Imagination fuels creativity and innovation by allowing your mind to explore ideas beyond reality. It plays a crucial role in problem-solving and artistic expression, making it essential for personal and professional growth. Discover how cultivating your imagination can transform your approach to challenges in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
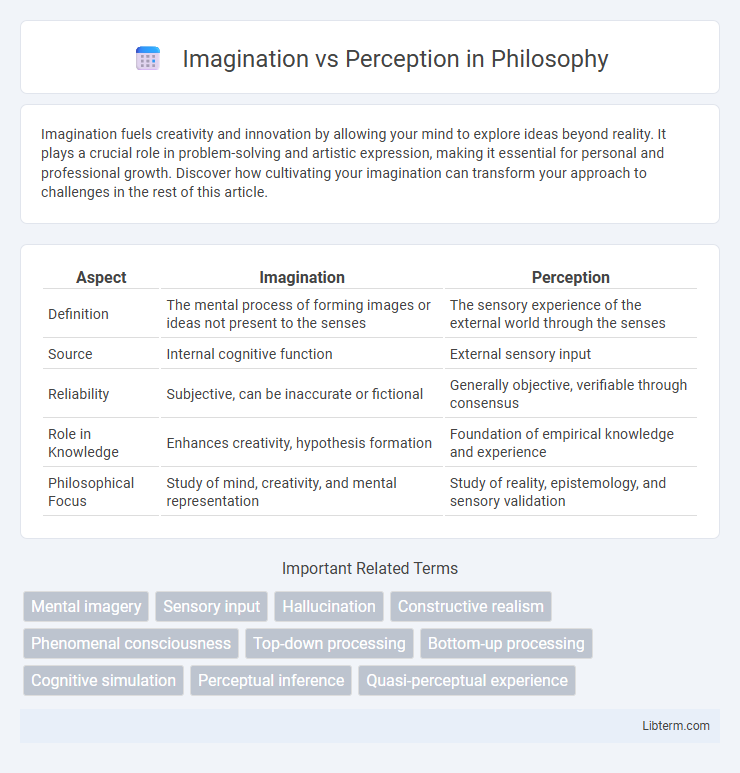
| Aspect | Imagination | Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The mental process of forming images or ideas not present to the senses | The sensory experience of the external world through the senses |
| Source | Internal cognitive function | External sensory input |
| Reliability | Subjective, can be inaccurate or fictional | Generally objective, verifiable through consensus |
| Role in Knowledge | Enhances creativity, hypothesis formation | Foundation of empirical knowledge and experience |
| Philosophical Focus | Study of mind, creativity, and mental representation | Study of reality, epistemology, and sensory validation |
Defining Imagination and Perception
Imagination involves the mental ability to create images, ideas, or sensations not directly derived from current sensory input, enabling visualization beyond present reality. Perception is the cognitive process of interpreting and organizing sensory information received from the environment to form a coherent understanding of surrounding stimuli. Distinguishing imagination from perception hinges on imagination's internal construction of scenarios versus perception's reliance on external sensory data.
The Neurological Basis: How Our Brain Distinguishes
Neuroscientific research reveals that imagination and perception engage overlapping yet distinct brain regions, with the primary visual cortex activating during perception and the prefrontal cortex playing a key role in imagination. Functional MRI studies demonstrate that while sensory input triggers bottom-up processing in the occipital lobe, imaginative processes rely on top-down modulation from higher-order cortical areas. This neural differentiation allows the brain to distinguish between actual sensory experiences and internally generated images, underpinning cognitive functions like memory, creativity, and decision-making.
The Role of Imagination in Creative Thinking
Imagination plays a critical role in creative thinking by enabling the mind to generate novel ideas and envision possibilities beyond immediate perception. It allows individuals to combine existing knowledge in unique ways, facilitating innovation and problem-solving. This cognitive process enhances creativity by transcending the limitations of sensory input and fostering abstract thought.
Perception: Interpreting Reality
Perception is the cognitive process through which sensory information is organized and interpreted to form an accurate understanding of reality. It involves the brain's integration of visual, auditory, tactile, and other sensory inputs to create a coherent experience of the environment. This interpretative mechanism enables humans to navigate and respond effectively to the dynamic stimuli surrounding them.
Interplay Between Imagination and Perception
The interplay between imagination and perception shapes how individuals interpret sensory information and construct mental images beyond immediate reality. Imagination enhances perception by filling gaps in sensory data, enabling creative problem-solving and anticipatory thinking, while perception grounds imagination in real-world stimuli. Neural mechanisms in the brain, such as the activation of the same cortical areas during both imagining and perceiving, highlight the close relationship between these cognitive processes.
Common Misconceptions About Both Concepts
Imagination is often mistaken for mere fantasy, but it actively constructs new ideas beyond sensory input, while perception is frequently misunderstood as passive reception, yet it involves complex interpretation of sensory data. Many believe imagination and perception operate independently, ignoring their dynamic interaction where perception informs imagination and imagination influences perception. The misconception that perception provides an objective reality overlooks its subjective nature shaped by prior knowledge and mental states.
Imagination vs Perception in Decision-Making
Imagination allows decision-makers to envision multiple possible outcomes and scenarios beyond immediate reality, enhancing creative problem-solving and long-term planning. Perception provides real-time sensory data and factual information that grounds decisions in the present context and actual conditions. Balancing imagination with accurate perception is crucial for effective decision-making, as it integrates innovative ideas with practical constraints.
Psychological Theories Explored
Psychological theories such as Gestalt Psychology emphasize the differences between imagination and perception by highlighting how the brain organizes sensory input to form coherent patterns during perception, whereas imagination involves internally generated images without direct sensory stimuli. Cognitive neuroscience explores neural correlates, showing that imagination activates similar brain regions as perception, particularly the visual cortex, but with less sensory fidelity and more reliance on memory networks. Psychoanalytic theory, pioneered by Freud, interprets imagination as a manifestation of unconscious desires and drives, contrasting with perception's grounding in external reality and sensory experience.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Imagination fuels creativity and problem-solving by enabling individuals to visualize new possibilities beyond immediate sensory input, enhancing innovation in fields like design and education. Perception allows accurate interpretation of real-world stimuli, guiding everyday decisions such as navigating traffic or recognizing social cues. Together, these cognitive processes optimize practical tasks by balancing envisioned scenarios with present realities, improving both planning and adaptive responses.
Enhancing Awareness: Balancing Imagination and Perception
Balancing imagination and perception enhances awareness by allowing individuals to creatively interpret sensory information while grounding their understanding in reality. Imagination broadens cognitive flexibility, enabling the exploration of possibilities beyond immediate experiences, whereas perception anchors awareness to the present environment through direct sensory input. Integrating both processes fosters a comprehensive awareness that supports accurate decision-making and innovative problem-solving.
Imagination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com