Fregean sense refers to the way meaning is conveyed in language beyond the mere reference of words or phrases, focusing on the mode of presentation that shapes how a concept is understood. This distinction helps clarify semantic nuances and improves communication precision in philosophy and linguistics. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of Fregean sense and its impact on meaning.
Table of Comparison
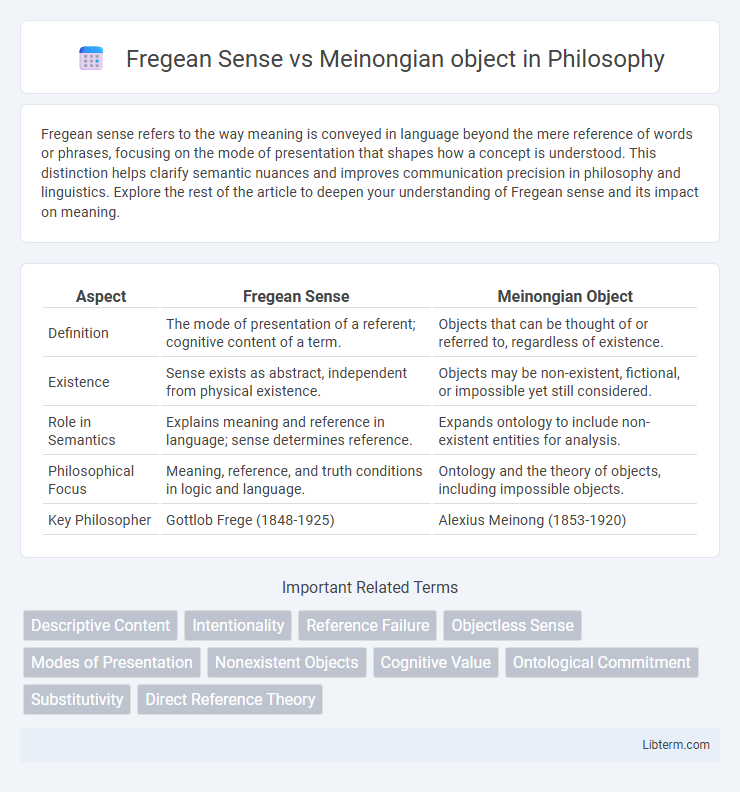
| Aspect | Fregean Sense | Meinongian Object |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The mode of presentation of a referent; cognitive content of a term. | Objects that can be thought of or referred to, regardless of existence. |
| Existence | Sense exists as abstract, independent from physical existence. | Objects may be non-existent, fictional, or impossible yet still considered. |
| Role in Semantics | Explains meaning and reference in language; sense determines reference. | Expands ontology to include non-existent entities for analysis. |
| Philosophical Focus | Meaning, reference, and truth conditions in logic and language. | Ontology and the theory of objects, including impossible objects. |
| Key Philosopher | Gottlob Frege (1848-1925) | Alexius Meinong (1853-1920) |
Introduction to Fregean Sense and Meinongian Object
Fregean Sense refers to the mode of presentation or the way in which a reference is given, emphasizing the cognitive aspect of meaning in linguistic expressions. Meinongian Object theory extends the ontology to include non-existent and impossible objects, arguing that these objects can still be meaningfully discussed and referenced despite lacking actual existence. Understanding the distinction highlights Frege's focus on linguistic sense and reference, while Meinong prioritizes the ontological status of entities beyond mere linguistic representation.
Historical Context: Frege vs. Meinong
Gottlob Frege's sense (Sinn) and reference (Bedeutung) emerged in the late 19th century as foundational concepts in analytic philosophy, emphasizing how linguistic expressions convey meaning beyond mere denotation. In contrast, Alexius Meinong developed his theory of objects (Gegenstande) around the same period, proposing a broader ontology that includes nonexistent and impossible objects, challenging classical notions of existence. The historical context of their rivalry reflects a shift from Frege's logicist approach in philosophy of language to Meinong's more ontologically permissive stance, influencing debates on meaning, reference, and objecthood in early 20th-century philosophy.
Defining Fregean Sense (Sinn)
Fregean Sense (Sinn) refers to the mode of presentation of an object, capturing the way in which the referent is given to the mind rather than the object itself. It distinguishes between the cognitive content of a term and its referent, allowing for meaningful identity statements despite co-referential expressions. Unlike Meinongian objects, which include non-existent entities, Fregean Sense operates strictly within the framework of actual referents by emphasizing the sense as a mental representation guiding reference.
The Nature of Meinongian Objects
Meinongian objects are entities that possess a form of being independent of existence, allowing for reference to non-existent and impossible objects within a robust ontological framework. These objects are characterized by their intrinsic properties, which are independent from existential status, contrasting with Fregean senses that prioritize the way a referent is presented in language and thought. The nature of Meinongian objects expands traditional ontology by accommodating objects with no existential correlate while maintaining meaningfulness in intentional contexts.
Reference and Meaning: Frege’s Perspective
Frege's theory distinguishes between sense (Sinn) and reference (Bedeutung), where sense involves the mode of presentation of an object, and reference is the actual object itself. In contrast to Meinongian objects, which can be non-existent yet still possess properties, Frege insists that meaningful expressions must have a definite reference in reality or be devoid of reference altogether. This framework ensures that meaning is tied to cognitive value and truth conditions, grounding semantic analysis in both the mode of presentation and the existence of the referent.
Existence and Nonexistent Objects: Meinong’s Theory
Meinong's Theory of objects distinguishes between existent and nonexistent objects by granting ontological status to nonexistent entities, allowing them to have properties despite lacking existence. Fregean Sense, in contrast, emphasizes the mode of presentation or cognitive value of an object, focusing on how reference is achieved without committing to the object's ontological status. This distinction highlights Meinong's acceptance of a broader ontology that includes nonexistent objects, challenging traditional existence-focused frameworks.
Comparative Analysis: Sense vs. Object
Fregean Sense refers to the mode of presentation of an object, emphasizing the cognitive aspect and how information is conveyed to the mind, whereas a Meinongian object includes non-existent or impossible entities that have no strict ontological status but remain subjects of reference. The Fregean approach prioritizes meaning and cognitive content over existence, contrasting Meinong's framework that categorizes objects by their being or non-being. This distinction highlights that Fregean sense is a semantic tool for understanding reference, while Meinongian objects expand the domain of discourse to include both existent and non-existent entities.
Philosophical Implications in Logic and Semantics
Fregean Sense emphasizes the cognitive content or mode of presentation of a referent, influencing the interpretation of meaning and truth conditions in logical systems. Meinongian objects, which include nonexistent and impossible entities, challenge classical logic by demanding an expanded ontology that accommodates objects without being. The philosophical implications center on how language and logic represent reference, with Frege's framework supporting precise semantic analysis and Meinong's approach provoking debates on the boundaries of existence and semantic reference.
Contemporary Debates and Applications
Contemporary debates on Fregean Sense versus Meinongian objects center on the ontological status of non-existent entities and the semantic role they play in language and cognition. Fregean Sense emphasizes the mode of presentation of an object, grounding meaning in cognitive content, while Meinongian theory allows for objects without being, expanding the scope of reference to include nonexistent or impossible entities. Applications in philosophy of language, logic, and artificial intelligence leverage these frameworks to address issues in intentionality, reference, and the treatment of fictional or hypothetical objects.
Conclusion: Synthesizing Fregean and Meinongian Views
Synthesizing Fregean and Meinongian views reveals a nuanced understanding of reference and meaning in philosophy of language and metaphysics. Frege's sense emphasizes the cognitive content or mode of presentation of an object, crucial for explaining informative identity statements and propositional attitudes. Meinongian object theory complements this by allowing objects that may not exist to still be meaningfully discussed, enriching the ontology to include non-existent entities and broadening the scope of semantic analysis.
Fregean Sense Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com