An occurrent property refers to a characteristic or state that an object actively exhibits or experiences at a particular moment in time, such as being hot or in motion. This contrasts with dispositional properties, which describe the potential for certain behaviors or responses under specific conditions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how occurrent properties influence our understanding of objects and events.
Table of Comparison
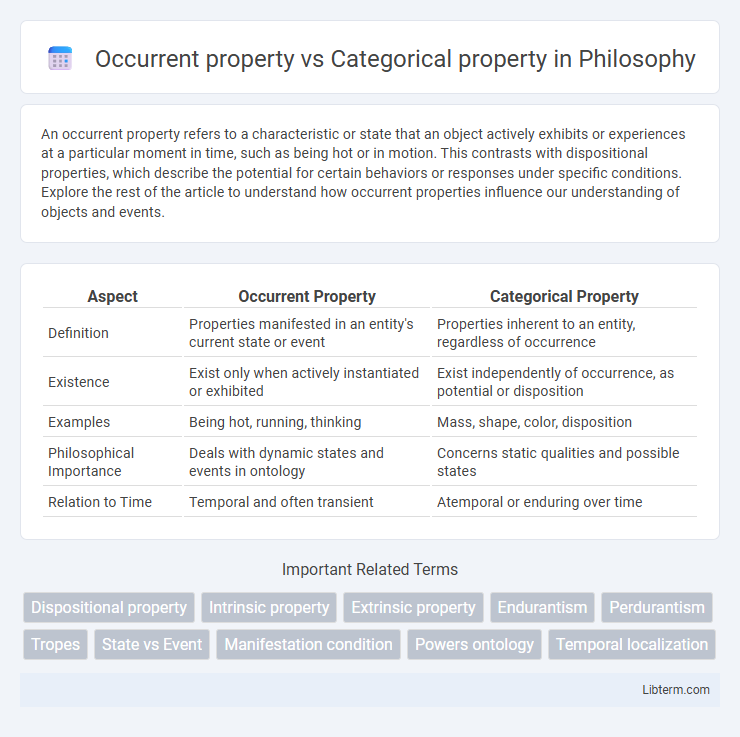
| Aspect | Occurrent Property | Categorical Property |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Properties manifested in an entity's current state or event | Properties inherent to an entity, regardless of occurrence |
| Existence | Exist only when actively instantiated or exhibited | Exist independently of occurrence, as potential or disposition |
| Examples | Being hot, running, thinking | Mass, shape, color, disposition |
| Philosophical Importance | Deals with dynamic states and events in ontology | Concerns static qualities and possible states |
| Relation to Time | Temporal and often transient | Atemporal or enduring over time |
Understanding Occurrent and Categorical Properties
Occurrent properties involve events or processes that unfold over time, such as running or thinking, highlighting temporal and dynamic aspects of reality. Categorical properties refer to inherent characteristics or qualities of objects, like color or shape, which remain invariant regardless of temporal changes. Understanding occurrent and categorical properties helps distinguish between dynamic processes and static attributes essential for ontology and metaphysics.
Defining Occurrent Properties
Occurrent properties are those that manifest in time through events or processes, such as running, thinking, or aging, and are inherently temporal and changeable. They differ from categorical properties, which are static attributes like color or mass that an object possesses continuously. Defining occurrent properties involves identifying traits tied to dynamic occurrences, emphasizing their dependency on temporal unfolding and change.
What Are Categorical Properties?
Categorical properties are intrinsic attributes of an object or entity that describe its potential or inherent capacities, existing independently of any specific occurrences or events. These properties define the essential qualities or dispositions, such as color, shape, or molecular structure, that remain constant regardless of temporal changes. Unlike occurrent properties, which manifest only during particular events or states, categorical properties represent the stable, enduring characteristics fundamental to an object's identity.
Key Differences Between Occurrent and Categorical Properties
Occurrent properties are temporal and dynamic, representing events or processes that unfold over time, such as running or heating, whereas categorical properties are static and enduring attributes like color or shape that do not depend on time. Occurrent properties can change or cease to exist, reflecting states or actions occurring at specific moments, while categorical properties consistently characterize an entity regardless of temporal variations. Understanding these distinctions is essential in metaphysics and ontology for accurately categorizing phenomena and analyzing their existence and persistence.
Philosophical Significance of Property Distinctions
Occurrent properties, such as being heated or moving, are temporally bound and manifest through changes over time, while categorical properties, like shape or mass, remain constant regardless of temporal context. The philosophical significance lies in understanding how these distinctions affect the ontology of objects, influencing debates on persistence, identity, and causality. Differentiating between occurrent and categorical properties helps clarify metaphysical discussions about the nature of properties and their role in the constitution of reality.
Examples of Occurrent Properties
Occurrent properties describe dynamic processes or events occurring in time, such as running, thinking, or lightning striking. These properties contrast with categorical properties, which are static and pertain to an object's intrinsic qualities, like color, shape, or mass. Examples of occurrent properties include the act of speaking, the process of heating water, and the event of a bird flying.
Examples of Categorical Properties
Categorical properties include characteristics such as shape, color, and mass, which remain constant regardless of an object's state or occurrence. For example, the spherical shape of a basketball or the red color of an apple exemplifies categorical properties. These properties contrast with occurrent properties, which depend on an object's current state or activity, like the temperature or motion of an object.
Implications in Metaphysics
Occurrent properties involve temporal states or events that an entity experiences, such as being hot or running, whereas categorical properties are timeless qualities like shape or mass that do not depend on an entity's temporal existence. In metaphysics, the distinction impacts debates on identity and persistence, as occurrent properties highlight dynamic change, while categorical properties support the notion of enduring essence. This differentiation informs theories of substance and ensures clarity in understanding how entities relate to their properties across time.
Occurrent vs Categorical Properties in Science
Occurrent properties in science refer to dynamic features that manifest only when an entity is in a particular state or undergoing a process, such as temperature or motion. Categorical properties, by contrast, are intrinsic and static characteristics like mass or molecular structure that define an entity regardless of its state. Understanding the distinction between occurrent and categorical properties is crucial for experimental design and theoretical modeling in disciplines like physics and chemistry.
Debates and Future Directions in Property Theory
Ongoing debates in property theory center on the ontological status and explanatory power of occurrent properties, which pertain to events or processes, versus categorical properties, seen as intrinsic and timeless. Recent discourse explores whether occurrent properties can be reduced to categorical ones or if they necessitate a distinct ontological category, impacting metaphysical frameworks and theories of causation. Future directions emphasize integrating insights from metaphysics, philosophy of science, and cognitive psychology to refine the conceptual boundaries and applicability of both property types in explaining reality.
Occurrent property Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com