experiments like Nagel's "What is it like to be a bat?" illustrate the challenge of capturing subjective experience (self-consciousness) through objective cognitive processes (access consciousness). The discourse examines whether access consciousness fully accounts for the richness of self-awareness or if an irreducible, introspective dimension remains essential to understanding consciousness.
Future Directions in Consciousness Research
Future directions in consciousness research emphasize unraveling the distinct neural correlates of self-consciousness and access consciousness through advanced neuroimaging techniques. Emphasis is placed on understanding how self-related information integrates with access mechanisms to influence subjective experience and cognitive control. Cutting-edge approaches involve computational modeling and brain-machine interfaces to map dynamic interactions between these two facets of consciousness and their role in decision-making and self-awareness.
Self-consciousness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com