Homonymy occurs when two or more words share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings, creating potential confusion in language interpretation. Understanding homonyms is crucial for effective communication, particularly in writing and speaking, as it enhances clarity and precision. Explore the nuances of homonymy further in the rest of the article to sharpen Your linguistic skills.
Table of Comparison
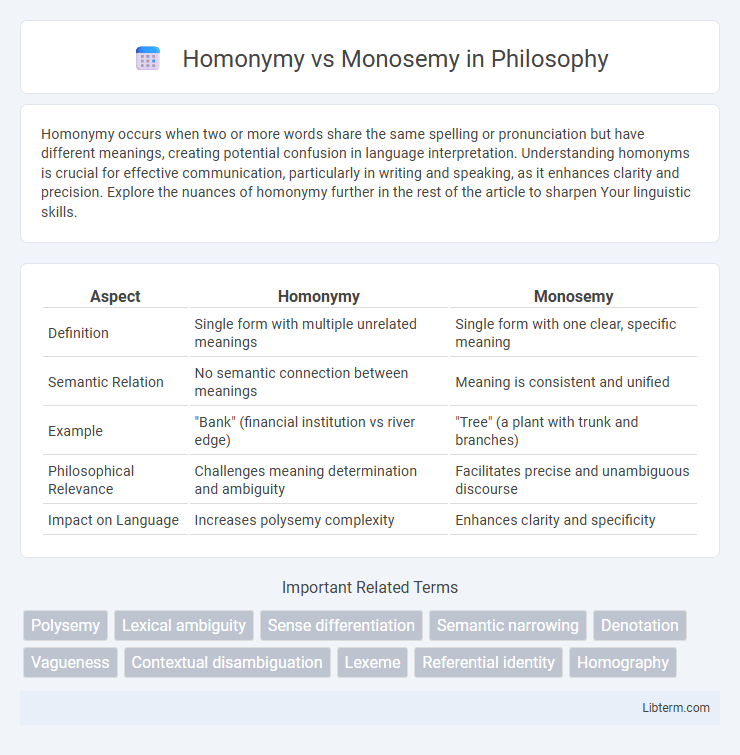
| Aspect | Homonymy | Monosemy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single form with multiple unrelated meanings | Single form with one clear, specific meaning |
| Semantic Relation | No semantic connection between meanings | Meaning is consistent and unified |
| Example | "Bank" (financial institution vs river edge) | "Tree" (a plant with trunk and branches) |
| Philosophical Relevance | Challenges meaning determination and ambiguity | Facilitates precise and unambiguous discourse |
| Impact on Language | Increases polysemy complexity | Enhances clarity and specificity |
Introduction to Homonymy and Monosemy
Homonymy occurs when a single word form has multiple unrelated meanings, such as "bat" referring to both a flying mammal and a sports equipment, whereas monosemy describes words that have a single, clear meaning without semantic ambiguity. In linguistic analysis, recognizing homonymy helps avoid confusion in communication by distinguishing distinct concepts sharing the same lexical form. Monosemous words play a crucial role in precise language use, supporting clarity and efficient information exchange.
Defining Homonymy: The Basics
Homonymy refers to the phenomenon where two or more words share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings, such as "bat" (an animal) and "bat" (a sports implement). It plays a crucial role in semantics and lexical ambiguity, distinguishing it from monosemy, where a word has a single, unambiguous meaning. Understanding homonymy is essential for natural language processing and lexical disambiguation tasks.
Understanding Monosemy: A Clearer Meaning
Monosemy refers to words that have a single, clear meaning, reducing ambiguity in language processing and comprehension. Unlike homonymy, where one word form corresponds to multiple unrelated meanings, monosemy ensures precise communication and easier semantic interpretation. This clarity benefits natural language processing tasks, such as text analysis and machine translation, by minimizing confusion caused by polysemous or homonymous terms.
Key Differences Between Homonymy and Monosemy
Homonymy occurs when a single word form has multiple unrelated meanings, such as "bank" referring to a financial institution or the side of a river, while monosemy describes words with a single, clear meaning. In homonymy, semantic ambiguity arises due to these distinct senses, complicating interpretation and language processing. Monosemy enables straightforward comprehension and precise communication by maintaining one consistent meaning per lexical item.
Types of Homonyms in Language
Homonyms are words sharing the same spelling or pronunciation but differing in meaning, categorized into homophones, which sound alike but have different spellings and meanings (e.g., "flower" and "flour"), and homographs, which are spelled identically but have distinct meanings and sometimes different pronunciations (e.g., "lead" as a metal and "lead" as to guide). True homonyms exhibit both identical spelling and pronunciation yet possess unrelated meanings, such as "bat" (the animal) and "bat" (used in sports). Monosemy contrasts with homonymy by referring to words with a single, unambiguous meaning, reducing lexical confusion in linguistic communication.
Examples of Monosemous Words
Monosemous words have a single, clear meaning, which distinguishes them from homonymous words that possess multiple unrelated meanings. Examples of monosemous words include "oxygen," which solely refers to the chemical element essential for respiration, and "triangle," specifically denoting a three-sided polygon in geometry. The precise meaning of monosemous words enhances clarity and reduces ambiguity in communication across disciplines.
Linguistic Importance of Homonymy
Homonymy plays a crucial role in linguistics by illustrating the complexity and ambiguity inherent in natural language, where a single word form has multiple unrelated meanings, such as "bat" (the animal) versus "bat" (sports equipment). This phenomenon challenges semantic theory and lexical disambiguation processes, driving advancements in computational linguistics and language acquisition studies. Understanding homonymy enhances natural language processing applications, including search engines and machine translation, by improving context-sensitive interpretation of ambiguous terms.
The Role of Monosemy in Communication
Monosemy enhances communication clarity by assigning a single, unambiguous meaning to each word, reducing potential misunderstandings often caused by homonymy, where words share form but differ in meaning. This semantic precision facilitates efficient information processing and supports effective language learning and natural language processing technologies. Emphasizing monosemy in lexicon design promotes clear message transmission, essential in technical, legal, and educational contexts.
Homonymy and Monosemy in Semantics
Homonymy occurs when two or more words share the same form but have unrelated meanings, posing challenges for semantic interpretation and language processing. Monosemy refers to words with a single, clear meaning, facilitating precise communication and reducing ambiguity in semantic analysis. Understanding the distinction between homonymy and monosemy is crucial for natural language processing, lexicography, and semantic theory development.
Conclusion: Implications for Language Learning
Homonymy, where a single word form has multiple unrelated meanings, presents unique challenges for language learners by increasing ambiguity and requiring contextual inference skills. Monosemy, with words having a single, clear meaning, facilitates more straightforward vocabulary acquisition and comprehension. Understanding the differences between homonymy and monosemy is crucial in designing effective language teaching strategies that enhance learners' ability to disambiguate meaning and improve communication accuracy.
Homonymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com