Ego shapes your perception of self and influences decision-making in daily life, impacting relationships and personal growth. Understanding the ego's role can lead to improved emotional intelligence and self-awareness. Explore the rest of this article to discover how mastering your ego can transform your mindset.
Table of Comparison
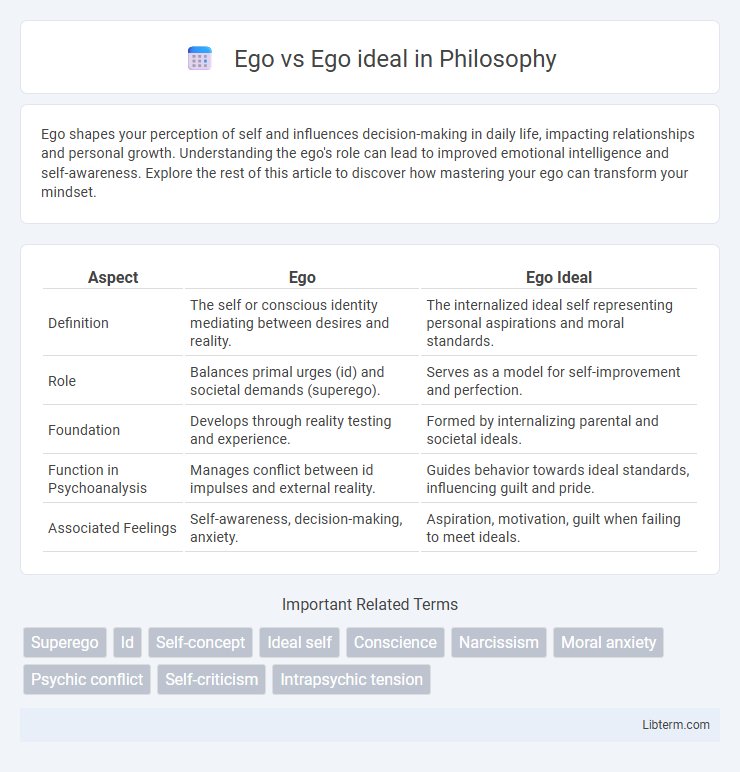
| Aspect | Ego | Ego Ideal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The self or conscious identity mediating between desires and reality. | The internalized ideal self representing personal aspirations and moral standards. |
| Role | Balances primal urges (id) and societal demands (superego). | Serves as a model for self-improvement and perfection. |
| Foundation | Develops through reality testing and experience. | Formed by internalizing parental and societal ideals. |
| Function in Psychoanalysis | Manages conflict between id impulses and external reality. | Guides behavior towards ideal standards, influencing guilt and pride. |
| Associated Feelings | Self-awareness, decision-making, anxiety. | Aspiration, motivation, guilt when failing to meet ideals. |
Understanding Ego and Ego Ideal: Core Definitions
The ego represents the conscious self, mediating between instinctual desires and reality by balancing the id, superego, and external world. The ego ideal is an internalized set of standards and aspirations derived from parental and societal influences, guiding behavior and self-evaluation. Understanding the dynamic between the ego and ego ideal is crucial for analyzing motivation, self-esteem, and psychological conflicts.
Origins of the Ego and Ego Ideal in Psychoanalytic Theory
The Ego and Ego Ideal originate from Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche, where the Ego mediates between the primal id and external reality, developing through early interactions and experiences. The Ego Ideal evolves as an internalized representation of societal and parental standards, guiding self-assessment and striving for perfection. These constructs are foundational in psychoanalytic theory, elucidating internal conflict and the regulation of behavior through unconscious and conscious processes.
Formation of the Ego: Functions and Characteristics
The formation of the ego is a complex psychological process involving the integration of conscious awareness and unconscious desires, serving as the mediator between the id, superego, and external reality. Key functions of the ego include reality-testing, impulse control, and maintaining a coherent self-identity, which are essential for adaptive behavior and decision-making. Characteristics of a well-formed ego encompass self-regulation, resilience to external stressors, and the capacity to balance immediate gratification with long-term goals.
Constructing the Ego Ideal: Sources and Influences
The ego ideal is constructed through internalization of parental standards, cultural norms, and societal expectations that shape an individual's aspirations and moral framework. Influences such as early childhood experiences, educational environments, and significant social interactions contribute to the formation and evolution of the ego ideal. This internalized ideal serves as a benchmark for self-evaluation, guiding behavior and emotional responses in the ongoing development of the ego.
Key Differences Between Ego and Ego Ideal
The ego operates as the conscious self that mediates between instinctual desires and reality, managing impulses and decision-making based on the real world, while the ego ideal represents the internalized standards and aspirations derived from parental and societal expectations, shaping one's sense of perfection and moral goals. Key differences include the ego's function in realistic problem-solving contrasted with the ego ideal's role in enforcing ideals and motivating self-improvement. The ego balances actual behavior with reality, whereas the ego ideal imposes a vision of the perfect self, often influencing feelings of pride or guilt.
Ego vs Ego Ideal: Role in Personality Development
Ego and Ego Ideal are pivotal components in personality development, with the Ego representing the conscious self that mediates reality and the Ego Ideal embodying internalized standards and aspirations derived from parental and societal influences. The Ego strives to reconcile desires with moral standards imposed by the Ego Ideal, shaping self-regulation, motivation, and identity formation. This dynamic interplay crucially influences behavior, self-esteem, and the development of a cohesive, mature personality framework.
The Psychological Impact of Ego-Ideal Discrepancy
The psychological impact of ego-ideal discrepancy often manifests as feelings of inadequacy, low self-esteem, and heightened anxiety due to the gap between one's real self and aspirational standards. This internal conflict triggers persistent negative self-evaluation and diminished motivation, contributing to depressive symptoms and impaired emotional well-being. Therapeutic approaches targeting ego-ideal alignment emphasize self-compassion and realistic goal setting to mitigate distress and promote psychological resilience.
Ego, Ego Ideal, and Mental Health: Connections and Conflicts
Ego functions as the mediator between reality and the unconscious, balancing desires with social norms, while the Ego Ideal represents internalized standards of perfection and moral goals. Conflicts arise when the Ego perceives the Ego Ideal as unattainable, leading to feelings of inadequacy, anxiety, or low self-esteem, which negatively impact mental health. Maintaining a dynamic balance between the Ego and Ego Ideal is crucial for psychological resilience and healthy self-regulation.
Strategies for Reconciling Ego with Ego Ideal
Strategies for reconciling the ego with the ego ideal center on aligning self-perception with aspirational standards to reduce internal conflict and foster psychological well-being. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy encourage individuals to identify discrepancies between current behaviors and ideal self-images, promoting adaptive changes through realistic goal setting and self-compassion. Mindfulness practices enhance self-awareness, allowing the ego to acknowledge imperfections without harsh judgment, thereby facilitating integration between actual self and ego ideal constructs.
Cultivating Self-Awareness in Balancing Ego and Ego Ideal
Cultivating self-awareness involves recognizing the distinctions between the ego, which represents the current sense of self, and the ego ideal, embodying aspirational standards and values. This practice enhances emotional intelligence by identifying when ego-driven reactions conflict with the ego ideal's pursuit of growth and integrity. Developing mindfulness techniques and reflective journaling supports aligning behavior with the ego ideal, fostering psychological balance and personal development.
Ego Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com