Descriptivism explores how language is actually used by speakers rather than prescribing strict rules, focusing on the evolving nature of communication and linguistic diversity. Understanding descriptivism can help you appreciate how meaning and usage change over time, reflecting cultural and social influences. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how descriptivism shapes language and impacts everyday communication.
Table of Comparison
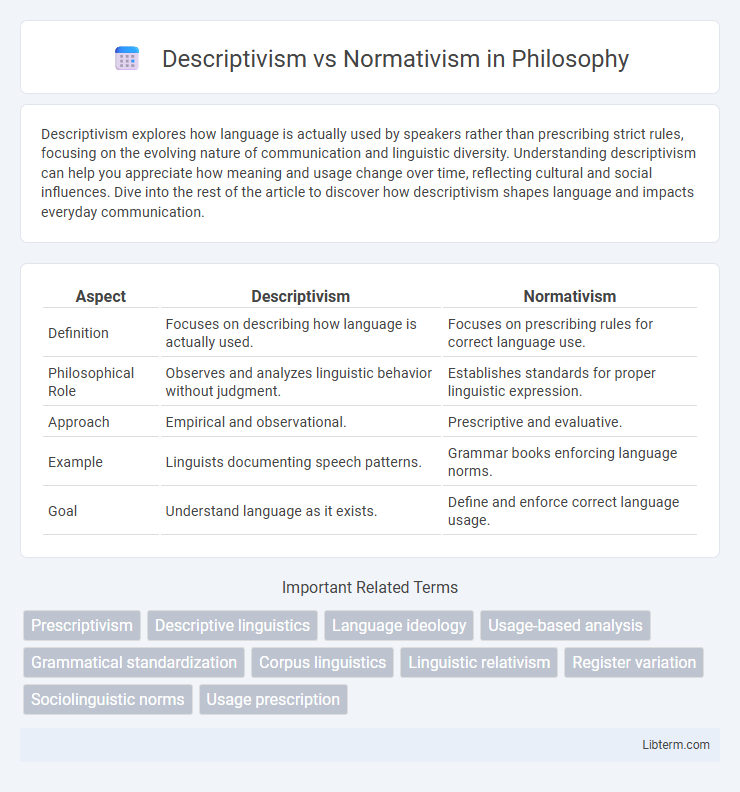
| Aspect | Descriptivism | Normativism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on describing how language is actually used. | Focuses on prescribing rules for correct language use. |
| Philosophical Role | Observes and analyzes linguistic behavior without judgment. | Establishes standards for proper linguistic expression. |
| Approach | Empirical and observational. | Prescriptive and evaluative. |
| Example | Linguists documenting speech patterns. | Grammar books enforcing language norms. |
| Goal | Understand language as it exists. | Define and enforce correct language usage. |
Understanding Descriptivism and Normativism
Descriptivism analyzes language based on how people actually speak and write, emphasizing observation and recording of natural usage without imposing rules. Normativism prescribes rules and standards for correct language use, aiming to maintain clarity, consistency, and tradition in communication. Understanding these approaches highlights the contrast between linguistic description focused on real-life usage and prescription centered on idealized correctness.
Historical Background of Both Approaches
Descriptivism, rooted in 19th-century linguistic studies by scholars like Wilhelm von Humboldt, emphasizes the analysis and documentation of language as it is naturally used without judgment. Normativism, dating back to classical authorities such as Dionysius Thrax and later codified in the 17th and 18th centuries by figures like Samuel Johnson, advocates for established rules and standards governing proper language use. Both approaches reflect evolving attitudes toward language: descriptivism arising from modern linguistics' empirical methods and normativism linked to prescriptive grammar traditions aimed at preserving linguistic purity.
Core Principles of Descriptivism
Descriptivism emphasizes the importance of observing and recording language use as it naturally occurs without imposing prescriptive rules or judgments. It focuses on actual linguistic behavior, variations, and changes within communities, highlighting that language evolves through social interaction. Core principles include acceptance of diverse dialects and recognition that language norms are descriptive patterns rather than fixed standards.
Key Tenets of Normativism
Normativism emphasizes prescribed language rules, advocating for strict adherence to established grammatical standards and proper usage to maintain linguistic clarity and coherence. It views language as a fixed system governed by authoritative norms, often resisting changes that deviate from traditional correctness. Normativism also prioritizes language purity, promoting standardized forms to ensure effective communication and preserve cultural heritage.
Applications in Linguistics and Philosophy
Descriptivism in linguistics focuses on observing and recording language as it is naturally used, emphasizing empirical data and linguistic variation across communities. Normativism prescribes rules and standards for "correct" language use, often influencing language education, grammar instruction, and philosophical debates about meaning and communication ethics. In philosophy, descriptivism addresses how language relates to reality by describing concepts, while normativism deals with the obligations and norms governing speech acts and meaning interpretation.
Major Differences Between Descriptivism and Normativism
Descriptivism emphasizes the observation and recording of language as it is naturally used, focusing on actual linguistic practices without judgment. In contrast, normativism prescribes rules and standards for proper language use, aiming to maintain grammatical correctness and linguistic purity. The major difference lies in descriptivism's objective approach to language variation versus normativism's emphasis on enforcing correctness and linguistic norms.
Advantages and Criticisms of Descriptivism
Descriptivism offers the advantage of reflecting actual language use, promoting inclusivity by acknowledging linguistic diversity and evolution without imposing rigid rules. Its approach enables linguists to document and analyze language naturally, supporting effective communication and understanding across different dialects and social groups. Criticisms of descriptivism include the argument that it may neglect language standards necessary for clarity in formal contexts and potentially allow the erosion of grammatical norms vital for maintaining linguistic precision.
Strengths and Limitations of Normativism
Normativism provides clear guidelines and standards for language use, promoting consistency and preserving linguistic traditions, which aids in effective communication and education. However, its limitations include resistance to language change and innovation, potentially stifling natural linguistic evolution and failing to accommodate diverse dialects and sociolects. This prescriptive approach may also marginalize non-standard language varieties, impacting inclusivity in language representation.
Real-life Examples and Case Studies
Descriptivism in language studies emphasizes observing how people naturally use language, as seen in real-life cases like the evolution of internet slang such as "LOL" and "BRB," which reflect actual communication patterns. Normativism enforces language rules, illustrated by prescriptive grammar guides like Strunk and White's *The Elements of Style*, which dictate correct usage and discourage deviations, often applied in formal writing or education. Case studies comparing courtroom language use showcase descriptivism by analyzing authentic speech patterns, while normativist approaches stress standardized language to ensure clarity and authority in legal documents.
Future Perspectives and Ongoing Debates
Future perspectives in the Descriptivism vs Normativism debate emphasize the integration of linguistic diversity with evolving social norms, reflecting shifts in digital communication and artificial intelligence language models. Ongoing debates focus on how prescriptive rules adapt without suppressing natural language change, highlighting the tension between language preservation and innovation. Emerging research explores hybrid approaches that balance descriptive accuracy with normative guidance to address multilingualism and inclusivity in global communication.
Descriptivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com