Propositional analysis breaks down complex statements into simpler components to clarify meaning and logical structure. It helps identify relationships and validate arguments by examining individual propositions within a statement. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of propositional analysis techniques.
Table of Comparison
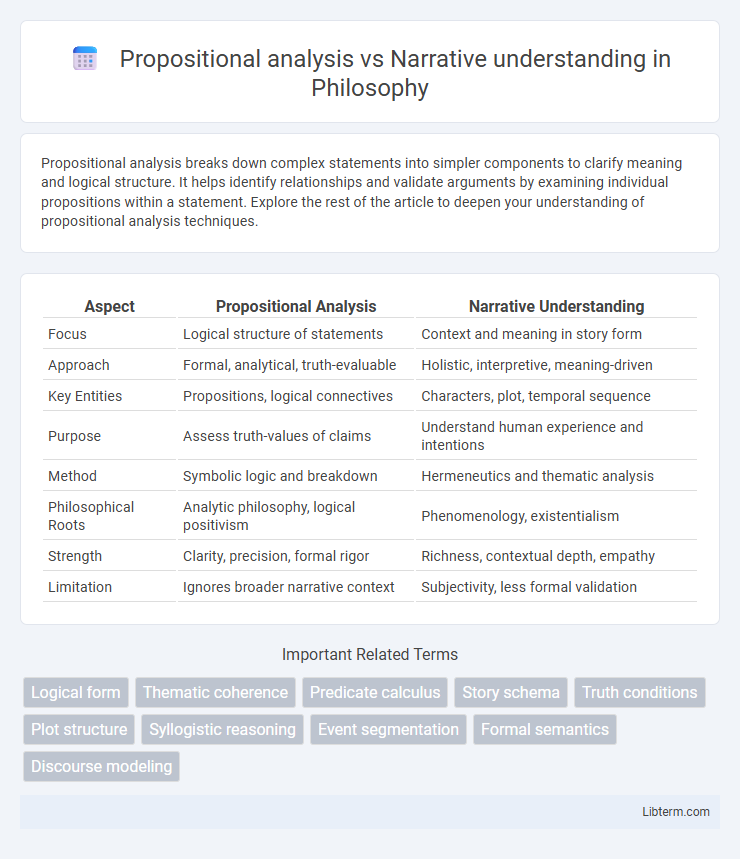
| Aspect | Propositional Analysis | Narrative Understanding |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Logical structure of statements | Context and meaning in story form |
| Approach | Formal, analytical, truth-evaluable | Holistic, interpretive, meaning-driven |
| Key Entities | Propositions, logical connectives | Characters, plot, temporal sequence |
| Purpose | Assess truth-values of claims | Understand human experience and intentions |
| Method | Symbolic logic and breakdown | Hermeneutics and thematic analysis |
| Philosophical Roots | Analytic philosophy, logical positivism | Phenomenology, existentialism |
| Strength | Clarity, precision, formal rigor | Richness, contextual depth, empathy |
| Limitation | Ignores broader narrative context | Subjectivity, less formal validation |
Introduction to Propositional Analysis and Narrative Understanding
Propositional analysis examines individual statements or propositions within a text to evaluate their truth value and logical relationships, emphasizing clarity and precision in argument structure. Narrative understanding focuses on interpreting the overarching story, context, and thematic elements, capturing the sequence and causality within events. Both approaches contribute to comprehensive text comprehension by addressing different levels of meaning extraction and cognitive processing.
Defining Propositional Analysis
Propositional analysis focuses on breaking down text into discrete propositions representing individual ideas or statements, enabling a detailed examination of semantic content and logical relations. It captures the core meaning units expressed as subject-predicate-object triples or similar structures, facilitating precise interpretation and information extraction. This method contrasts with narrative understanding, which emphasizes the overall story structure, plot coherence, and thematic connections beyond isolated propositions.
Exploring Narrative Understanding
Narrative understanding delves into interpreting the sequence of events, characters' motivations, and thematic elements to construct a coherent and meaningful story framework. It emphasizes grasping the causal relationships and emotional nuances that shape the story's progression beyond isolated factual propositions. This approach enables deeper comprehension of plot dynamics and the implicit messages conveyed through storytelling.
Key Differences Between Propositional and Narrative Approaches
Propositional analysis focuses on breaking down text into discrete units of meaning, emphasizing logical structure and factual accuracy, while narrative understanding prioritizes the overall storyline, context, and characters' intentions. The key difference lies in propositional analysis's emphasis on explicit informational content versus narrative understanding's emphasis on implicit meaning and thematic coherence. Propositional approaches utilize formal logic to analyze statements, whereas narrative approaches rely on interpretation and the integration of events into a meaningful sequence.
Cognitive Processes in Propositional Analysis
Propositional analysis involves breaking down sentences into basic semantic units called propositions, enabling precise identification of relationships among concepts such as agents, actions, and objects. This cognitive process relies heavily on working memory and syntactic parsing to extract meaningful components from fragmented linguistic input. Unlike narrative understanding, which integrates broader context and thematic coherence, propositional analysis focuses on detailed semantic encoding and logical structure for accurate comprehension.
Cognitive Processes in Narrative Understanding
Cognitive processes in narrative understanding involve constructing mental models that integrate propositional information with contextual and temporal coherence, enabling inferences beyond explicit statements. Propositional analysis breaks down narratives into discrete, logically structured units of meaning, yet narrative understanding requires higher-level processes such as schema activation, causal reasoning, and perspective-taking to grasp the story's deeper implications. These cognitive mechanisms work synergistically to transform raw propositions into meaningful, coherent narrative comprehension.
Applications of Propositional Analysis
Propositional analysis excels in applications such as information extraction, knowledge representation, and automated reasoning by breaking down complex statements into fundamental logical units called propositions. This method enhances natural language processing tasks like sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation by enabling precise interpretation of the relationships between concepts and actions. Propositional analysis improves decision support systems and semantic search engines through its ability to systematically map and evaluate the truth conditions of statements within textual data.
Applications of Narrative Understanding
Narrative understanding plays a crucial role in fields such as artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and education by enabling systems to interpret, summarize, and generate coherent stories from complex data. Applications include improving chatbots' conversational abilities, enhancing content recommendation algorithms through context awareness, and supporting automated essay scoring by assessing plot structure and character development. Unlike propositional analysis, which focuses on logical relationships between individual statements, narrative understanding captures temporal, causal, and thematic elements essential for deeper comprehension and human-like interaction.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Approach
Propositional analysis excels at breaking down complex information into discrete, logical units, enhancing clarity and facilitating precise reasoning, but it can struggle with capturing the holistic and emotional aspects of narratives. Narrative understanding effectively interprets stories by recognizing context, character development, and thematic elements, providing richer meaning and engagement, yet it may lack the rigorous structure needed for detailed logical analysis. Each approach serves distinct purposes: propositional analysis suits formal, structured data evaluation, while narrative understanding is better for contextual and experiential interpretation.
Integrating Propositional and Narrative Methods
Integrating propositional analysis with narrative understanding enhances comprehension by combining the precise breakdown of ideas with the contextual flow of stories. This hybrid approach leverages propositional logic to identify key concepts and relationships while using narrative techniques to capture themes, characters, and temporal sequences. The fusion of these methods improves semantic interpretation and supports more effective communication in educational, psychological, and computational linguistics applications.
Propositional analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com