Pragmatic approaches focus on practical solutions and real-world applications rather than theoretical considerations. They prioritize efficiency and results, adapting strategies to the context for maximum effectiveness. Discover how adopting a pragmatic mindset can transform your decision-making by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
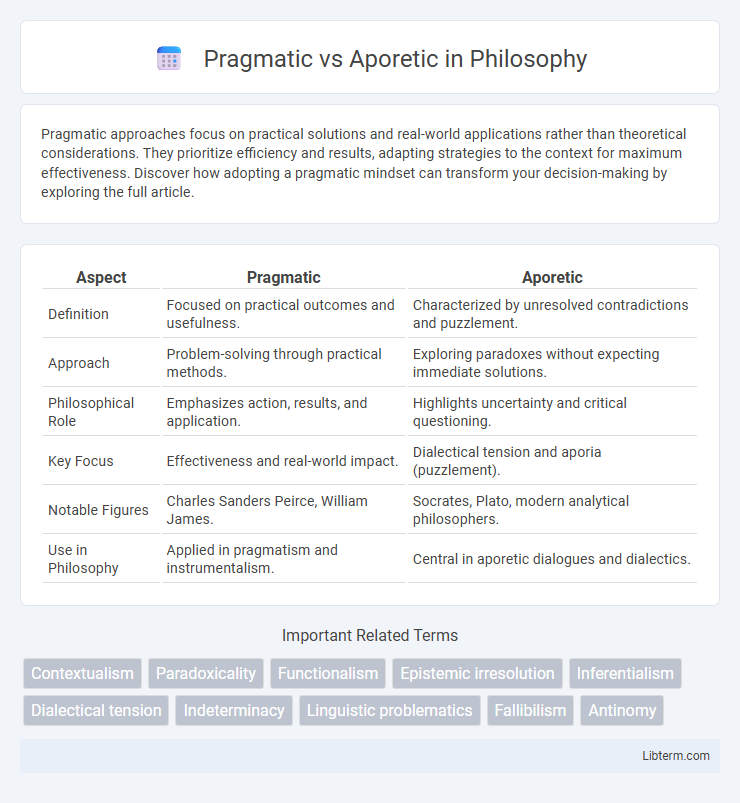
| Aspect | Pragmatic | Aporetic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused on practical outcomes and usefulness. | Characterized by unresolved contradictions and puzzlement. |
| Approach | Problem-solving through practical methods. | Exploring paradoxes without expecting immediate solutions. |
| Philosophical Role | Emphasizes action, results, and application. | Highlights uncertainty and critical questioning. |
| Key Focus | Effectiveness and real-world impact. | Dialectical tension and aporia (puzzlement). |
| Notable Figures | Charles Sanders Peirce, William James. | Socrates, Plato, modern analytical philosophers. |
| Use in Philosophy | Applied in pragmatism and instrumentalism. | Central in aporetic dialogues and dialectics. |
Introduction to Pragmatic and Aporetic Thinking
Pragmatic thinking emphasizes practical approaches and solutions that prioritize effectiveness and real-world application, often driving decision-making based on tangible outcomes and experience. Aporetic thinking involves encountering and exploring genuine puzzles or contradictions without immediate resolution, encouraging deep inquiry and reflection to understand complex problems more fully. Together, these cognitive frameworks offer complementary strategies for navigating challenges by balancing actionable insight with thoughtful contemplation.
Defining Pragmatic: Focus on Practical Solutions
Pragmatic approaches prioritize practical solutions that address real-world problems efficiently and effectively, emphasizing actionable outcomes over theoretical considerations. This mindset values adaptability and results-driven methods, often leveraging empirical evidence and experience to guide decision-making. In contrast to aporetic perspectives, which dwell on irresolvable doubts or paradoxes, pragmatic strategies aim to resolve issues through tangible, workable interventions.
Understanding the Aporetic Approach: Embracing Doubt and Paradox
The aporetic approach centers on embracing doubt and paradox to deepen philosophical inquiry, contrasting with the pragmatic method that prioritizes practical outcomes. It involves recognizing irresolvable contradictions and using them as a catalyst for critical thinking and conceptual clarity. This method encourages open-ended exploration, promoting intellectual humility and continuous questioning as tools for advancing knowledge.
Historical Origins of Pragmatic and Aporetic Methods
The pragmatic method, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy with thinkers like Aristotle and later developed by Charles Sanders Peirce, emphasizes practical consequences and real-world applications as the basis for meaning and truth. The aporetic method originates in the Socratic tradition, characterized by dialogues revealing contradictions and unresolved questions to stimulate critical thinking and intellectual humility. Both methods shaped Western philosophical inquiry, with pragmatism focusing on solution-oriented outcomes and aporeticism on exploring philosophical puzzles and paradoxes.
Key Differences Between Pragmatic and Aporetic Perspectives
The pragmatic perspective centers on practical outcomes and actionable solutions, emphasizing usefulness and effectiveness in real-world applications, while the aporetic perspective highlights inherent contradictions and unresolved problems, focusing on philosophical inquiry and doubt. Pragmatism seeks to resolve issues through experience and results, whereas aporeticism maintains a stance of skepticism and continuous questioning without definitive answers. Key differences lie in pragmatism's goal-oriented approach versus aporeticism's emphasis on exploring paradoxes and epistemic limits.
Pragmatic Thinking in Modern Problem-Solving
Pragmatic thinking in modern problem-solving emphasizes practical, actionable solutions grounded in real-world context and measurable outcomes. It prioritizes efficiency and adaptability, leveraging empirical data and iterative testing to address complex challenges effectively. This approach contrasts with aporetic thinking, which centers on exploring dilemmas and contradictions without immediate resolution.
Aporetic Thought in Philosophy and Critical Inquiry
Aporetic thought in philosophy centers on the recognition of puzzles or contradictory issues that defy straightforward resolution, fostering deeper critical inquiry. It encourages questioning foundational assumptions and promotes dialectical reasoning to navigate uncertainty and paradox. This approach contrasts pragmatic methods by prioritizing conceptual exploration over practical problem-solving outcomes.
Case Studies: Pragmatic vs Aporetic Approaches in Action
Case studies demonstrate the pragmatic approach's focus on practical solutions and measurable outcomes, often applied in business and technology sectors to address real-world problems efficiently. In contrast, aporetic approaches emphasize exploring paradoxes and complex questions without immediate resolution, common in philosophical and theoretical research to deepen understanding of ambiguous issues. Comparative analysis reveals that pragmatic methods prioritize actionable results, while aporetic strategies foster critical thinking and conceptual development.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Method
Pragmatic methods excel in practical problem-solving and real-world applicability, offering direct solutions based on observable outcomes but may overlook deeper theoretical complexities and long-term implications. Aporetic approaches strengthen critical thinking and reveal fundamental contradictions, fostering deeper philosophical inquiry yet often result in unresolved dilemmas that hinder immediate decision-making. Balancing pragmatic decisiveness with aporetic reflection can optimize both actionable results and intellectual rigor in complex scenarios.
Choosing Between Pragmatic and Aporetic Approaches
Choosing between pragmatic and aporetic approaches depends on the desired outcome: a pragmatic approach emphasizes practical solutions and actionable results, often prioritizing efficiency and real-world applicability. In contrast, an aporetic approach involves embracing uncertainty and unresolved contradictions to deepen critical thinking and philosophical inquiry, fostering a more reflective and exploratory mindset. Decision-makers should assess whether immediate problem-solving or cultivating intellectual ambiguity better suits their objectives and context.
Pragmatic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com