Self-ideal represents the vision of the best version of yourself, guiding your goals, behaviors, and decision-making toward personal growth and fulfillment. Cultivating a clear self-ideal helps align your daily actions with your deepest values, enhancing motivation and resilience during challenges. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical steps for defining and living your self-ideal effectively.
Table of Comparison
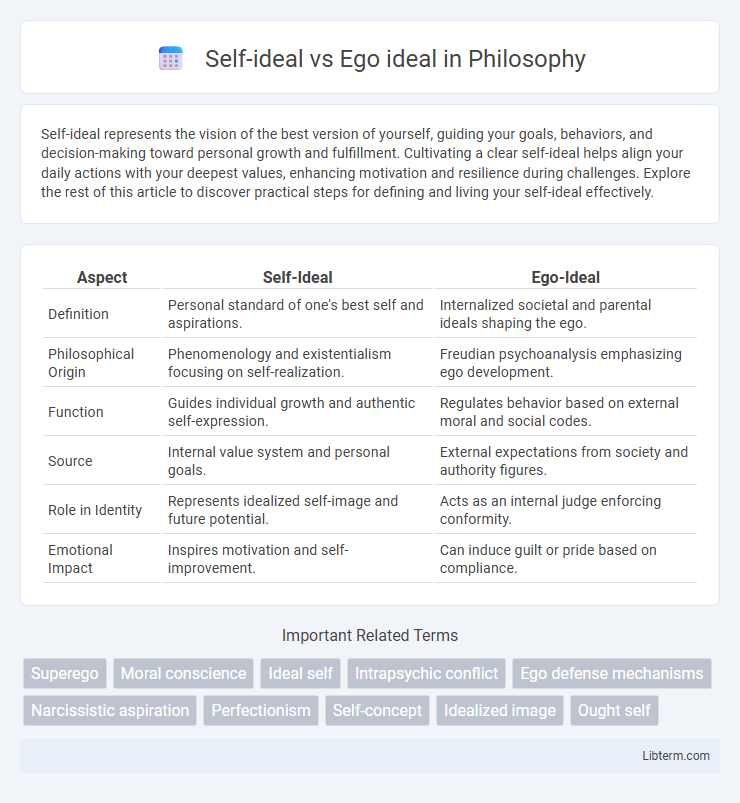
| Aspect | Self-Ideal | Ego-Ideal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal standard of one's best self and aspirations. | Internalized societal and parental ideals shaping the ego. |
| Philosophical Origin | Phenomenology and existentialism focusing on self-realization. | Freudian psychoanalysis emphasizing ego development. |
| Function | Guides individual growth and authentic self-expression. | Regulates behavior based on external moral and social codes. |
| Source | Internal value system and personal goals. | External expectations from society and authority figures. |
| Role in Identity | Represents idealized self-image and future potential. | Acts as an internal judge enforcing conformity. |
| Emotional Impact | Inspires motivation and self-improvement. | Can induce guilt or pride based on compliance. |
Understanding Self-Ideal and Ego Ideal: Core Definitions
Self-ideal represents an individual's aspirational image of who they wish to become, embodying personal goals, values, and desired traits. Ego ideal functions as an internalized standard often shaped by parental and societal expectations, guiding behavior through idealized norms and moral standards. Understanding the distinction between self-ideal and ego ideal reveals the dynamic interplay between personal ambition and external influences in shaping identity and motivation.
Origins of Self-Ideal and Ego Ideal in Psychology
The origins of the Self-Ideal and Ego Ideal in psychology trace back to psychoanalytic theory, primarily developed by Sigmund Freud and later expanded by Jacques Lacan. The Self-Ideal represents an individual's internalized vision of personal perfection, derived from early life experiences, parental guidance, and societal expectations. The Ego Ideal functions as a regulatory standard, shaped by the superego, that guides behavior by imposing moral and ethical aspirations rooted in cultural and familial influences.
Key Differences Between Self-Ideal and Ego Ideal
Self-ideal represents a person's aspirations and goals for their own self-improvement, embodying their vision of the best version of themselves. Ego ideal, rooted in psychoanalytic theory, functions as an internalized set of standards and ideals derived from parental and societal expectations, guiding behavior through feelings of pride or guilt. The key difference lies in self-ideal being a self-chosen target aimed at personal growth, whereas ego ideal is imposed by external influences shaping the individual's conscience and moral judgments.
The Role of Self-Ideal in Personal Development
The self-ideal functions as an internal blueprint that shapes personal development by guiding goals, values, and behavior toward an envisioned version of oneself. This internalized standard motivates growth and self-improvement by influencing decision-making and fostering resilience in the face of challenges. Unlike the ego ideal, which is often shaped by external expectations, the self-ideal represents a personalized vision critical for authentic identity formation and psychological well-being.
Ego Ideal and Its Impact on Self-Esteem
The ego ideal represents the internalized standards and aspirations shaped by parental guidance and societal expectations, serving as a benchmark for personal achievement. When individuals perceive alignment between their behaviors and the ego ideal, self-esteem is reinforced, fostering a positive self-concept. Conversely, discrepancies between the ego ideal and actual self can lead to feelings of inadequacy and diminished self-worth.
How Self-Ideal Shapes Motivation and Goals
The self-ideal functions as an internalized vision of one's ideal self, directly influencing motivation by setting aspirational goals that drive personal growth and achievement. It operates as a standard against which individuals measure their current behaviors and accomplishments, fostering goal-oriented actions aimed at self-improvement. Unlike the ego ideal, which represents external expectations and societal norms, the self-ideal is deeply rooted in personal values and desires, making it a powerful motivator in shaping long-term ambitions and purposeful behavior.
The Influence of Ego Ideal on Behavior and Choices
The ego ideal serves as an internalized standard derived from parental and societal expectations, guiding behavior by motivating individuals to strive for perfection and moral integrity. It influences choices by setting aspirational goals that shape self-discipline, decision-making, and long-term planning, often driving individuals to align actions with their idealized self-image. Failure to meet the ego ideal can result in feelings of guilt or inadequacy, impacting emotional well-being and reinforcing the pursuit of behavior consistent with these internalized ideals.
Common Pitfalls: When Self-Ideal and Ego Ideal Conflict
Conflicts between Self-Ideal and Ego Ideal often lead to internal tension and decreased self-esteem, as the Self-Ideal represents authentic personal goals while the Ego Ideal reflects societal or parental expectations. This dissonance can cause confusion, anxiety, and diminished motivation when individuals struggle to reconcile personal values with external pressures. Recognizing and addressing these conflicting ideals through self-reflection or therapy helps improve psychological well-being and promotes a more coherent self-identity.
Strategies to Harmonize Self-Ideal and Ego Ideal
Strategies to harmonize self-ideal and ego ideal involve aligning personal values with realistic aspirations through reflective self-assessment and goal-setting techniques. Cognitive-behavioral approaches help identify discrepancies between these ideals, promoting adaptive changes in self-perception and motivation. Mindfulness practices enhance self-awareness, reducing internal conflicts by fostering acceptance and integration of evolving identity aspects.
Cultivating a Healthy Balance for Emotional Wellbeing
Self-ideal represents the person we aspire to become, reflecting our core values and long-term goals, while ego ideal is shaped by internalized standards from authority figures and societal expectations. Cultivating a healthy balance between self-ideal and ego ideal promotes emotional wellbeing by fostering self-compassion and realistic self-assessment, reducing anxiety and self-criticism. Techniques such as mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral strategies, and reflective journaling help individuals align their ambitions with authentic self-understanding and external influences.
Self-ideal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com