Dualism explores the concept that reality consists of two fundamental substances: mind and matter, highlighting the distinction between mental and physical phenomena. This perspective influences various fields, including philosophy, psychology, and neuroscience, by addressing the nature of consciousness and its interaction with the body. Discover how dualism shapes our understanding of existence and its ongoing relevance in modern debates by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
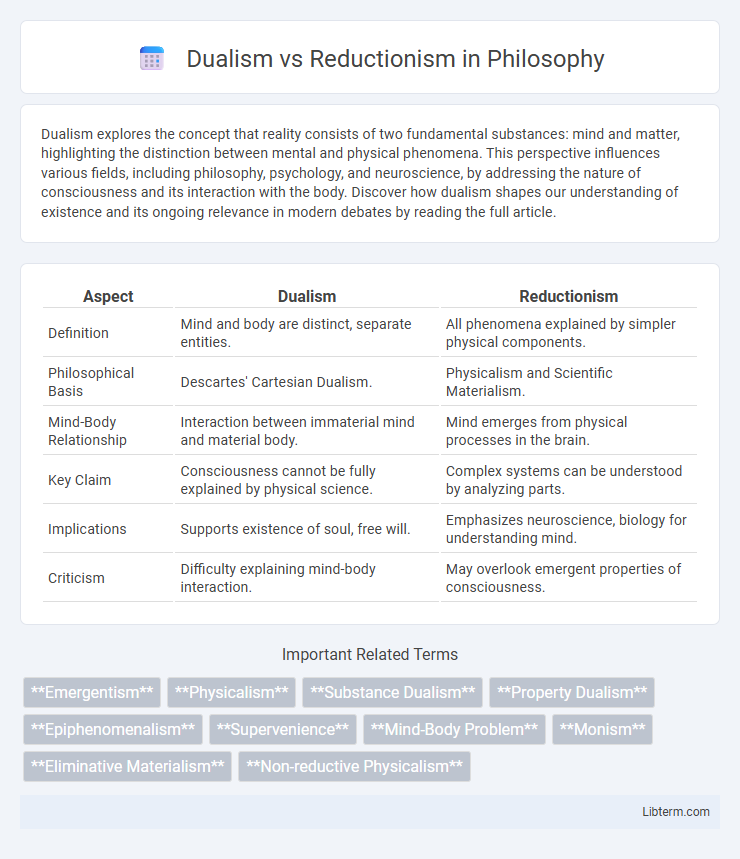
| Aspect | Dualism | Reductionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mind and body are distinct, separate entities. | All phenomena explained by simpler physical components. |
| Philosophical Basis | Descartes' Cartesian Dualism. | Physicalism and Scientific Materialism. |
| Mind-Body Relationship | Interaction between immaterial mind and material body. | Mind emerges from physical processes in the brain. |
| Key Claim | Consciousness cannot be fully explained by physical science. | Complex systems can be understood by analyzing parts. |
| Implications | Supports existence of soul, free will. | Emphasizes neuroscience, biology for understanding mind. |
| Criticism | Difficulty explaining mind-body interaction. | May overlook emergent properties of consciousness. |
Understanding Dualism: Core Concepts
Dualism posits that mind and body are fundamentally distinct entities, where mental states cannot be fully explained by physical processes alone. This philosophical view emphasizes the separation between consciousness and material substance, suggesting that subjective experiences possess unique properties beyond neural activity. Key concepts include the interaction problem, which explores how immaterial mind influences the physical brain, and the notion of qualia, referring to individual instances of subjective awareness.
Reductionism Explained: An Overview
Reductionism explained centers on the idea that complex systems and phenomena can be understood by dissecting them into their simplest components. This approach is prominent in scientific disciplines such as biology, chemistry, and physics, where it emphasizes analyzing molecular, cellular, or atomic levels to explain higher-order functions. Reductionism facilitates precise experimental methods and theoretical models by linking basic parts to emergent properties, offering clarity in understanding complex biological and physical processes.
Historical Roots of Dualism and Reductionism
Dualism finds its historical roots in the philosophy of Rene Descartes, who posited a fundamental distinction between mind and body as separate substances. Reductionism emerged from the scientific revolution, influenced by thinkers like Isaac Newton, emphasizing the explanation of complex phenomena by breaking them down into simpler, physical components. These contrasting origins highlight dualism's focus on metaphysical separation versus reductionism's grounding in empirical, mechanistic analysis.
Key Philosophers and Thinkers
Rene Descartes is a central figure in dualism, asserting the separation of mind and body as distinct substances, influencing Cartesian Dualism. In contrast, reductionism is championed by thinkers like Thomas Hobbes and later by behaviorists such as B.F. Skinner, who argue that mental states and consciousness can be explained entirely by physical processes and neurological interactions. Contemporary philosophers like Daniel Dennett further advance reductionism by advocating for a scientific understanding of the mind through neuroscience and cognitive science.
Dualism in Mind-Body Problem
Dualism in the mind-body problem posits that the mind and body are distinct entities, with the mind characterized by non-physical qualities such as consciousness and subjective experience. Rene Descartes is a key figure advocating substance dualism, arguing that mental states cannot be fully explained by physical processes alone. This perspective challenges reductionism, which attempts to explain mental phenomena entirely through neurobiological mechanisms, emphasizing the irreducibility of mental properties to physical states.
Reductionist Approach in Science
The reductionist approach in science seeks to understand complex phenomena by breaking them down into their simplest components, emphasizing the analysis of fundamental particles, molecules, and biological processes. This method enables precise, empirical investigation and has driven significant advancements in fields such as molecular biology, neuroscience, and physics. By isolating variables and studying systems at microscopic levels, reductionism offers quantifiable insights, though it sometimes overlooks emergent properties arising from complex interactions.
Comparative Analysis: Dualism vs Reductionism
Dualism posits that mind and body are distinct entities, emphasizing the separation of mental and physical states, while reductionism argues that complex phenomena, including consciousness, can be fully explained by their simplest components, often at a molecular or neurological level. Dualism supports the existence of non-physical substances or properties, as seen in Cartesian dualism, contrasting with reductionism's approach to modeling mental states solely through brain activity and neural mechanisms. The comparative analysis reveals that dualism challenges the explanatory limits of physical sciences, whereas reductionism advances a unified scientific framework by integrating psychological phenomena into biological and chemical substrates.
Implications for Consciousness Studies
Dualism posits that consciousness exists as a non-physical entity distinct from the brain, suggesting that subjective experience cannot be fully explained by neural processes alone. Reductionism argues that all aspects of consciousness can be understood by analyzing brain functions and neural interactions at a physical level. The implications for consciousness studies involve ongoing debates on whether subjective experiences require explanations beyond neurobiology or can be wholly accounted for within physicalist frameworks.
Criticisms and Limitations of Both Theories
Dualism faces criticism for its failure to provide a clear explanation of how mind and body interact, often leading to the problem of causal interaction. Reductionism is limited by its tendency to oversimplify complex mental processes by reducing them solely to biological or physical components, neglecting subjective experiences. Both theories struggle to fully account for the richness of consciousness, with dualism criticized for dualistic separation and reductionism for ignoring emergent properties.
Future Directions in Dualism and Reductionism Debates
Future directions in dualism and reductionism debates emphasize integrating neuroscientific advances with philosophical frameworks to better understand consciousness. Emerging technologies such as brain imaging and AI provide empirical data that challenge strict reductionist views while encouraging nuanced dualistic interpretations. Interdisciplinary research may foster new models reconciling mental phenomena with physical processes, potentially transforming theories of mind-body interaction.
Dualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com