Holistic thinking involves understanding complex systems by recognizing the interconnections between their parts rather than analyzing elements in isolation. This approach enhances problem-solving by considering the broader context and long-term consequences. Discover how adopting holistic thinking can transform your perspective and improve decision-making throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
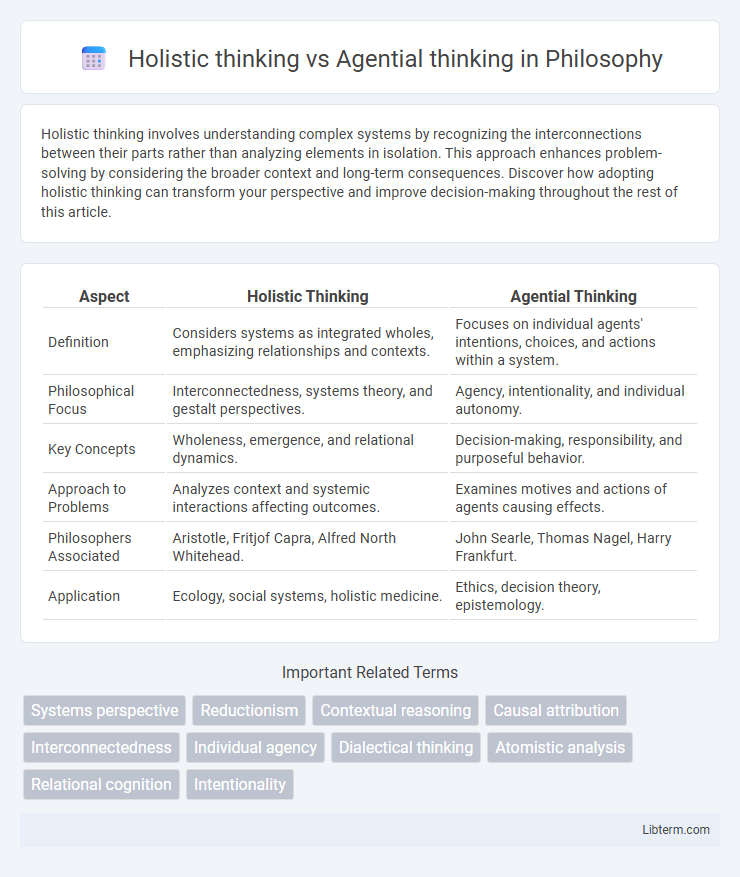
| Aspect | Holistic Thinking | Agential Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Considers systems as integrated wholes, emphasizing relationships and contexts. | Focuses on individual agents' intentions, choices, and actions within a system. |
| Philosophical Focus | Interconnectedness, systems theory, and gestalt perspectives. | Agency, intentionality, and individual autonomy. |
| Key Concepts | Wholeness, emergence, and relational dynamics. | Decision-making, responsibility, and purposeful behavior. |
| Approach to Problems | Analyzes context and systemic interactions affecting outcomes. | Examines motives and actions of agents causing effects. |
| Philosophers Associated | Aristotle, Fritjof Capra, Alfred North Whitehead. | John Searle, Thomas Nagel, Harry Frankfurt. |
| Application | Ecology, social systems, holistic medicine. | Ethics, decision theory, epistemology. |
Introduction to Holistic and Agential Thinking
Holistic thinking emphasizes understanding systems as integrated wholes, recognizing patterns and relationships within complex contexts. Agential thinking centers on individual action and decision-making, highlighting the capacity of agents to influence outcomes through intentional behavior. Both approaches offer complementary perspectives for analyzing situations, combining system-wide insights with focused human agency.
Defining Holistic Thinking
Holistic thinking involves understanding systems by recognizing the interconnections and relationships among components, emphasizing patterns and contexts rather than isolated elements. It requires a broad perspective that integrates various factors to comprehend the whole rather than focusing on individual parts. This cognitive approach contrasts with agential thinking, which centers on individual actions and specific agents within a system.
Understanding Agential Thinking
Agential thinking emphasizes individual agency, focusing on how people actively interpret, shape, and influence their environments through intentional actions. It highlights decision-making processes, personal responsibility, and adaptive problem-solving within dynamic contexts. Understanding agential thinking reveals how individuals exercise control and creativity in complex social and organizational systems.
Historical Roots and Cultural Influences
Holistic thinking, rooted in Eastern philosophies such as Confucianism and Taoism, emphasizes interconnectedness and the dynamic relationships between elements within a system, reflecting cultural values of balance and harmony. Agential thinking, often traced to Western traditions influenced by Enlightenment ideals, prioritizes individual agency, causality, and linear logic, highlighting autonomy and control in decision-making processes. These divergent cognitive styles reflect deep historical and cultural frameworks that shape perception, reasoning, and problem-solving across societies.
Key Differences Between Holistic and Agential Perspectives
Holistic thinking emphasizes interconnectedness and the system-wide context, viewing elements as part of an integrated whole, while agential thinking focuses on individual agents and their autonomous decision-making abilities. Holistic perspectives prioritize relationships, patterns, and collective dynamics, in contrast to agential approaches that highlight intentional actions, choices, and causal impact of distinct actors. Key differences include the scope of analysis--system level versus individual level--and the interpretation of influence through networks versus discrete agents.
Advantages and Limitations of Holistic Thinking
Holistic thinking offers the advantage of understanding complex systems by recognizing interconnections and patterns, fostering better decision-making in dynamic environments. Limitations include potential overgeneralization and difficulty isolating specific factors for targeted action, which can lead to inefficiency in problem-solving. While holistic thinking enhances long-term strategic planning, it may struggle in situations requiring precise, immediate responses.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Agential Thinking
Agential thinking excels in providing clear, actionable solutions by focusing on individual actors and their choices, enabling precise accountability and targeted interventions. However, its strength in simplification can also be a weakness, as it may overlook broader systemic factors and interdependencies that influence outcomes. This narrow focus risks misattributing causes, potentially leading to ineffective or incomplete strategies in complex environments.
Impact on Decision-Making and Problem Solving
Holistic thinking enhances decision-making and problem-solving by emphasizing the interconnectedness of systems, leading to more comprehensive and sustainable solutions. Agential thinking prioritizes individual actions and control, driving solutions that focus on immediate, practical outcomes and personal accountability. The impact on decision-making varies as holistic thinkers anticipate long-term consequences, while agential thinkers optimize short-term effectiveness in complex scenarios.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Holistic thinking emphasizes understanding systems by examining the relationships between their parts, making it highly effective in environmental management and urban planning, as seen in sustainable city development projects. Agential thinking focuses on individual actions and decision-making, which is critical in behavioral economics and personalized healthcare, demonstrated by tailored intervention programs improving patient outcomes. Case studies in corporate strategy reveal that combining holistic system insights with agential decision-making leads to more adaptive and resilient organizational practices.
Integrating Holistic and Agential Approaches in Modern Life
Integrating holistic and agential thinking enhances decision-making by combining the broad perspective of interconnected systems with the proactive focus on individual agency and choice. Holistic thinking considers the complex interactions within environments, while agential thinking emphasizes deliberate actions shaping outcomes, fostering adaptability in dynamic social and professional contexts. This synergy supports comprehensive problem-solving, balancing systemic awareness with personal responsibility for effective results.
Holistic thinking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com