Rule interpretation determines the intended meaning and application of rules within legal, organizational, or procedural contexts. It involves analyzing language, purpose, and precedent to ensure consistent and fair enforcement. Explore the article to understand how rule interpretation impacts your decision-making and compliance efforts.
Table of Comparison
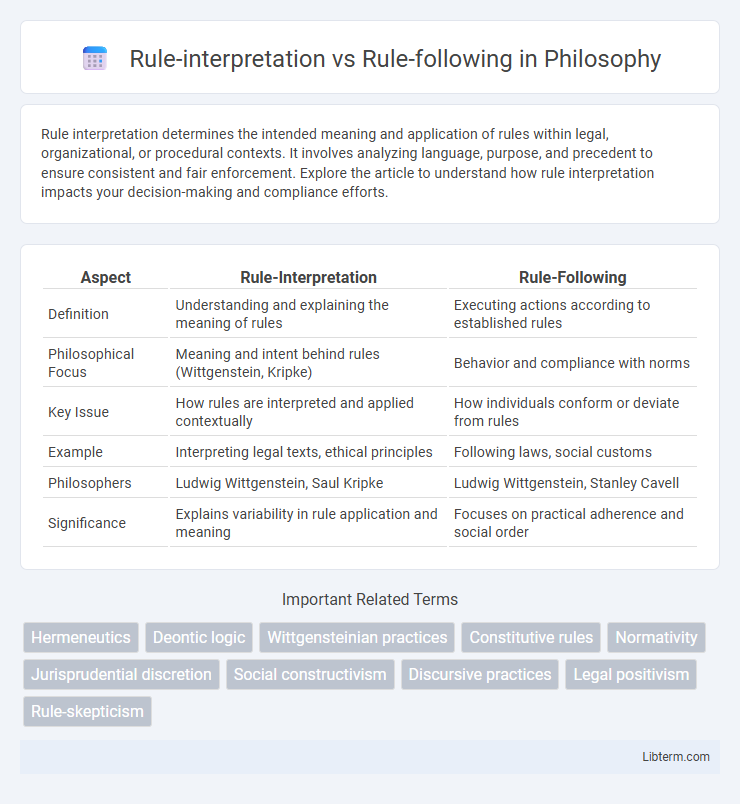
| Aspect | Rule-Interpretation | Rule-Following |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and explaining the meaning of rules | Executing actions according to established rules |
| Philosophical Focus | Meaning and intent behind rules (Wittgenstein, Kripke) | Behavior and compliance with norms |
| Key Issue | How rules are interpreted and applied contextually | How individuals conform or deviate from rules |
| Example | Interpreting legal texts, ethical principles | Following laws, social customs |
| Philosophers | Ludwig Wittgenstein, Saul Kripke | Ludwig Wittgenstein, Stanley Cavell |
| Significance | Explains variability in rule application and meaning | Focuses on practical adherence and social order |
Understanding Rule-Interpretation
Understanding rule interpretation involves grasping how individuals or systems assign meaning to rules beyond their explicit wording. This process requires analyzing context, intentions, and potential implications to apply rules effectively in varied scenarios. Rule interpretation is essential in legal frameworks, artificial intelligence, and linguistic analysis to ensure flexibility and accuracy in rule application.
Defining Rule-Following
Rule-following involves consistently adhering to established guidelines or instructions within a specific context, ensuring predictable and uniform behavior. It emphasizes the application of explicit rules without deviation, prioritizing compliance and external validation over subjective interpretation. This concept is fundamental in fields such as law, programming, and linguistics, where precise execution of rules guarantees functionality and coherence.
Key Differences Between Rule-Interpretation and Rule-Following
Rule-interpretation involves analyzing the underlying meaning, purpose, and context of a rule to determine its application in varying situations, whereas rule-following emphasizes strict adherence to the explicit wording and established procedures of the rule. Key differences include flexibility versus rigidity, with rule-interpretation allowing for adaptive judgment and rule-following enforcing consistent compliance. The philosophical debate often centers on whether understanding a rule's intent (hermeneutics) outweighs mechanical obedience to its letter, impacting areas like law, ethics, and linguistic pragmatics.
The Philosophy Behind Rule-Interpretation
The philosophy behind rule-interpretation emphasizes the dynamic relationship between written guidelines and their practical application, highlighting how context shapes meaning beyond fixed instructions. Philosophers like Ludwig Wittgenstein argue that understanding rules requires recognizing their use within language games, where interpretation is essential to navigating ambiguous or evolving norms. This view contrasts with strict rule-following, suggesting that meaning and adherence depend on flexible, context-sensitive judgment rather than rote compliance.
The Practicality of Rule-Following
Rule-following emphasizes consistent adherence to established norms, ensuring predictability and stability in decision-making processes. Its practicality lies in simplifying complex scenarios by providing clear guidelines, reducing ambiguity and enhancing efficiency in organizational and social contexts. While rule-interpretation allows flexibility, rule-following maintains order and coherence, crucial for effective governance and systematic operations.
Real-World Examples of Rule-Interpretation
Real-world examples of rule-interpretation abound in legal settings where judges apply constitutional principles to modern cases, such as the Supreme Court's rulings on digital privacy rights in the age of smartphones. In the workplace, managers often interpret company policies to address unforeseen situations, exemplified by flexible remote work arrangements during the COVID-19 pandemic despite pre-existing rigid attendance rules. These instances illustrate the dynamic nature of rule-interpretation, demonstrating how contextual understanding and evolving social norms influence the practical application of fixed regulations.
Real-World Applications of Rule-Following
Rule-following is essential in real-world applications such as legal systems, programming, and organizational management, where precise adherence to established guidelines ensures consistency and fairness. Automated systems and artificial intelligence rely heavily on rule-following algorithms to execute tasks accurately, from financial transactions to autonomous vehicle navigation. Understanding rule-following mechanisms enhances the development of reliable protocols that maintain order and efficiency within complex societal frameworks.
Challenges in Rule-Interpretation
Challenges in rule-interpretation arise from ambiguous language, contextual variability, and the need for subjective judgment that complicates consistent application. Unlike rule-following, which relies on clear, predefined instructions, rule-interpretation demands understanding intent, reconciling conflicting norms, and adapting to novel situations. This complexity often leads to disputes, inconsistent enforcement, and difficulties in maintaining fairness across different scenarios.
Benefits and Limitations of Rule-Following
Rule-following provides clear structure and consistency, ensuring predictable outcomes in legal and organizational contexts, which enhances fairness and accountability. However, strict adherence may limit flexibility, hindering the ability to adapt to unique or evolving situations, thereby potentially causing rigid or unjust results. Balancing rule-following with interpretative judgment is essential to navigate complex scenarios effectively.
Choosing Between Rule-Interpretation and Rule-Following
Choosing between rule-interpretation and rule-following hinges on the context in which rules apply and the desired flexibility in decision-making. Rule-following emphasizes strict adherence to established guidelines, ensuring consistency and predictability, while rule-interpretation allows adaptation to nuanced circumstances by discerning the underlying purpose of rules. Effective decision-making balances these approaches by evaluating the potential consequences of rigid compliance versus contextual adjustment, particularly in legal, organizational, or ethical frameworks.
Rule-interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com