Causal luck refers to the phenomenon where factors beyond your control influence the outcomes of your actions, raising challenging questions about responsibility and moral judgment. Understanding how causal luck operates helps clarify why similar actions may result in very different consequences for different individuals. Explore the rest of this article to discover how causal luck shapes ethics and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
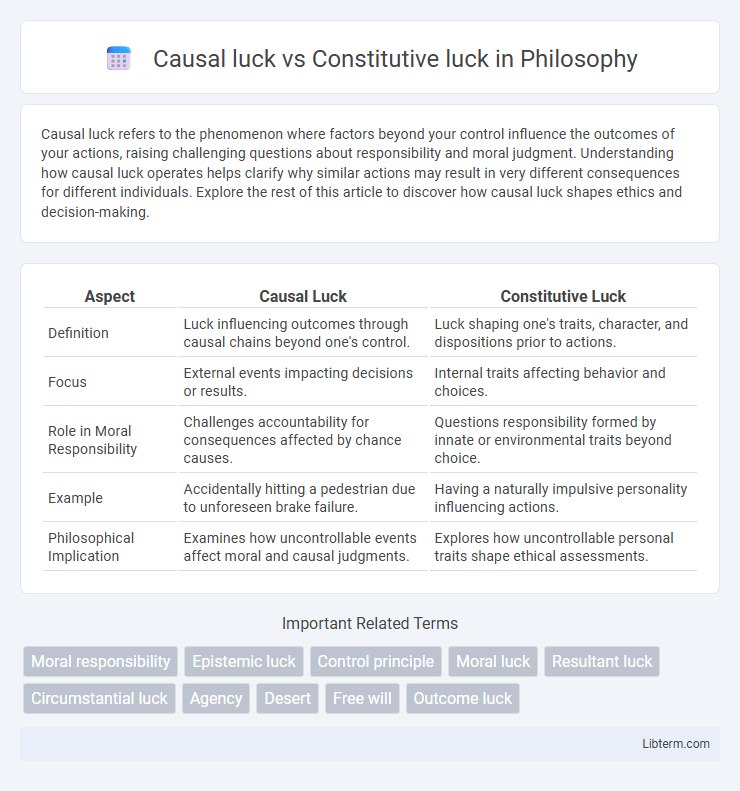
| Aspect | Causal Luck | Constitutive Luck |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Luck influencing outcomes through causal chains beyond one's control. | Luck shaping one's traits, character, and dispositions prior to actions. |
| Focus | External events impacting decisions or results. | Internal traits affecting behavior and choices. |
| Role in Moral Responsibility | Challenges accountability for consequences affected by chance causes. | Questions responsibility formed by innate or environmental traits beyond choice. |
| Example | Accidentally hitting a pedestrian due to unforeseen brake failure. | Having a naturally impulsive personality influencing actions. |
| Philosophical Implication | Examines how uncontrollable events affect moral and causal judgments. | Explores how uncontrollable personal traits shape ethical assessments. |
Introduction to Moral Luck
Moral luck examines how factors beyond an agent's control influence moral judgment, distinguishing between causal luck and constitutive luck. Causal luck refers to external events that affect the outcomes of actions, while constitutive luck pertains to an individual's inherent traits or dispositions that shape their decisions and character. Exploring these types highlights the complex interaction between free will, responsibility, and uncontrollable circumstances in ethical evaluation.
Defining Causal Luck
Causal luck refers to the influence of prior events and circumstances beyond an individual's control that shape outcomes, emphasizing how external causes affect actions and consequences. It involves factors such as genetic inheritance, environmental conditions, and historical events that intervene before a decision or action occurs. Distinguishing causal luck from constitutive luck highlights the difference between external causal chains and internal traits or dispositions shaping a person's character.
Understanding Constitutive Luck
Constitutive luck refers to the traits, dispositions, and characteristics one is born with or develops through uncontrollable factors, impacting behavior and decisions. It shapes an individual's ethical and psychological makeup, influencing how they respond to situations and moral dilemmas. Understanding constitutive luck is essential for evaluating personal responsibility and moral judgment, as it highlights the limits of control over one's inherent qualities.
Key Differences Between Causal and Constitutive Luck
Causal luck refers to the outcomes influenced by external events or circumstances beyond an individual's control, such as accidents or chance encounters, affecting the consequences of actions. Constitutive luck involves traits, dispositions, or characteristics inherent to a person, shaped by factors like genetics or upbringing, which impact their decision-making and moral responsibility. Key differences between causal and constitutive luck lie in their domains: causal luck pertains to external events causing effects, while constitutive luck concerns internal qualities defining the agent's identity.
Philosophical Foundations: Theories on Moral Luck
Causal luck refers to the uncontrollable events and circumstances leading to an action, while constitutive luck concerns the innate traits and dispositions shaping a person's character. Both concepts challenge traditional notions of moral responsibility by highlighting how factors beyond an individual's control influence ethical judgments. Philosophical theories on moral luck explore these ideas to question the fairness of praising or blaming individuals for outcomes partly determined by luck.
Real-World Examples of Causal Luck
Causal luck occurs when external events influence the outcomes of an individual's actions, such as a driver narrowly avoiding an accident due to unexpected traffic light changes or a student receiving a last-minute exam cancellation because of a sudden storm. In the 2020 Tokyo Olympics, athletes' performances were impacted by causal luck when weather disruptions altered competition schedules, directly affecting their physical and mental readiness. These real-world scenarios demonstrate how factors beyond personal control can significantly shape success and failure.
Real-World Examples of Constitutive Luck
Constitutive luck refers to the traits and dispositions a person is born with, which shape their decisions and life outcomes independently of their control. Real-world examples include inheriting a high IQ or a predisposition to certain mental health conditions, which influence one's potential for academic success or challenges. These innate characteristics significantly affect personal development, career paths, and social interactions, illustrating the role of constitutive luck in shaping individual destinies.
Implications for Moral Responsibility
Causal luck influences the outcomes of actions beyond an individual's control, affecting the fairness in assigning moral responsibility. Constitutive luck pertains to the traits and dispositions one inherits, which shape decision-making capacities and ethical behavior. Understanding these forms of luck challenges traditional accountability, suggesting moral judgment must account for factors outside a person's control.
Critiques and Debates in Moral Philosophy
Critiques of causal luck emphasize challenges in assigning moral responsibility due to factors beyond an agent's control, such as chance events influencing outcomes. Debates around constitutive luck focus on the origins of a person's traits and dispositions, questioning whether individuals can be held accountable for inherent characteristics shaped by genetic and environmental factors. Moral philosophers argue whether these types of luck undermine traditional notions of praise and blame, prompting ongoing discussions on the fairness and coherence of moral judgment.
Conclusion: Navigating Luck in Moral Judgments
Navigating moral judgments requires discerning the influence of causal luck, which involves external events beyond an agent's control, and constitutive luck, referring to traits and dispositions shaped by factors outside their influence. Recognizing these distinctions helps refine assessments of responsibility by separating uncontrollable circumstances from the agent's deliberate actions and character. This nuanced understanding supports more just evaluations in ethical and legal contexts, highlighting the importance of fairness in attributing moral praise or blame.
Causal luck Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com