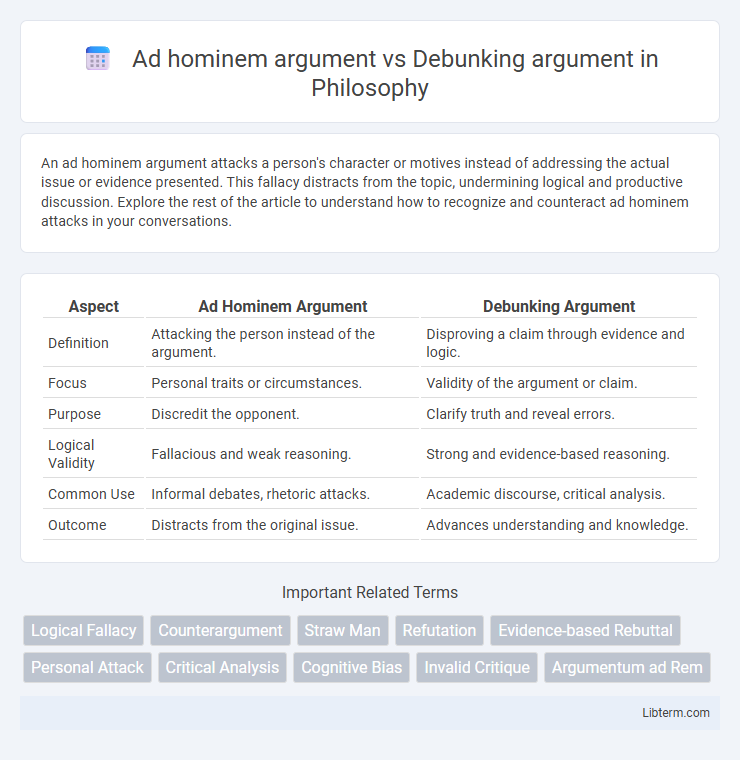
An ad hominem argument attacks a person's character or motives instead of addressing the actual issue or evidence presented. This fallacy distracts from the topic, undermining logical and productive discussion. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to recognize and counteract ad hominem attacks in your conversations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ad Hominem Argument | Debunking Argument |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Attacking the person instead of the argument. | Disproving a claim through evidence and logic. |
| Focus | Personal traits or circumstances. | Validity of the argument or claim. |
| Purpose | Discredit the opponent. | Clarify truth and reveal errors. |
| Logical Validity | Fallacious and weak reasoning. | Strong and evidence-based reasoning. |
| Common Use | Informal debates, rhetoric attacks. | Academic discourse, critical analysis. |
| Outcome | Distracts from the original issue. | Advances understanding and knowledge. |
Understanding Ad Hominem Arguments
Ad hominem arguments attack an opponent's character or personal traits instead of addressing the actual issue or argument presented, thereby diverting attention from the logical merits of the discussion. Understanding ad hominem fallacies is crucial for recognizing when debates shift from evidence-based reasoning to personal attacks, which undermine constructive dialogue. Effective critical thinking involves identifying these fallacies to maintain focus on valid counterarguments rather than irrelevant personal criticisms.
What Constitutes a Debunking Argument
A debunking argument systematically disproves a claim by presenting evidence-based reasoning and factual counterexamples that expose inaccuracies or falsehoods. Unlike an ad hominem argument, which attacks the character or motives of the individual making the claim rather than addressing the argument itself, a debunking argument targets the content and logic of the assertion. Effective debunking relies on critical analysis, empirical data, and logical consistency to invalidate misinformation or misconceptions.
Core Differences: Ad Hominem vs Debunking
Ad hominem arguments attack the character or traits of the person making a claim rather than addressing the claim itself, undermining the argument through personal criticism. Debunking arguments focus on exposing the falsity or inaccuracies within the claim by presenting evidence, logic, or factual refutation. The core difference lies in targeting the individual versus targeting the claim's validity.
Psychological Impact on Audience Perception
Ad hominem arguments often undermine the credibility of the opponent by attacking personal traits, which can trigger emotional bias and reduce rational engagement among the audience. Debunking arguments rely on evidence and logic to dismantle claims, fostering critical thinking and enhancing the audience's trust in factual accuracy. Psychological studies indicate that ad hominem attacks may provoke defensive responses, while debunking encourages analytical processing and openness to changing beliefs.
Logical Fallacies Explained: Ad Hominem
Ad hominem arguments attack the person making a claim rather than addressing the claim's validity, representing a common logical fallacy that undermines rational debate. Debunking arguments focus on disproving false claims through evidence and sound reasoning, avoiding personal attacks. Understanding that ad hominem fallacies divert attention from factual analysis is crucial in identifying and countering flawed reasoning effectively.
The Role of Evidence in Debunking
Debunking arguments rely heavily on empirical evidence and logical reasoning to refute false claims while ad hominem arguments attack the character or motives of the opponent instead of addressing the actual issue. The role of evidence in debunking is crucial because it provides verifiable support that invalidates misinformation or fallacious reasoning. Effective debunking strengthens critical thinking and promotes rational discourse by focusing on facts rather than personal attacks.
Common Examples in Contemporary Debates
Ad hominem arguments commonly appear in political debates where individuals attack opponents' character instead of addressing policy issues, such as calling someone dishonest without evidence. Debunking arguments often involve fact-checking or presenting scientific data to refute misinformation, like correcting false claims about vaccines with peer-reviewed studies. Social media platforms frequently witness ad hominem attacks contrasted with debunking efforts aimed at clarifying misinformation in public health or climate change discussions.
Consequences of Employing Ad Hominem Tactics
Employing ad hominem tactics often undermines rational discourse by shifting focus from the argument's validity to personal attacks, leading to a breakdown in constructive communication. This approach can erode trust between parties and diminish the credibility of the attacker, ultimately hindering conflict resolution and collaborative problem-solving. Frequent reliance on ad hominem arguments contributes to polarized environments where meaningful debate is replaced by hostility and misinformation.
Strengthening Arguments with Debunking Techniques
Debunking arguments strengthen discourse by systematically identifying and correcting false claims using evidence-based analysis, enhancing overall argument credibility. Unlike ad hominem attacks, which target a person's character rather than the argument, debunking focuses on the validity of the argument itself, promoting rational evaluation. Effective debunking includes fact-checking, logical reasoning, and presenting counter-evidence, reinforcing the strength of the original position while minimizing fallacious distractions.
Best Practices for Constructive Argumentation
Ad hominem arguments undermine constructive dialogue by attacking an opponent's character rather than addressing the topic, diverting focus from evidence and logic. Effective debunking arguments rely on fact-based analysis, clear evidence, and respectful tone to dismantle misinformation and promote understanding. Best practices in constructive argumentation emphasize critical thinking, active listening, and maintaining focus on the issue to foster meaningful and productive discussions.
Ad hominem argument Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com