Stoicism teaches the importance of focusing on what you can control while accepting what you cannot, fostering resilience and inner peace. By practicing mindfulness, self-discipline, and rational thinking, you can better navigate life's challenges and maintain emotional balance. Explore the rest of this article to discover how Stoic principles can transform your mindset and daily habits.
Table of Comparison
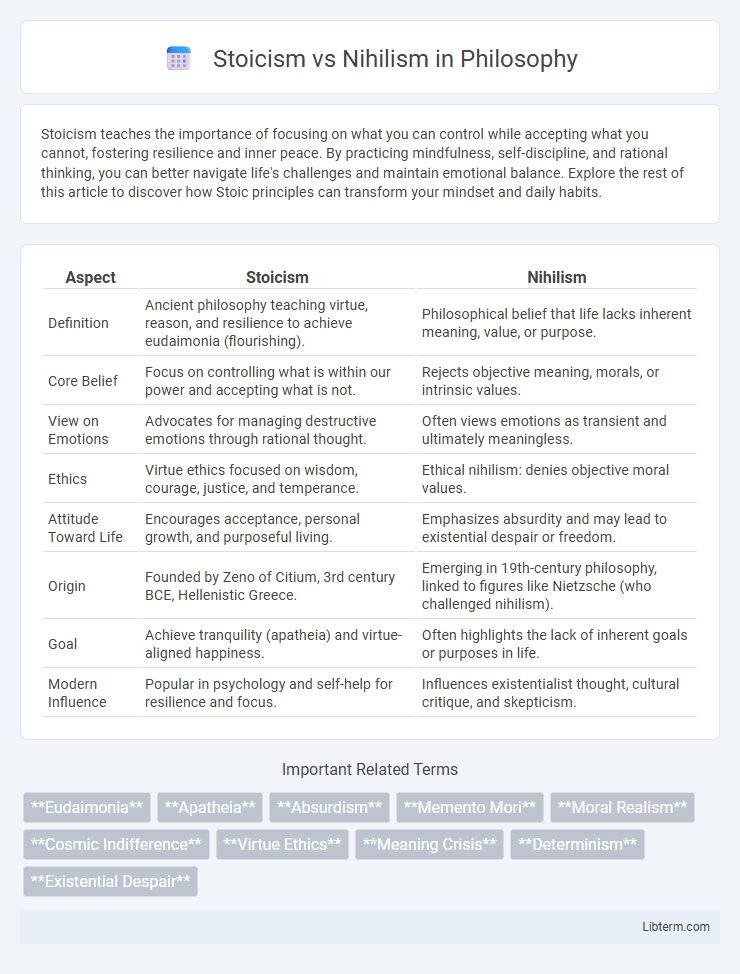
| Aspect | Stoicism | Nihilism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ancient philosophy teaching virtue, reason, and resilience to achieve eudaimonia (flourishing). | Philosophical belief that life lacks inherent meaning, value, or purpose. |
| Core Belief | Focus on controlling what is within our power and accepting what is not. | Rejects objective meaning, morals, or intrinsic values. |
| View on Emotions | Advocates for managing destructive emotions through rational thought. | Often views emotions as transient and ultimately meaningless. |
| Ethics | Virtue ethics focused on wisdom, courage, justice, and temperance. | Ethical nihilism: denies objective moral values. |
| Attitude Toward Life | Encourages acceptance, personal growth, and purposeful living. | Emphasizes absurdity and may lead to existential despair or freedom. |
| Origin | Founded by Zeno of Citium, 3rd century BCE, Hellenistic Greece. | Emerging in 19th-century philosophy, linked to figures like Nietzsche (who challenged nihilism). |
| Goal | Achieve tranquility (apatheia) and virtue-aligned happiness. | Often highlights the lack of inherent goals or purposes in life. |
| Modern Influence | Popular in psychology and self-help for resilience and focus. | Influences existentialist thought, cultural critique, and skepticism. |
Understanding Stoicism: Core Principles
Stoicism centers on the core principles of virtue, wisdom, and rational control over emotions, advocating acceptance of fate and focusing on what is within one's control. It emphasizes living in harmony with nature and reason, promoting resilience through the practice of self-discipline and inner tranquility. Unlike nihilism, which denies inherent meaning or value in life, Stoicism provides a framework for purposeful living through ethical behavior and mental fortitude.
Exploring Nihilism: Fundamental Beliefs
Nihilism fundamentally asserts that life lacks inherent meaning, purpose, or intrinsic value, challenging traditional moral and existential frameworks. It often emphasizes the absence of objective truths, leading to a rejection of established societal norms and ethical codes. This philosophical stance contrasts with Stoicism by denying the possibility of deriving stable meaning or virtue from external circumstances or universal reason.
Origins and Historical Development
Stoicism originated in the early 3rd century BCE in Athens, founded by Zeno of Citium, emphasizing virtue, reason, and living in accordance with nature to achieve tranquility. Nihilism, with roots tracing back to 19th-century Russian intellectuals like Ivan Turgenev and philosophers such as Friedrich Nietzsche, centers on the rejection of inherent meaning, values, and beliefs. Historically, Stoicism evolved through Roman thinkers like Seneca and Marcus Aurelius, while Nihilism emerged as a philosophical response to existential despair and the collapse of traditional moral frameworks during the modern era.
View of Meaning and Purpose
Stoicism asserts that meaning and purpose are found through virtue, rationality, and living in harmony with nature's order, emphasizing personal growth and resilience despite external circumstances. Nihilism rejects inherent meaning or purpose in life, viewing existence as fundamentally meaningless and any search for objective value as futile. While Stoicism encourages acceptance and purposeful action within a meaningful framework, Nihilism embraces the absence of intrinsic meaning, often leading to existential skepticism or freedom from imposed values.
Approach to Suffering and Adversity
Stoicism teaches the acceptance of suffering as a natural part of life and emphasizes resilience through rational control over emotions and focusing on what is within one's power. Nihilism views suffering as inherently meaningless, often leading to existential despair or detachment due to the belief that life lacks intrinsic purpose. While Stoicism promotes active engagement and personal growth amid adversity, Nihilism tends to underscore the futility and absence of inherent value in such experiences.
Ethics and Moral Frameworks
Stoicism promotes a virtue-based ethical framework centered on living in harmony with nature and reason, emphasizing self-control, wisdom, and resilience as pathways to eudaimonia, or flourishing. Nihilism challenges the existence of inherent meaning or objective moral values, often leading to moral relativism or skepticism about ethical norms. While Stoicism offers practical guidance for ethical behavior and personal growth, Nihilism questions the foundation of ethics, inviting individuals to construct their own moral frameworks or embrace existential freedom.
Role of Emotion and Rationality
Stoicism emphasizes the mastery of emotions through rational thought, advocating for emotional resilience and acceptance of events beyond one's control to achieve tranquility. Nihilism often rejects inherent meaning and may lead to emotional detachment or existential despair, challenging traditional rational frameworks for finding purpose. The contrast lies in Stoicism's use of rationality to regulate emotions constructively, whereas Nihilism questions the foundation of meaning that grounds emotional responses.
Influence on Modern Thought
Stoicism profoundly influences modern cognitive-behavioral therapy by promoting resilience and emotional regulation through acceptance of what cannot be controlled. Nihilism challenges contemporary existentialist and postmodern perspectives by questioning inherent meaning and values in life, prompting deeper philosophical inquiry. Both philosophies shape modern thought by addressing human purpose and ethical frameworks amidst uncertainty.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Stoicism promotes resilience and emotional control by encouraging individuals to focus on what they can control and accept what they cannot, leading to reduced stress and enhanced decision-making in daily life. Nihilism, while often associated with the rejection of inherent meaning, can encourage personal freedom by liberating individuals from societal norms and expectations, promoting authentic self-expression. Practically, Stoicism offers structured techniques such as negative visualization and mindfulness, whereas Nihilism challenges one to create personal meaning, influencing motivation and goal-setting differently.
Choosing Between Stoicism and Nihilism
Choosing between Stoicism and Nihilism involves evaluating their core principles: Stoicism promotes resilience, virtue, and acceptance of fate, emphasizing purposeful living despite external challenges. Nihilism asserts the absence of inherent meaning or value in life, often leading to a rejection of moral frameworks and existential purpose. Opting for Stoicism provides a structured approach to cope with adversity and find meaning, whereas Nihilism confronts the void of meaning, which can either liberate or paralyze individual outlooks.
Stoicism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com