Nomothetic approaches focus on identifying general laws and patterns that apply across individuals, emphasizing broad principles rather than unique personal experiences. This method is widely used in psychology and social sciences to develop theories with predictive power. Explore the rest of the article to understand how nomothetic research shapes our knowledge and impacts your field.
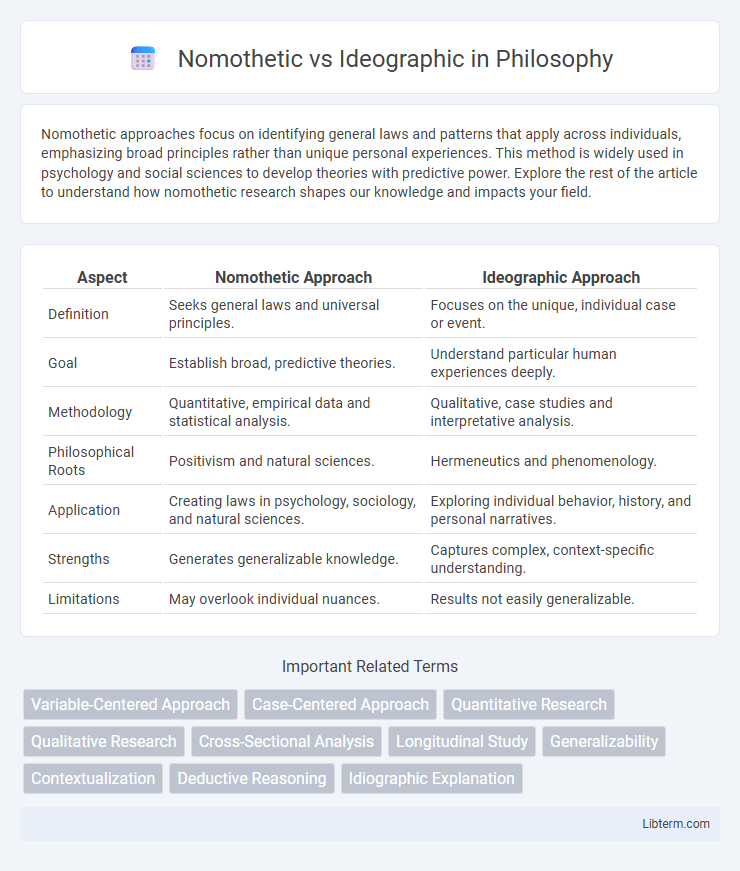
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nomothetic Approach | Ideographic Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seeks general laws and universal principles. | Focuses on the unique, individual case or event. |
| Goal | Establish broad, predictive theories. | Understand particular human experiences deeply. |
| Methodology | Quantitative, empirical data and statistical analysis. | Qualitative, case studies and interpretative analysis. |
| Philosophical Roots | Positivism and natural sciences. | Hermeneutics and phenomenology. |
| Application | Creating laws in psychology, sociology, and natural sciences. | Exploring individual behavior, history, and personal narratives. |
| Strengths | Generates generalizable knowledge. | Captures complex, context-specific understanding. |
| Limitations | May overlook individual nuances. | Results not easily generalizable. |
Understanding Nomothetic and Ideographic Approaches
Nomothetic approaches emphasize establishing general laws and universal principles through quantitative methods, enabling broad predictions and explanations across populations. Ideographic approaches prioritize understanding the unique, subjective experiences of individuals using qualitative data, providing in-depth insights into specific cases. Grasping these approaches helps tailor research strategies to either generalize findings or explore detailed personal contexts effectively.
Historical Background of the Concepts
The concepts of nomothetic and ideographic approaches originated in the 19th century within the philosophy of science and psychology, primarily attributed to Wilhelm Windelband. Nomothetic research seeks general laws applicable across populations, rooted in natural sciences like physics and biology, while ideographic inquiry focuses on the unique, detailed study of individual cases, aligning with disciplines such as history and anthropology. These foundational distinctions shaped qualitative and quantitative methodologies in social sciences, emphasizing the contrast between generalization and individualization in research design.
Defining Nomothetic: Universal Laws in Research
Nomothetic approaches in research aim to identify universal laws and generalizable principles that apply across populations, enabling predictions and explanations of broad phenomena. This method emphasizes quantitative data, statistical analysis, and the search for patterns or regularities to establish objective truths. By focusing on generalizability, nomothetic research contrasts with ideographic studies that prioritize individual uniqueness and subjective experiences.
Exploring Ideographic: Focus on Individual Cases
Exploring ideographic approaches centers on the in-depth analysis of individual cases, emphasizing unique personal experiences and context-specific details rather than generalizing across populations. This method is crucial in qualitative research, psychology, and anthropology, where understanding the complexity of singular phenomena reveals nuanced insights. By prioritizing subjective interpretations, ideographic studies provide rich, detailed data that can inform tailored interventions and theories grounded in real-world specificity.
Key Differences Between Nomothetic and Ideographic Methods
Nomothetic methods emphasize generalization by identifying universal laws through quantitative data and large sample sizes, while ideographic methods focus on in-depth understanding of unique individual cases using qualitative approaches. Nomothetic research prioritizes statistical analysis and predictability, contrasted with ideographic research's emphasis on context, complexity, and detailed narrative descriptions. These fundamental differences impact their applications in psychology, sociology, and other social sciences, where nomothetic approaches seek broad patterns and ideographic approaches value subjective meanings.
Applications of Nomothetic Approach in Psychology
The nomothetic approach in psychology emphasizes the identification of general laws and principles that apply across populations, making it highly valuable in experimental research and large-scale behavioral studies. It facilitates the development of standardized diagnostic criteria and predictive models in clinical psychology, enhancing the understanding of common psychological disorders. Applications also include the use of statistical methods to analyze group data, supporting evidence-based practices and interventions.
Applications of Ideographic Approach in Psychology
The ideographic approach in psychology emphasizes the detailed study of individual cases, allowing for a deep understanding of unique personal experiences and subjective phenomena. This method is widely applied in clinical psychology, where idiographic techniques such as case studies, narrative analysis, and unstructured interviews provide vital insights into a person's mental health and therapeutic needs. By prioritizing individual differences, the ideographic approach enriches personalized treatment plans and enhances the effectiveness of psychological interventions.
Advantages and Limitations of Nomothetic vs Ideographic
Nomothetic approaches offer the advantage of generalizability by identifying universal laws and patterns across populations, enabling prediction and replication in psychological research. However, their limitation lies in potentially overlooking individual differences and contextual nuances that can be critical for understanding unique behaviors. Ideographic methods provide in-depth insights into individual cases, capturing complex personal experiences but often face challenges in generalization and scientific replication across broader groups.
Integrative Perspectives: Combining Both Approaches
Integrative perspectives in psychology combine nomothetic and ideographic approaches to provide a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior by balancing generalizable laws with individual uniqueness. This hybrid methodology leverages large-scale quantitative data to identify patterns while incorporating qualitative case studies to capture personal experiences and context-specific nuances. Such an approach enhances research validity and practical application by addressing both universal principles and individual variability in psychological phenomena.
Future Trends in Nomothetic and Ideographic Research
Future trends in nomothetic research highlight the integration of big data analytics and machine learning to enhance predictive accuracy across large populations. Ideographic approaches are increasingly embracing digital ethnography and personalized AI-driven methodologies to capture nuanced individual differences in real-time contexts. Hybrid models combining nomothetic scalability with ideographic depth are emerging as a key direction to balance generalizability and individual variability in psychological and social science research.
Nomothetic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com