Paronyms are words that have similar sounds or spellings but differ in meaning, often causing confusion in both writing and speech. Understanding the subtle distinctions between paronyms can enhance your vocabulary and improve communication clarity. Explore the full article to master common paronyms and avoid frequent language pitfalls.
Table of Comparison
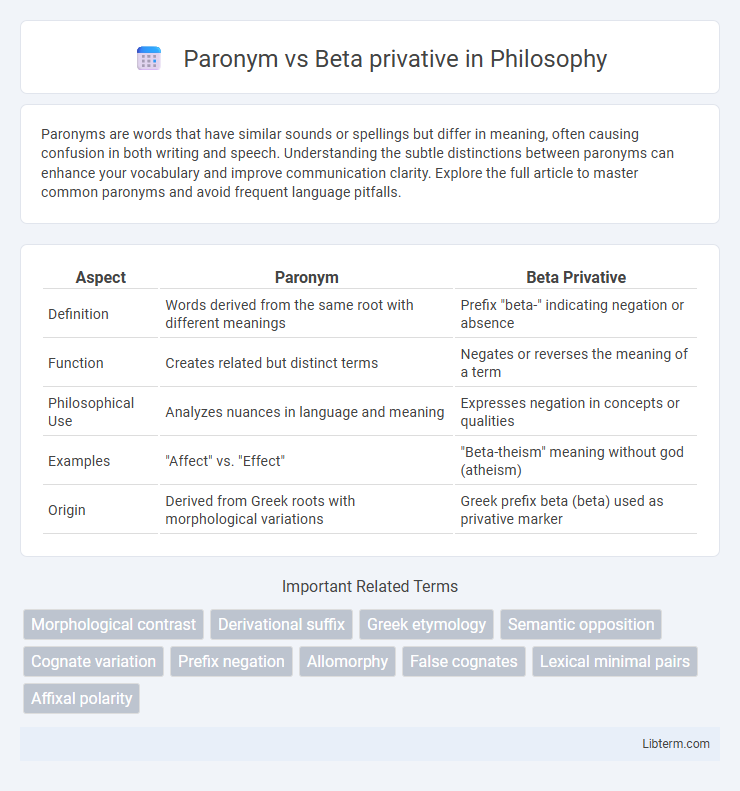
| Aspect | Paronym | Beta Privative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words derived from the same root with different meanings | Prefix "beta-" indicating negation or absence |
| Function | Creates related but distinct terms | Negates or reverses the meaning of a term |
| Philosophical Use | Analyzes nuances in language and meaning | Expresses negation in concepts or qualities |
| Examples | "Affect" vs. "Effect" | "Beta-theism" meaning without god (atheism) |
| Origin | Derived from Greek roots with morphological variations | Greek prefix beta (beta) used as privative marker |
Introduction to Paronym and Beta Privative
Paronyms are words that share a similar form or sound but have different meanings, often leading to confusion in language use. The beta privative is a linguistic prefix derived from Greek, used to negate or reverse the meaning of the root word it attaches to, such as in "atheist" meaning "without god." Understanding paronyms and the role of the beta privative enhances clarity in lexical semantics and etymological studies.
Defining Paronym: Meaning and Examples
Paronyms are words that are phonetically similar but differ in meaning and origin, often creating confusion in usage, such as "affect" and "effect." The beta privative is a prefix derived from Ancient Greek, usually indicated by the letter beta (b), which negates the meaning of the root word it attaches to, like "atheist" meaning "without god." Understanding paronyms helps distinguish words with close sounds or spellings while recognizing beta privative aids in interpreting negated or opposite concepts in linguistics.
Understanding Beta Privative: Origins and Usage
Beta privative is a linguistic prefix derived from the Greek beta (b) combined with privative elements, signifying negation or absence in words. It originates from Ancient Greek, where it was used to form words that express the lack or opposite of a quality, such as "atheos" meaning without god (a- + theos). Understanding the beta privative helps distinguish it from paronyms--words that sound alike but have different meanings--by highlighting its role in morphological negation and semantic transformation.
Etymological Roots: Paronym vs Beta Privative
Paronym derives from the Greek word "paronymos," meaning "bearing a resemblance in name," indicating words with similar roots but distinct meanings. Beta privative originates from the Greek prefix "beta" (b), used as a negation marker to form words with opposite or negative meanings by adding it to the root. The etymological distinction lies in paronyms sharing related roots that create semantic nuances, whereas beta privative involves morphological negation applied directly to the root.
Semantic Differences between Paronym and Beta Privative
Paronyms are words structurally similar due to shared roots but differ in meaning, while beta privatives specifically negate or invert the meaning of the base word. The semantic difference lies in the extent of opposition: paronyms may exhibit partial or nuanced semantic variation, whereas beta privatives express clear negation or absence. Understanding this distinction is crucial for precise linguistic analysis and accurate interpretation of word formation.
Common Misconceptions and Confusions
Paronyms are words that sound similar but have different meanings, often causing confusion in language use and interpretation. Beta privative, a linguistic prefix denoting negation or absence, is frequently mistaken for a paronym due to its phonetic resemblance to certain word parts. Understanding the distinction between paronyms and beta privative clarifies misconceptions, as paronyms involve similarity in form with different meanings, while beta privative specifically functions as a negation marker within word morphology.
Paronym in Linguistics: Applications and Importance
Paronyms in linguistics refer to words that are similar in form but differ in meaning, playing a crucial role in language acquisition and lexical distinction. Their applications extend to psycholinguistics, where understanding paronyms aids in studying word recognition and semantic processing. Recognizing paronyms helps prevent ambiguity in communication and enhances vocabulary learning by highlighting subtle differences between closely related words.
The Role of Beta Privative in Word Formation
The beta privative is a linguistic prefix used to negate or reverse the meaning of a base word, playing a crucial role in word formation by creating antonyms or words with opposite meanings. Unlike paronyms, which are words that sound similar but have different meanings, beta privatives systematically transform a word's semantic field through negation, such as in "atheist" (where "a-" negates "theist"). This morphological process enhances the flexibility and expressiveness of language by enabling precise and efficient formation of new terms that convey absence or opposition.
Examples in Modern and Ancient Languages
Paronyms are words that sound similar but have different meanings, such as "affect" and "effect" in English, while beta privative refers to a prefix (b- or a-) in ancient Greek that negates the meaning of a word, like atheos (atheos) meaning "without god." In Modern languages, paronyms are common in English and Romance languages, for example, Spanish "actual" (current) versus "actual" (real, in English), whereas beta privative is primarily observed in classical languages like Ancient Greek and Sanskrit, where prefixes like a- or a- denote negation or absence. Ancient Greek examples include athemeleia (athemeleia, "carelessness") contrasted with themelios (themeleios, "fundamental"), demonstrating the contrast between standard root meaning and negated form.
Conclusion: Distinguishing Paronym from Beta Privative
Paronym involves words derived from the same root with related meanings, while Beta privative indicates negation or absence through a prefix. Distinguishing paronym from Beta privative relies on analyzing etymology and semantic function rather than mere phonetic similarity. Recognizing this difference aids in precise language interpretation and prevents semantic confusion in linguistic studies.
Paronym Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com