Fuzzy logic offers a powerful way to handle uncertainty and approximate reasoning by mimicking human decision-making processes. It allows systems to interpret data that is not precise, enabling more flexible and adaptive control in applications ranging from industrial automation to artificial intelligence. Explore the rest of this article to understand how fuzzy logic can enhance your problem-solving strategies.
Table of Comparison
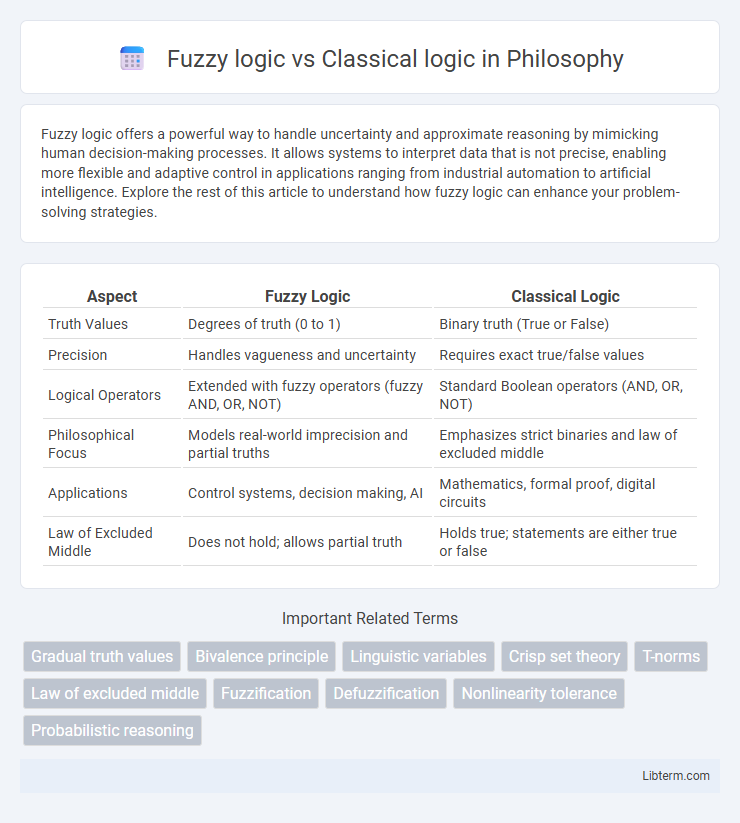
| Aspect | Fuzzy Logic | Classical Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Truth Values | Degrees of truth (0 to 1) | Binary truth (True or False) |
| Precision | Handles vagueness and uncertainty | Requires exact true/false values |
| Logical Operators | Extended with fuzzy operators (fuzzy AND, OR, NOT) | Standard Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) |
| Philosophical Focus | Models real-world imprecision and partial truths | Emphasizes strict binaries and law of excluded middle |
| Applications | Control systems, decision making, AI | Mathematics, formal proof, digital circuits |
| Law of Excluded Middle | Does not hold; allows partial truth | Holds true; statements are either true or false |
Introduction to Fuzzy Logic and Classical Logic
Fuzzy logic extends classical logic by handling reasoning that is approximate rather than fixed and exact, allowing truth values to range between 0 and 1 instead of being strictly true or false as in classical logic. Classical logic operates on binary principles with clear-cut rules and crisp boundaries, ideal for deterministic systems but limited in dealing with uncertainty and vagueness. Fuzzy logic introduces degrees of truth through membership functions, enabling more flexible and human-like decision-making processes in complex, real-world scenarios.
Core Principles of Classical Logic
Classical logic operates on binary truth values where statements are either true or false, adhering strictly to the law of excluded middle and non-contradiction. It employs formal deductive reasoning based on fixed, precise rules, ensuring definitive conclusions in well-defined scenarios. This rigid structure contrasts with fuzzy logic, which permits degrees of truth and handles uncertainty by enabling partial membership in sets.
Fundamentals of Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic extends classical logic by allowing truth values to range continuously between 0 and 1, rather than being strictly true or false. This approach models uncertainty and vagueness more effectively through membership functions and linguistic variables, enabling reasoning with imprecise or ambiguous information. Its fundamentals include the concepts of fuzzy sets, fuzzy rules, and inference mechanisms that mimic human decision-making processes better than binary classical logic.
Key Differences Between Fuzzy and Classical Logic
Fuzzy logic allows partial truth values between 0 and 1, enabling reasoning with uncertainty and vagueness, while classical logic operates on binary true or false values. In classical logic, propositions are either completely true or completely false, making it rigid for real-world scenarios where ambiguity exists. Fuzzy logic's flexibility in handling imprecise data makes it suitable for complex systems like control processes and decision-making under uncertainty.
Applications of Classical Logic in Technology
Classical logic underpins the functionality of digital circuits, enabling binary decision-making essential for computer processors and software algorithms. It is fundamental in database query optimization and automated theorem proving, ensuring precise computation and logical consistency. Classical logic also supports formal verification methods used in hardware design and cybersecurity, guaranteeing system reliability and security.
Real-World Uses of Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic offers a flexible approach to reasoning that handles uncertainty and imprecision, making it ideal for real-world applications like control systems in appliances, automotive technologies, and decision-making processes in artificial intelligence. Unlike classical logic, which operates on binary true or false values, fuzzy logic evaluates degrees of truth, enabling nuanced responses in environments with ambiguous or incomplete information. Industries such as consumer electronics, automotive engineering, and robotics leverage fuzzy logic to enhance system adaptability and performance under variable conditions.
Flexibility and Precision: A Comparative Analysis
Fuzzy logic offers greater flexibility by allowing values between true and false, capturing real-world uncertainties and nuances that classical logic's binary framework cannot. Classical logic provides unmatched precision with clear boolean values, ideal for applications requiring definitive outcomes and strict reasoning. This comparative analysis highlights fuzzy logic's adaptability in handling ambiguous data, contrasted with classical logic's strength in delivering exact, unambiguous conclusions.
Advantages and Limitations of Classical Logic
Classical logic offers clear binary truth values, making it effective for systems requiring precise, unambiguous reasoning and deterministic outcomes. Its main advantages include well-defined inference rules and simplicity in implementation, which suit traditional computing and formal proofs. However, classical logic's limitations arise in handling vagueness and uncertainty, as it cannot represent degrees of truth or partial information, restricting its applicability in complex, real-world, or fuzzy environments.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic excels in handling uncertain, imprecise, or vague information, making it ideal for real-world applications like control systems and decision-making where binary true/false evaluation is insufficient. Its strength lies in modeling approximate reasoning and human-like reasoning, allowing gradual transitions between truth values rather than rigid boundaries. However, fuzzy logic can suffer from computational complexity and a lack of standardized methods for membership function design, which affects system consistency and interpretability compared to classical logic's clear-cut, deterministic framework.
Choosing the Right Logic System for Your Needs
Fuzzy logic allows for reasoning with degrees of truth, making it ideal for complex decision-making in uncertain or imprecise environments, whereas classical logic relies on binary true/false values suitable for clear-cut, deterministic problems. Selecting fuzzy logic benefits applications in control systems, expert systems, and natural language processing where nuance and partial truth are critical. Classical logic remains optimal for mathematical proofs, formal verification, and scenarios demanding strict logical consistency.
Fuzzy logic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com