Anthropology explores the diverse cultures, societies, and biological aspects of humanity across time and space. By examining archaeological findings, language development, and social structures, it reveals insights into human evolution and cultural dynamics. Discover how anthropology can deepen your understanding of human connections in the full article.
Table of Comparison
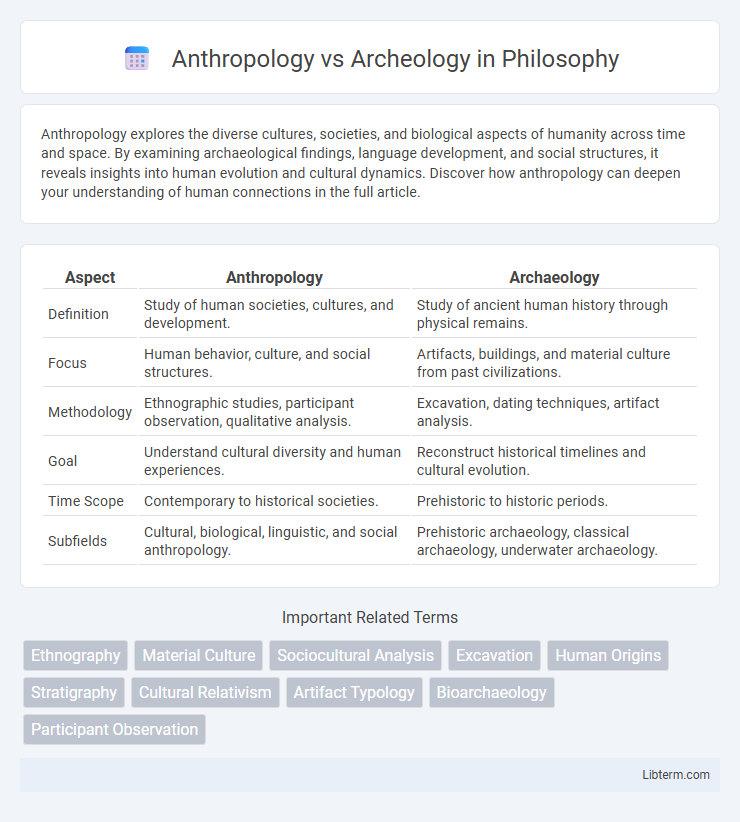
| Aspect | Anthropology | Archaeology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of human societies, cultures, and development. | Study of ancient human history through physical remains. |
| Focus | Human behavior, culture, and social structures. | Artifacts, buildings, and material culture from past civilizations. |
| Methodology | Ethnographic studies, participant observation, qualitative analysis. | Excavation, dating techniques, artifact analysis. |
| Goal | Understand cultural diversity and human experiences. | Reconstruct historical timelines and cultural evolution. |
| Time Scope | Contemporary to historical societies. | Prehistoric to historic periods. |
| Subfields | Cultural, biological, linguistic, and social anthropology. | Prehistoric archaeology, classical archaeology, underwater archaeology. |
Introduction to Anthropology and Archeology
Anthropology explores human culture, behavior, and biological aspects through its four main subfields: cultural, biological, linguistic, and archaeological anthropology. Archaeology, a sub-discipline of anthropology, specializes in studying past human societies by analyzing material remains like artifacts, architecture, and landscapes. Both fields rely on interdisciplinary methods to reconstruct human history, but archaeology predominantly emphasizes physical evidence to understand ancient civilizations.
Defining Anthropology: Scope and Branches
Anthropology encompasses the comprehensive study of human beings, their culture, biology, language, and evolution, integrating four primary branches: cultural anthropology, biological anthropology, linguistic anthropology, and archaeology. Each branch examines distinct but interconnected aspects of humanity, with cultural anthropology focusing on social practices and beliefs, biological anthropology analyzing genetic and physiological traits, linguistic anthropology studying language development and usage, and archaeology investigating material remains from past societies. This multidisciplinary framework highlights anthropology's broad scope in understanding human life across time and space, distinguishing it from archaeology's more specialized focus on uncovering and interpreting ancient artifacts and structures.
What is Archeology? Key Concepts and Methods
Archeology is the scientific study of human history and prehistory through the excavation and analysis of artifacts, architecture, and cultural landscapes. Key concepts include stratigraphy, typology, and radiocarbon dating, which help establish chronological context and cultural development. Methods involve field surveys, systematic excavation, and laboratory analysis to reconstruct past human behaviors and societal evolution.
Historical Development of Both Disciplines
Anthropology and archaeology emerged as distinct academic disciplines in the 19th century, with anthropology focusing broadly on human societies, cultures, and biological aspects, while archaeology specialized in studying past human activities through material remains. Early anthropologists like Franz Boas shaped cultural anthropology by emphasizing ethnographic fieldwork, whereas archaeologists such as Sir Mortimer Wheeler advanced systematic excavation methods and stratigraphy to interpret historical contexts. Over time, both fields integrated interdisciplinary approaches, but their historical development highlights anthropology's focus on living cultures and human variation, contrasted with archaeology's concentration on reconstructing ancient civilizations through artifacts.
Core Differences Between Anthropology and Archeology
Anthropology studies human cultures, behaviors, languages, and biological aspects across time, offering a broad understanding of humanity. Archaeology, a subfield of anthropology, specifically investigates past human societies through material remains such as artifacts, architecture, and fossils. The core difference lies in anthropology's holistic approach to both contemporary and historical humans, while archaeology primarily focuses on uncovering and interpreting physical evidence from ancient civilizations.
Overlapping Areas and Interdisciplinary Approaches
Anthropology and archaeology intersect significantly in the study of past human societies, sharing methodologies like excavation and artifact analysis to reconstruct cultural histories. Both disciplines utilize interdisciplinary approaches, integrating insights from fields such as biology, geology, and history to enhance understanding of human evolution and cultural development. The collaboration between anthropologists and archaeologists enriches interpretations of material culture and social dynamics across different temporal and spatial contexts.
Fieldwork Techniques in Anthropology vs Archeology
Fieldwork techniques in anthropology emphasize participant observation, ethnographic interviews, and immersive cultural engagement to study living societies, focusing on behaviors, rituals, and social structures. Archaeology fieldwork centers on systematic excavation, stratigraphic analysis, and artifact recovery to uncover past human activities and material culture from ancient sites. Both disciplines utilize mapping and survey methods, but anthropology prioritizes real-time cultural interaction while archaeology relies on physical evidence extraction and contextual site analysis.
Career Paths: Opportunities in Each Discipline
Career paths in Anthropology include roles such as cultural anthropologist, academic researcher, and social scientist, offering opportunities in universities, NGOs, and government agencies focused on human behavior and societies. Archaeology careers often involve field excavation, museum curation, and heritage management, with employment in historical preservation organizations, research institutions, and cultural resource management firms. Both disciplines provide specialized career options, but Anthropology emphasizes human culture and social structures, while Archaeology focuses on uncovering and interpreting material remains from past civilizations.
Real-World Applications and Impact on Society
Anthropology provides deep insights into human behavior, culture, and social structures that inform public policy, healthcare, and education by promoting cultural sensitivity and social equity. Archaeology uncovers material evidence of past civilizations, offering valuable knowledge for heritage preservation, tourism development, and understanding historical context essential for modern societal identity. Both disciplines contribute to shaping informed communities by bridging the past and present, influencing areas such as law, urban planning, and cultural resource management.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Anthropology and Archeology
Anthropology provides a broad understanding of human culture, behavior, and biology across time, while archaeology specifically investigates past human societies through material remains. Choosing between anthropology and archaeology depends on whether you prefer a holistic study of humans or a focused examination of historical artifacts and sites. Career goals and personal interests in either cultural analysis or uncovering ancient evidence should guide the decision.
Anthropology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com