The intentional stance is a strategy in philosophy and cognitive science where one interprets the behavior of entities by treating them as rational agents with beliefs, desires, and intentions. This approach allows for predicting and explaining actions without needing to understand the complex inner workings of the entity. Explore the rest of the article to discover how adopting the intentional stance can enhance your understanding of human and artificial intelligence.
Table of Comparison
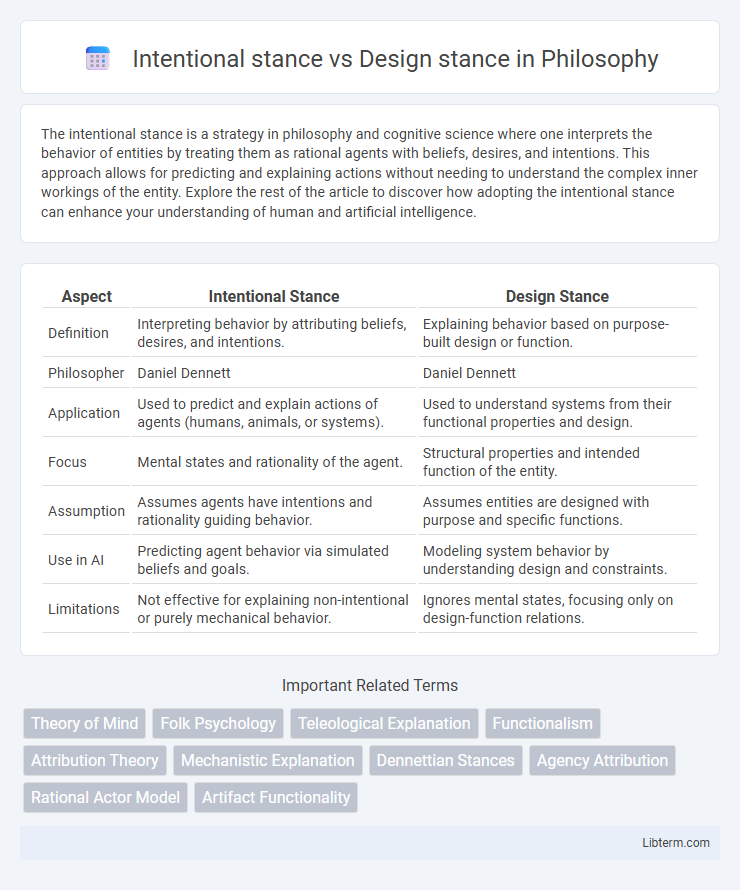
| Aspect | Intentional Stance | Design Stance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpreting behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and intentions. | Explaining behavior based on purpose-built design or function. |
| Philosopher | Daniel Dennett | Daniel Dennett |
| Application | Used to predict and explain actions of agents (humans, animals, or systems). | Used to understand systems from their functional properties and design. |
| Focus | Mental states and rationality of the agent. | Structural properties and intended function of the entity. |
| Assumption | Assumes agents have intentions and rationality guiding behavior. | Assumes entities are designed with purpose and specific functions. |
| Use in AI | Predicting agent behavior via simulated beliefs and goals. | Modeling system behavior by understanding design and constraints. |
| Limitations | Not effective for explaining non-intentional or purely mechanical behavior. | Ignores mental states, focusing only on design-function relations. |
Understanding the Intentional Stance
The intentional stance involves interpreting the behavior of an entity by attributing beliefs, desires, and rationality to explain and predict its actions, which enhances understanding in complex systems like humans or AI agents. This approach contrasts with the design stance, which explains behavior based solely on the system's physical makeup and purpose without assuming mental states. Employing the intentional stance enables deeper insight into decision-making processes, making it crucial for fields such as cognitive science, artificial intelligence, and philosophy of mind.
Defining the Design Stance
The Design Stance involves interpreting an object's behavior based on its intended function and design rather than its mental states or beliefs. This perspective assumes that the object operates according to a purpose built into its structure, such as a clock designed to tell time or a toaster built to brown bread. By attributing functionality rooted in design, the Design Stance simplifies predictions of behavior without requiring understanding of intentions or goals.
Philosophical Foundations of Each Stance
The intentional stance, rooted in philosopher Daniel Dennett's framework, attributes beliefs, desires, and rationality to agents, treating them as rational actors with mental states to predict behavior. The design stance, by contrast, interprets entities based on their functional design and purpose, assuming they operate according to built-in mechanisms without attributing mental states. Philosophically, the intentional stance aligns with folk psychology and mentalistic explanations, while the design stance draws from teleological explanations rooted in functional analysis and engineering principles.
Key Differences Between Intentional and Design Stances
The intentional stance interprets behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and intentions to an agent, treating it as a rational entity with mental states. The design stance understands behavior by focusing on the system's function and purpose, assuming it operates according to its design or programming without assigning mental states. Key differences include the intentional stance's reliance on psychological reasoning versus the design stance's emphasis on mechanical or functional explanation.
Applications in Artificial Intelligence
The Intentional stance in Artificial Intelligence involves interpreting AI behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and rationality, enabling more intuitive human-AI interactions and improved adaptive learning systems. The Design stance focuses on understanding AI based on its programmed functions and algorithms, facilitating debugging, optimization, and system reliability assessments. Combining both stances enhances AI applications by aligning system design with human-like reasoning and practical functionality.
Role in Cognitive Science
The Intentional stance in cognitive science involves interpreting behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and intentions to agents, facilitating prediction of actions through mental state reasoning. The Design stance, in contrast, explains behavior by considering the functional properties and purpose of a system's components, treating the system as if it were designed to perform specific tasks. These stances serve complementary roles in understanding cognition, with the Intentional stance emphasizing mental representation and the Design stance focusing on adaptive mechanisms and functional organization.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
The intentional stance excels in predicting complex behaviors by attributing beliefs, desires, and rationality to agents, enhancing understanding in social interactions but struggles with non-agentive systems lacking mental states. The design stance offers precise predictions by assuming functional design and purpose in artifacts, streamlining problem-solving in engineered systems but falls short in explaining unpredictable or emergent phenomena in biological or cognitive domains. Both approaches complement each other; the intentional stance provides insight into mental causation, while the design stance emphasizes mechanistic explanations grounded in system architecture.
Real-World Examples: Intentional vs Design Stance
The intentional stance involves interpreting behavior by attributing beliefs and desires, as seen when people predict a chess player's moves based on strategy. In contrast, the design stance focuses on understanding an entity by its function and design, such as a thermostat regulating temperature without attributing intentions. Real-world applications include using the intentional stance to analyze human actions, while robots are often understood through the design stance due to their programmed responses.
Implications for Mind and Machine Perception
The intentional stance interprets entities by attributing beliefs and desires, enhancing mind perception through ascribing mental states, which is pivotal for understanding human-like cognition in machines. The design stance simplifies interpretation by focusing on purpose and function, streamlining machine perception by treating systems as goal-oriented mechanisms without assuming consciousness. Emphasizing the intentional stance in AI development fosters advanced mental state attribution, improving human-machine interaction, while the design stance facilitates efficient task execution by emphasizing functional design over cognitive complexity.
Future Directions in Stance Theory
Future directions in stance theory emphasize integrating intentional stance with design stance to enhance predictive accuracy in AI systems and human-computer interaction. Research is focusing on developing hybrid models that combine the mental state attribution of the intentional stance with the functional analysis of the design stance. Advances in cognitive science and machine learning are expected to refine these models for better anticipatory reasoning and adaptive behavior prediction.
Intentional stance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com