Individualism emphasizes personal freedom, self-expression, and independence as core values shaping identity and decision-making. It promotes the idea that each person should prioritize their own goals and values while respecting the rights of others to do the same. Discover how embracing individualism can empower your life by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
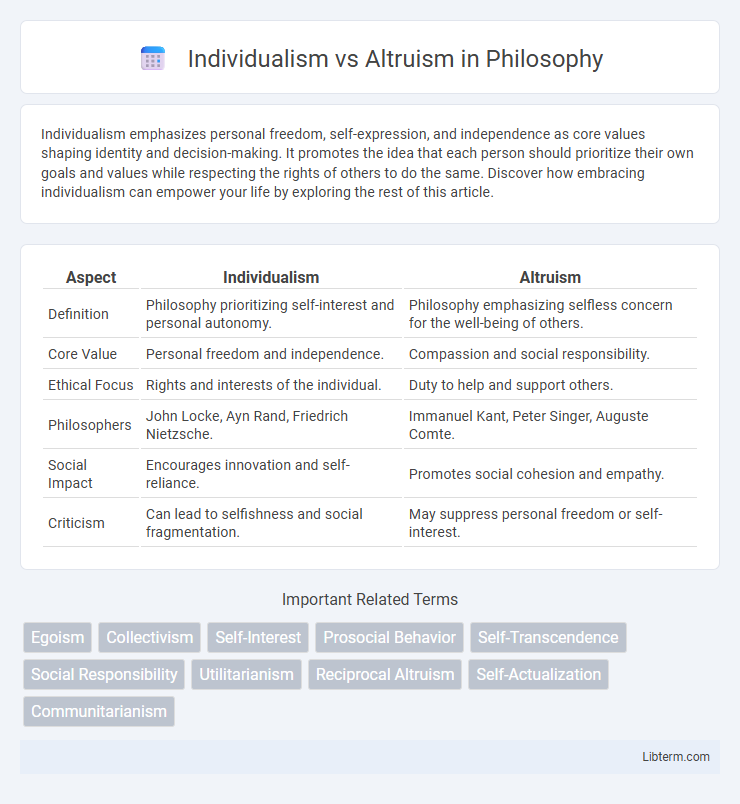
| Aspect | Individualism | Altruism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophy prioritizing self-interest and personal autonomy. | Philosophy emphasizing selfless concern for the well-being of others. |
| Core Value | Personal freedom and independence. | Compassion and social responsibility. |
| Ethical Focus | Rights and interests of the individual. | Duty to help and support others. |
| Philosophers | John Locke, Ayn Rand, Friedrich Nietzsche. | Immanuel Kant, Peter Singer, Auguste Comte. |
| Social Impact | Encourages innovation and self-reliance. | Promotes social cohesion and empathy. |
| Criticism | Can lead to selfishness and social fragmentation. | May suppress personal freedom or self-interest. |
Understanding Individualism: Core Principles and Values
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the pursuit of individual goals as central to human fulfillment. Core principles include the primacy of individual rights, freedom of expression, and the belief that individuals are best positioned to determine their own interests. This philosophy values independence over collective responsibility, promoting personal accountability and innovation.
The Essence of Altruism: Definition and Key Characteristics
Altruism is defined as the selfless concern for the well-being of others, prioritizing their needs over personal gain. Key characteristics include empathy, voluntary sacrifice, and actions motivated by genuine care without expecting rewards. This ethical principle contrasts with individualism by emphasizing collective welfare and social interconnectedness.
Historical Perspectives on Individualism and Altruism
Historical perspectives on individualism emphasize the rise of personal autonomy during the Enlightenment, championed by philosophers such as John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who argued for individual rights and self-determination. Altruism, rooted in religious and philosophical traditions like Christianity and Confucianism, highlights the moral duty to prioritize others' welfare over personal gain. The dialectic between individualism and altruism has shaped social, political, and ethical thought, influencing modern debates on community responsibility and personal freedom.
Cultural Influences Shaping Individualism vs Altruism
Cultural influences significantly shape the balance between individualism and altruism by promoting values that prioritize personal autonomy or communal well-being. Societies with collectivist traditions, such as many East Asian cultures, emphasize altruism and social harmony, encouraging individuals to consider group needs above their own. In contrast, Western cultures often highlight individualism, fostering self-expression and personal achievement as key cultural values.
Psychological Factors Impacting Personal and Collective Choices
Psychological factors influencing individualism versus altruism include cognitive biases, empathy levels, and social identity, which shape how people prioritize personal goals over collective well-being or vice versa. Neurobiological mechanisms such as mirror neurons and oxytocin release modulate altruistic behavior by enhancing emotional connection and cooperation within groups. Cultural conditioning and moral development stages further affect decision-making processes, determining the balance between self-interest and prosocial actions in varying social contexts.
Individualism in Modern Society: Benefits and Challenges
Individualism in modern society promotes personal freedom, self-expression, and innovation, driving economic growth and technological advancements. However, it can also lead to social isolation, weakening community bonds, and increased mental health issues due to heightened competition and pressure for individual success. Balancing individual rights with collective responsibility remains a key challenge for sustainable social development.
Altruism in Practice: Examples and Real-World Impact
Altruism in practice manifests through acts such as volunteering at community shelters, donating to charitable organizations, and participating in disaster relief efforts that directly improve others' well-being. Studies show that altruistic behavior enhances social cohesion, reduces inequality, and fosters trust within diverse communities, leading to stronger societal resilience. Real-world initiatives like humanitarian aid programs demonstrate how altruism tangibly addresses global challenges including poverty, hunger, and health crises.
Balancing Self-Interest and Collective Good
Balancing self-interest and collective good involves integrating individualism's focus on personal goals with altruism's emphasis on community well-being. Effective cooperation emerges when individuals pursue their aspirations while contributing to social welfare, fostering sustainable development. Psychological studies indicate that moderate altruism enhances personal happiness and societal cohesion, promoting ethical decision-making and shared responsibilities.
Individualism vs Altruism in the Workplace and Community
Individualism in the workplace promotes personal achievement, autonomy, and innovation, fostering environments where employees prioritize their own goals and success. Altruism in the community encourages cooperation, empathy, and support, leading to stronger social bonds and collective well-being. Balancing individualism and altruism ensures both personal growth and community resilience in professional and social settings.
Finding Harmony: Integrating Individualism and Altruism for Future Societies
Balancing individualism and altruism fosters societies where personal freedoms coexist with community well-being, promoting sustainable development and social cohesion. Emphasizing empathy alongside autonomy enables innovative solutions that address collective challenges while respecting diverse identities. Future societies thrive by integrating self-interest with social responsibility, creating frameworks where cooperation enhances both individual fulfillment and communal progress.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com